Summary
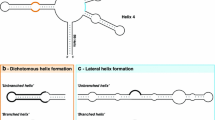
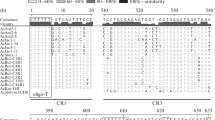
The internal transcribed spacer (ITS) 1 and 2, the 5.8S rRNA gene, and adjacent 18S rRNA and 25S rRNA coding regions of two Cucurbitaceae (Cucurbita pepo, zucchini, ITS 1: 187 bp, and ITS 2: 252 bp in length, andCucumis sativus, cucumber, ITS 1: 229 bp, and ITS 2: 245 bp in length) have been sequenced. The evolutionary pattern shown by the ITSs of these plants is different from that found in vertebrates. Deletions, insertions, and base substitutions have occurred in both spacers; however, it is obvious that some selection pressure is responsible for the preservation of stem-loop structures. The dissimilarity of the 5′ region of ITS 2 found in higher plants has consequences for proposed models on U3 snRNA-ITS 2 interaction in higher eukaryotes.
The two investigated Cucurbitaceae species show a G+C content of ITS 1 that nearly equals that of ITS 2. An analysis of the ITS sequences reveals that in 19 out of 20 organisms published, the G+C content of ITS 1 nearly equals that of ITS 2, although it ranges from 20% to 90% in different organisms (GC balance). Moreover, the balanced G+C content of the ITSs in a given species seems to be similar to that of so-called expansion segments (ESs) in the 25/28S rRNA coding region. Thus, ITSs show a phenomenon called molecular coevolution with respect to each other and to the ESs. In the ITSs of Cucurbitaceae the balanced G+C composition is at least partly achieved by C to T transitions, via deamination of 5-methylcytosine. Other mutational events must be taken into account. The appearance of this phenomenon is discussed in terms of functional constraints linked to the structures of these spacers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachellerie JP, Michot B, Raynal F (1983) Recognition signals for mouse pre-rRNA processing. Mol Biol Rep 9:79–86
Bernardi G, Olofsson B, Filipski J, Zerial M, Salinas J, Cuny G, Meunier-Rotival M, Rodier F (1985) The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science 228:953–958
Bernardi G, Mouchiroud D, Gautier C, Bernardi G (1988) Compositional patterns in vertebrate genomes: conservation and change in evolution. J Mol Evol 28:7–18
Boothroyd JC, Wang A, Campbell DA, Wang CC (1987) An unusually compact ribosomal DNA repeat in the protozoanGiardia lamblia. Nucleic Acids Res 15:4065–4084
Brimacombe R, Maly P, Zweib C (1983) The structure of ribosomal RNA and its organization relative to ribosomal protein. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 28:1–48
Chambers C, Dutta SK, Crouch RJ (1986)Neurospora crassa ribosomal DNA: sequence of internal transcribed spacer and comparison withN. intermedia andN. sitophila. Gene 44:159–164
Clark CG (1987) On the evolution of ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol 25:343–350
Coulondre C, Miller JH, Farabaugh PJ, Gilbert W (1978) Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots inEscherichia coli. Nature 274:775–780
Crouch RJ, Kanaya S, Earl PL (1983) A model for the involvement of the small nucleolar RNA (U3) in processing eukaryotic ribosomal RNA. Mol Biol Rep 9:75–78
Dover GA, Flavell RB (1984) Molecular coevolution: DNA divergence and the maintenance of function. Cell 38:622–623
Ebel JP, Branlant C, Carbon P, Ehresmann B, Ehresmann C, Krol A, Stiegler P (1983) Sequence and secondary structure conservation in ribosomal RNAs in the course of evolution. In: Pullman B, Jortner J (eds) Nucleic acids—the vectors of life. D Reidel, Durdrecht, pp 387–401
Eckenrode VK, Arnold J, Meagher RB (1985) Comparison of the nucleotide sequence of soybean 18S rRNA with the sequences of other small-subunit rRNAs. J Mol Evol 21:259–269
Ellis RE, Sulston JE, Coulson AR (1986) The rDNA ofC. elegans: sequence and structure. Nucleic Acids Res 14:2345–2364
Furlong JC, Maden BEH (1983) Patterns of major divergence between the internal transcribed spacers of ribosomal DNA inXenopus borealis andXenopus laevis, and of minimal divergence within ribosomal coding regions. EMBO J 2:443–448
Ganal M, Hemleben V (1986) Structure and evolution of ribosomal RNA genes in closely related Cucurbitaceae. Plant Syst Evol 154:63–77
Ganal M, Torres R, Hemleben V (1988) Complex structure of the ribosomal DNA spacer ofCucumis sativus (cucumber). Mol Gen Genet 212:548–554
Gerbi S (1986) Evolution of ribosomal DNA. In: MacIntyre R (ed) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Plenum Press, New York, pp 419–517
Gruenbaum Y, Naveh-Many T, Cedar H, Razin A (1981) Sequence specificity of methylation in higher plant DNA. Nature 292:860–862
Hagenbüchle O, Santer M, Steitz JA (1978) Conservation of the primary structure at the 3′ end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell 13:551–563
