Summary
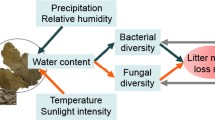
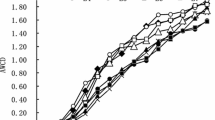
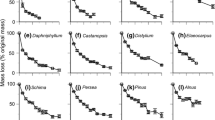
The application of dithane M-45, 2, 4-D and carbofuran at the rates of 1, 5 and 10 mg (active ingredients) per g air-dry litter caused insignificant variations in the microbial populations in decomposing leaf litter. The qualitative nature of mycoflora, was altered, a little, with regard to the total number of species and relative abundance of a few species. The variations in CO2 evolution was significant only in relation to the fungicidal treatment. Percent weight loss of treated and untreated litter differed insignificantly at the end except in the case of fungicidal treatment. The present study infers that the used concentrations of the test pesticides may be recommended in tropical forestry as their application does not pose any potential threat to the process of natural decomposition of the leaf litter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander M 1969 Microbial degradation and biological effects of pesticides in soil. pp 209–240.In Soil Biology: Review of Research, UNESCO, Paris.
Atlas R M, Pramer D and Bartha R 1978 Assessment of pesticide effects on non-target soil microorganisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 10, 231–239.
Audus L J 1964 Herbicide behaviour in the soil. II Interactions with soil microorganisms. pp 163–206.In The Physiology and Biochemistry of Herbicides. Ed. L J Audus. Academic Press. New York, USA.
Bollen W B 1961 Interactions between pesticides and soil microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 15, 69–92.
Cole M A and Turgeon A J 1978 Microbial activity in soil and litter underlying bandane and calcium arsenate treated trufgrass. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 10, 181–186.
Cullimore D R 1971 Interaction between herbicides and soil microorganisms. Residue Rev. 35, 65–80.
Eno C F 1958 Insecticides and the soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 6, 348–351.
Eno C F and Everett P H 1958 Effects of soil applications of ten chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticides on soil microorganisms and the growth of stringless Black Valentine beam Soil Sci. Soc. Am Proc. 22, 235–238.
Fletcher W W 1960 The effect of herbicides on soil micro-organisms. pp 20–62.In Herbicides and the Soil. Eds E K Woodford and G R Sagar. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford England.
Gottschalk M R and Shure D J 1979 Herbicide effects on leaf litter decomposition processes in an oak-hickory forest. Ecology 60, 143–151.
Kuthubutheen A J and Pugh G J F 1979 The effects of fungicides on soil fungal populations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 11 297–303.
Lewis J A, Papavizas G C and Tora T S 1978 Effects of some herbicides on microbial activity in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 10, 137–141.
Macauley B J 1975 Biodegradation of litter inEucalyptus pauciflora communities. I Techniques for comparing the effects of some fungi and insects. Soil Biol. Biochem. 7, 341–344.
Pramer D and Bartha R 1972 Preparation and processing of soil samples for biodegradation studies. Evir. Lett. 2, 217–224.
Rai B and Srivastava A K 1982 Decomposition of leaf litter in relation to microbial populations and their activity in a tropical dry mixed deciduous forest. Pedobioligia 24, 151–159.
Rai B and Srivastava A K 1982 Microbial decomposition of leaf litter as influenced by fertilizers. Plant and Soil 66, 195–204.
Smith N R and Wenzel M E 1947 Soil microorganisms are affected by some of the new insecticides. Soil Sci. Soc. Am Proc. 12, 227–233.
Weary G C and Merriam H G 1978 Litter decomposition in a red maple woodlot under natural conditions and under insecticide treatment. Ecology 59, 180–184.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, B., Srivastava, A.K. Microbial decomposition of leaf litter as influenced by pesticides. Plant Soil 74, 265–272 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02143616
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02143616