Summary
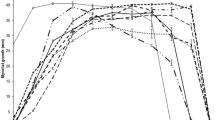
The effect of different sulphur and phosphorus compounds on the growth and reproduction of three fungi causing storage rot, viz.,Fusarium solani, Botryodiplodia ananassae andMacrophomina phaseoli has been studied. Sixteen different sources of sulphur were used and out of them magnesium sulphate was found to be most favourable for the growth and reproduction of all the three fungi. Sodium sulphite and sodium bisulphite were toxic. Potassium metabisulphite prevented growth ofF. solani and M. phaseoli while it supported moderate growth ofB. ananassae. Only magnesium sulphate could induce the sporulation ofB. ananassae while sporulation and sclerotial development ofF. solani andM. phaseoli respectively varied with the type of sulphur sources used. Optimum concentration of magnesium sulphate was also determined and it was found that the growth and sporulation ofF. solani andB. ananassae were best at 0.375 g/l and 0.75 g/l.M. phaseoli tolerated higher doses of this substance as the best growth and excellent sclerotial development were recorded at 3.0 g/l (the maximum concentration used). Phosphorus was found to be essential for the present fungi as none of them could grow in complete absence of this substance. Onthophosphates and nucleic acid, were found to be favourable sources for growth and reproduction of the 3 organisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, G. M. (1921) Studies in the physiology of the fungi. 14. Sulphur nutrition: the use of thiosulphate as influenced by hydrogen-ion concentration. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard.8: 237–281.
Agarwal, G. P. (1957) Sulphur and phosphorus nutrition of two strains ofFusarium coeruleum (Lib.)Sacc. Phyton,8: 43–51.
Agarwal, G. P. (1958) An addition to the literature on sulphur and phosphorus requirements of fungi. J. Indian bot. Soc.27: 375–379.
Agarwal, G. P. &S. Ganguli (1960) Nitrogen and sulphur requirements ofPestalotiopsis versicolor (Speg.)Steyaert. Phyton.14: 159–165.
Barner, H. D. &E. C. Cantino (1952) Nutritional relationships in a new species ofBlastocladiella. Amer. J. Bot.39: 746–751.
Bhargava, K. S. (1945) Physiological studies on some members of the family Saprolegniaceae II. Sulphur and phosphorus requirements. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci.21B: 344–349.
Challenger, F. (1953) The biological importance of organic compounds of sulphur. Endeavour.12: 173–181.
Garrett, S. D. (1936) Soil conditions and the ‘Take All’ diseases of Wheat. Ann. appl. Biol.23: 667–699.
Haglund, W. A. &T. H. King (1962) Sulfur nutrition ofAphanomyces euteiches. Phytopathology.52: 315–317.
Hungate, F. P. &T. J. Mannell (1952) Genetics.37: 709–719.
Lilly, V. G. &H. L. Barnett (1951) Physiology of the fungi. McGraw Hill Book Co., New York.
Mann, T. (1944) Studies on the metabolism of mould fungi I. Phosphorus metabolism in moulds. Biochem. J.38: 339–345.
Mehrotra, B. S. (1949) D. Phil. Thesis, University of Allahabad.
Mosher, W. A., D. H. Saunders, L. B. Kingery &R. J. Williams (1936) Nutritional requirements of the pathogenic mouldTrichophyton interdigitale. Plant Physiol.11: 795–806.
Saksena, R. K. &D. Kumar (1962) Some physiological studies on Sphaeropsidales. Proc. Nav. Acad. Sci. (India)32B: 37–49.
Saksena, R. K., S. K. Jain &S. M. H. Jafri (1952) Sulphur and nitrogen requirements of the genusPythium. J. Indian bot. Soc.31: 281–286.
Schade, A. L. (1940) The nutrition ofLeptomitus. Amer. J. Bot.27: 376–384.
Srivastava, J. P. (1951) Studies onCurvularia lunata (Walker). Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (India)21B: 117–137.
Steinberg, R. A. (1936) Effect of barium salts uponAspergillus niger and their bearing upon the sulfur and zinc metabolism of the fungus in an optimum solution. Bot. Gaz.97: 666–671.
Steinberg, R. A. (1941) Sulfur and trace element nutrition ofAspergillus niger. J. agric. Res.63: 109–127.
Tandon, M. P. (1950) D. Phil. Thesis, University of Allahabad.
Tandon, R. N. (1961) Physiological studies of some pathogenic fungi, S.R.C. Monograph, Uttar Pradesh.
Tandon, R. N. &S. N. Bhargava (1960) Some physiological studies onPestalotia sp. causing leaf spot disease ofLivistona rotundifolia. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (India)30B: 257–265.
Tandon, R. N. &S. N. Bhargava (1962) Hydrogen-ion concentration and temperature effects on three pathogenic fungi. Abs. of contributed papers. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (India) Annual Session, p. 36.
Tandon, R. N. &S. N. Bhargava (1962) Physiological studies onPestalotiopsis glandicola (Cast.)Steyaert. Bot. Mag. Saugar University, Prof. S. K. Pande's commemoration volume.
Tandon, R. N. &K. S. Bilgrami (1957) Cultural Studies ofPestalotia mangiferae (Butl.) with special reference to its sporulation I. The influence of nutrients. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (India)27B: 98–105.
Tandon, R. N. &K. S. Bilgrami (1958) Sulphur requirements of two species ofPhyllosticta. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (India)28B: 293–297.
Volkonsky, M. (1933) ‘Sur les conditions de culture et le pouvoir de synthèse deSaprolegnia sp. Etude qualitative de l'alimentation carbonée azotée et sulfrée’. Ann. Inst. Pasteur, Paris.50: 703–730.
Volkinsky, M. (1934) ‘Sur la nutrition de quelques champignons saprophytes et parasites’. Ann. Inst. Pasteur, Paris.52: 76–101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhargava, S.N., Tandon, R.N. Sulphur and phosphorus requirements of three fungi causing diseases in storage. Mycopathologia et Mycologia Applicata 21, 169–178 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02052572
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02052572