Hall LMC, Maden BEH (1980) Nucleotide sequence through the 18S–28S intergene region of a vertebrate ribosomal transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res 8:5993–6005
Hancock JM, Dover GA (1988) Molecular coevolution among cryptically simple expansion segements of eukaryotic 26S/28S rRNAs. Mol Biol Evol 5:377–391
Hancock JM, Tautz D, Dover GA (1988) Evolution of the secondary structures and compensatory mutations of the ribosomal RNAs ofDrosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 5:393–414
Hanson MR (1989) Tracking down plant genes: path, patterns, and footprints. The Plant Cell 1:169–172
Hemleben V, Grierson D, Dertmann H (1977) The use of equilibrium centrifugation in actinomycin D-caesiumchloride for the purification of ribosomal DNA. Plant Sci Lett 9:129–135
Hemleben V, Leweke B, Roth A, Stadler I (1982) Organization of highly repetitive satellite DNA of two Cucurbitaceae species (Cucumis melo andCucumis sativus). Nucleic Acids Res 10:631–644
Hindenach BR, Stafford DW (1984) Nucleotide sequence of the 18S–16S rRNA intergene region of the sea urchin. Nucleic Acids Res 12:1737–1747
Jacq B (1981) Sequence homologies between eukaryotic 5.8S rRNA and the 5′ end of prokaryotic 23S rRNA: evidences for a common evolutionary origin. Nucleic Acids Res 9:2913–2932
Jeppesen C, Stebbins-Boaz B, Gerbi SA (1988) Nucleotide sequence determination and secondary structure ofXenopus U3 snRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 16:2127–2148
Kavanagh TA, Timmis JN (1988) Structure of melon rDNA and nucleotide sequence of the 17–25S spacer region. Theor Appl Genet 76:673–680
Kiss T, Toth M, Solymosy F (1985) Plant small nuclear RNAs. Nucleolar U3 snRNA is present in plants: partial characterization. Eur J Biochem 152:259–266
Kiss T, Kiss M, Abel S, Solymosy F (1988) Nucleotide sequence of the 17S–25S spacer region from tomato rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res 16:7179
Larson R, Messing J (1982) Apple II software for M13 shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 10:39–49
Maden BEH, Moss M, Salim M (1982) Nucleotide sequence of an external transcribed spacer inXenopus laevis rDNA: sequences flanking the 5′ and 3′ ends of 18S rRNA are noncomplementary. Nucleic Acids Res 10:2387–2398
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
McCarrol R, Olsen GJ, Stahl YD, Woese CR, Sogin ML (1983) Nucleotide sequence of theDictyostelium discoideum small-subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid inferred from the gene sequence: evolutionary implications. Biochemistry 22:5858–5868
McKay RM, Spencer DF, Doolittle WF, Gray MW (1980) Nucleotide sequences of wheat-embryo cytosol 5-S and 5.8-S ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Eur J Biochem 112:561–576
Messing J, Vieira J (1982) A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand or double-digest restriction enzyme fragments. Gene 19:269–276
Messing J, Carlson J, Hagen G, Rubenstein I, Oleson A (1984) Cloning and sequencing of the ribosomal RNA gene in maize: the 17S region. DNA 3:31–40
Michot B, Bachellerie J-P, Raynal F (1983) Structure of mouse rRNA precursors. Complete sequence and potential folding of the spacer regions between 18S and 28S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 11:3375–3391
Nazar RN (1980) A 5.8 S rRNA-like sequence in prokaryotic 23S rRNA. FEBS Lett 119:212–214
Nazar RN (1982) The eukaryotic 5.8 and 5 S ribosomal RNAs and related rDNAs. In: Busch H, Rothblum L (eds) The cell nucleus-rDNA part B, vol XI. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–28
Nazar RN, Wong WM, Abrahamson JLA (1987) Nucleotide sequence of the 18–25S ribosomal RNA intergenic region from a thermophile,Thermomyces lanuginosus. Biol Chem 262:7523–7527
Ninio J (1979) Prediction of pairing schemes in RNA molecules-loop contributions and energy of wobble and non-wobble pairs. Biochimie 61:1133–1150
Noller HF (1984) Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem 53:119–162
Normore WM, Brown JR (1970) Guanine plus cytosine (G+C) composition of bacteria. In: Sober HA (ed) Handbook of biochemistry—selected data for molecular biology. CRC, Cleveland OH, pp H24-H79
Ozaki T, Hoshikawa Y, Iida Y, Iwabuchi M (1984) Sequence analysis of the transcribed and 5′ non-transcribed regions of the ribosomal RNA gene inDictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res 12:4171–4184
Parker KA, Steitz JA (1987) Structural analyses of the human U3 ribonucleoprotein particle reveal a conserved sequence available for base pairing with pre-rRNA. Mol Cell Biol 7:2899–2913
Parker KA, Bruzik JP, Steitz JA (1988) An in vitro interaction between the human U3 snRNP and 28S rRNA sequences near the alpha-sarcin site. Nucleic Acids Res 16:10493–10509
