Summary
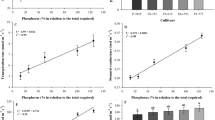
Experimental assessment of differences between cultivars of crop species or ecotypes of wild species from different localities in their capacities for ion absorption and transport is made difficult by the problem of obtaining seed material of comparable ionic content. When young seedlings are used this problem is particularly acute if the seeds of the different cultivars have not been raised under identical soil conditions. Propagation of material from ecotypes under controlled conditions is one approach to the solution of this problem. Six maize cultivars have been selected for similarity of phosphate content and the capacity for phosphate absorption from 5 μM KH2PO4 has been shown to vary by threefold whereas the proportion of the accumulated phosphate that reaches the shoot differs by much less. This level of phosphate supply approached that likely to induce deficiency and when the concentration is reduced to 1 μM differences in transport capacity of up to fourfold were observed when the rate of arrival at the tip of the first leaf was continuously monitored. The rapidity with which the transport is shut off by adding 1 mM D(+) mannose to the root environment also varies significantly indicating that sizeable differences in either the accumulation of mannose or the activity of phosphomannoisomerase exist in these cultivars.
Ecotypes ofArmeria maritima collected from three sites, inland serpentine, inland mine dumps and coastal salt marsh were maintained as stock plants on the same peat mixture. Samples taken from these stocks were raised on a standard culture solution to provide genetically different material grown under constant conditions. The capacities for ion uptake were shown to differ very considerably and these differences were accentuated when the plants were grown in a range of concentrations of MgSO4, NaCl and MnSO4. The absorption of phosphate and its incorporation into nucleic acids were increased temporarily in the presence of 50 mM MgSO4 but the pattern of these changes was different in the three ecotypes. The absorption of Na, Cl, and Rb was measured after treatment with a range of concentrations of NaCl and the effect of treatment with MnSO4 on subsequent absorption of Mn and SO4 was also measured. The coastal plants were significantly more efficient in their absorption of these ions when treated at the lower levels of NaCl (0.5 and 10.0 mM). The short term absorption rates were not reflected in the overall accumulation of sodium over periods of 10 weeks and the coastal plants appeared to reduce the root content of sodium by transfer to the shoot and by increased active pumping to the exterior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen R J L 1940 The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem. J. 34, 858–865.
Brown J C 1977 Genetically controlled chemical factors involved in absorption and transport of iron by plants. Bioinorganic Chem. 11, 93–103.
Clark R B 1978 Differential response of maize inbreds to zinc. Agron. J. 20, 1057–1060.
Clark R B and Brown J C 1974 Differential phosphorus uptake by phosphorus stressed corn inbreds. Crop Science 14, 505–508.
El Bassam N 1981 Genetical variation in efficiency of plant root systems.In Structure and Function of Plant Roots. Eds. R Brouwer, O Gasparikova, J Kolek and B C Loughman. pp 237–245. Martinus Nijhoff, The Hague.
Goodwin-Bailey C I 1978 An Experimental Study of Inland and Maritime Populations ofArmeria maritima (Mill.) Willd. D. Phil. Thesis. University of Oxford.
Graham R D 1981 Genetics of the copper efficiency factor in rye.In Copper in Soils and Plants. Eds. J F Loneragan, A D Robson and R D Graham. Academic Press, Sydney, New York.
Hill J, Robson A D and Loneragan J F 1978 The effects of copper and nitrogen supply on the retranslocation of copper in four cultivars of wheat. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 29, 925–939.
Kime M J, Longhman B C, Ratcliffe R G and Williams R J P 1982 The application of31P nuclear magnetic resonance to higher plant tissue. 1. Detection of spectra. J. Exp. Bot. 33, 665–669.
Loughman B C 1966 The mechanism of absorption and utilization of phosphate by barley plants in relation to subsequent transport to the shoot. New Phytol. 65, 388–397.
Loughman B C 1978 Metabolic factors and the utilization of phosphorus by plants.In Phosphorus in the Environment: its Chemistry and Biochemistry. Eds. R Porter and D W Fitzimons. pp 154–174. Elsevier, Amsterdam and New York.
Loughman B C 1981 Metabolic aspects of transport of ions by cells and tissues of roots. Plant and Soil 63, 47–55.
Pollard A S, Parr A J and Loughman B C 1977 Boron in relation to membrane function in higher plants. J. Exp. Bot 28, 831–839.
Rivier L and Pilet P E 1981 Absicic acid levels in the root tips of sevenZea mays varieties. Phytochemistry 20, 17–19.
Sarić M and Škorić D 1981 Relationship between the root and above ground parts of different sunflower inbreds regarding the content of some mineral elements.In Structure and Function of Plant Roots. Eds. R Brouwer, O. Gasparikova, J. Kolek and B C Loughman. pp 399–401. Martinus Nijhoff, The Hague.
Silberbush M, Shomer-Ilan A and Waisel Y 1981 Root surface phosphatase activities in ecotypes ofAegilops peregrina (Hack.) Marie et Weil. Physiol. Plant. 53, 501–504.
Zobel R W 1975 The genetics of root development.In The Development and Function of Roots. Eds. J G Torrey and D J Clarkson. pp 261–275. Academic Press, London, New York, San Francisco.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loughman, B.C., Roberts, S.C. & Goodwin-Bailey, C.I. Varietal differences in physiological and biochemical responses to changes in the ionic environment. Plant Soil 72, 245–259 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181964
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181964