Perry RP (1976) Processing of RNA. Annu Rev Biochem 45:605–629
Prestayko AW, Tanato M, Busch H (1970) Low molecular weight RNA associated with nucleolar 28S RNA. J Mol Biol 47:505–515
Pustell J, Kafatos FC (1984) A convenient and adaptable package of computer programs for DNA and protein sequence management, analysis, and homology determination. Nucleic Acids Res 12:643–655
Rafalski JA, Wiewiorowski M, Söll D (1983) Organization of ribosomal DNA in yellow lupine (Lupinus luteus) and sequence of the 5.8 S RNA gene. FEBS Lett 152:241–246
Reddy R, Henning D, Busch H (1979) Nucleotide sequence of nucleolar U3B RNA. J Biol Chem 254:11097–11105
Reddy R, Rothblum LI, Subrahmanyam CS, Liu M-H, Henning D, Cassidy B, Busch H (1983) The nucleotide sequence of 8S RNA bound to preribosomal RNA of Novikoff hepatoma. J Biol Chem 258:584–589
Salinas J, Matassi G, Montero LM, Bernardi G (1988) Compositional compartmentalization and compositional patterns in the nuclear genomes of plants. Nucleic Acids Res 16:4269–4285
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5476
Schaak J, Mao J, Söll D (1982) The 5.8S RNA gene sequence and the ribosomal repeat ofSchizosaccharomyces pombe. Nucleic Acids Res 10:2851–2864
Schiebel K, Hemleben V (1989) Nucleotide sequence of the 18S–25S spacer region from rDNA of mung bean. Nucleic Acids Res 17:2852
Schwarz Z, Kössel H (1980) The primary structure of 16S rDNA fromZea mays chloroplast is homologous toE. coli 16S rRNA. Nature 283:739–742
Shapiro HS (1970) Distribution of purines and pyrimidines in deoxyribonucleic acids. In: Sober HA (ed) Handbook of biochemistry—selected data for molecular biology. CRC, Cleveland OH, pp H80-H99
Sogin ML, Elwood HJ, Gunderson JH (1986) Evolutionary diversity of eukaryotic small-subunit rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1383–1387
Spencer DF, Collings JC, Schnare MN, Gray MW (1987) Multiple spacer sequences in the nuclear large subunit ribosomal RNA gene ofCrithidia fasciculata. EMBO J 6:1063–1071
Subrahmanyam CS, Cassidy B, Busch H, Rothblum LI (1982) Nucleotide sequence of the region between the 18S rRNA sequence and the 28S rRNA sequence of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 10:3667–3680
Sulston JE, Brenner S (1974) The DNA ofCaenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 77:95–104
Tague BW, Gerbi SA (1984) Processing of the large rRNA precursor: two proposed categories of RNA-RNA interactions in eukaryotes. J Mol Evol 20:362–367
Takaiwa F, Oono K, Sugiura M (1985) Nucleotide sequence of the 17S–25S spacer region from rice rDNA. Plant Mol Biol 4:355–364
Tanaka Y, Dyer TA, Brownlee GG (1980) An improved direct RNA sequence method; its application toVicia faba 5.8S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:1259–1272
Tautz D, Hancock JM, Webb DA, Tautz C, Dover GA (1988)Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 5:366–376
Tinoco I, Borer PN, Dengler B, Levine MD, Uhlenbeck OC, Crothers DM, Gralla J (1973) Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nature New Biol 246:40–41
Tu J, Zillig W (1982) Organization of rRNA structural genes in the archaebacteriumThermoplasma acidophilum. Nucleic Acids Res 10:7231–7245
Vaughn JC, Sperbeck SJ, Ramsey WJ, Lawrence CB (1984) A universal model for the secondary structure of 5.8S ribosomal RNA molecules, their contact sites with 28S ribosomal RNAS, and their prokaryotic equivalent. Nucleic Acids Res 12:7479–7502
Veldman GM, Brand RC, Klootwijk J, Planta RJ (1980) Some characteristics of processing sites in ribosomal precursor RNA of yeast. Nucleic Acids Res 8:2907–2920
Veldman GM, Klootwijk J, van Heerikhuizen H, Planta RJ (1981) The nucleotide sequence of the intergenic region between the 5.8S and 26S rRNA genes of the yeast ribosomal RNA operon. Possible implications for the interaction betweet 5.8S and 26S rRNA and the processing of the primary transcript. Nucleic Acids Res 9:4847–4862
Vossbrinck CR, Woese CR (1986) Eukaryotic ribosomes that lack a 5.8S RNA. Nature 320:287–288
Wise JA, Weiner AM (1980)Dictyostelium small nuclear RNA D2 is homologous to rat nucleolar RNA U3 and is encoded by a dispersed multigene family. Cell 22:109–118
Woese CR, Gutell R, Gupta R, Noller HF (1983) Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev 47:621–669
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Zieve G, Penman S (1976) Small RNA species of the HeLa cell: metabolism and subcellular localization. Cell 8:19–31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres, R.A., Ganal, M. & Hemleben, V. GC balance in the internal transcribed spacers ITS 1 and ITS 2 of nuclear ribosomal RNA genes. J Mol Evol 30, 170–181 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02099943
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02099943