Abstract
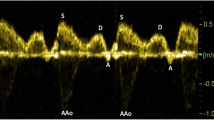
The objective of the investigation was to determine what effect intracranial pathology has on alterations of superior sagittal sinus blood flow, and to determine the role of color flow Doppler imaging of the superior sagittal sinus in the diagnosis of intracranial pathology in the neonate and infant. One hundred examinations were performed prospectively in 96 patients. The velocity was determined with an angle correction at 30–60° and was obtained with and without gentle transducer compression. Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis was identified in two patients by the absence of flow. Multiplet-tests for independent measures showed no clinically significant differences between flow velocities with regard to intracranial hemorrhage, ventriculomegaly, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy or prematurity. The authors conclude that color flow Doppler can accurately diagnose superior sagittal sinus thrombosis and may be used to screen high risk neonates such as those with thrombosis elsewhere or those treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. No clinically significant associations were found between superior sagittal sinus flow velocity and any of the parameters evaluated in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor GA, Walker LK (1992) Intracranial venous system in newborns treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: Doppler US evaluation after ligation of the right jugular vein. Radiology 183: 453–456
Govaert P, Voet D, Achten E, Vanhaesebrouck P et al (1992) Noninvasive diagnosis of superior sagittal sinus thrombosis in a neonate. Am J Perinatol 9: 201–204
Gould SJ, Howard S, Hope PL, Reynolds EO (1987) Periventricular intraparenchymal cerebral haemorrhage in preterm infants: the role of venous infarction. J Pathol 151: 197–202
Winkler P, Helmke K (1989) Duplex-scanning of the deep venous drainage in the evaluation of blood flow velocity of the cerebral vascular system in infants. Pediatr Radiol 19: 79–90
Cowan F, Thoresen M (1985) Changes in superior sagittal sinus blood velocities due to postural alterations and pressure on the head of the newborn infant. Pediatrics 75: 1038–1047
Nüssel F, Huber P (1989) High resolution computed tomography of superior sagittal sinus-thrombosis and abnormalities. Neuroradiology 31: 307–311
Justich E, Lammer J, Fritsch G, Beitzke A, Walter GF (1984) CT diagnosis of thrombosis of dural sinuses in childhood. Eur J Radiol 4: 294–295
Virapongse C, Cazenave C, Quisling R, Sarwar M, Hunter S (1987) The empty delta sign: frequency and significance in 76 cases of dural sinus thrombosis. Radiology 162: 779–785
Wong WS, Tsuruda JS, Liberman RL, Chirino A, Vogt JF, Gangitano E (1989) Color Doppler imaging of intracranial vessels in the neonate. AJR 152: 1065–1070
Barkovich J (1990) Infections of the nervous system. In: Norman D (ed) Pediatric neuroimaging. Raven, New York, pp 296–301
Front D, Israel O, Even-Sapir E, Feinsud M (1986) Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis: assessment with Tc-99m labeled red blood cells. Radiology 158: 453–456
Bridgers SL, Strauss E, Smith EO, Reed D, Ezekowitz MD (1986) Demonstration of superior sagittal sinus thrombosis by indium-111 platelet scintigraphy. Arch Neurol 43: 1079–1081
Taylor GA (1992) Intracranial venous system in the newborn: evaluation of normal anatomy and flow characteristics with color Doppler US. Radiology 183: 449–452
Pfannschmidt J, Jorch G (1989) Transfontanelle pulsed Doppler measurement of blood flow velocity in the internal jugular vein, straight sinus, and internal cerebral vein in preterm and term neonates. Ultrasound Med Biol 15: 9–12
Fenton AC, Papathoma E, Evans DH, Finst P, Levene MI (1991) Neonatal cerebral venous flow velocity measurement using a color flow Doppler system. J Clin Ultrasound 19: 69–72
Konishi Y, Kuriyama M, Sudo M, Konishi K, Hayakawa K, Ishii Y (1987) Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis in neonates. Pediatr Neurol 3: 222–225
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bezinque, S.L., Slovis, T.L., Touchette, A.S. et al. Characterization of superior sagittal sinus blood flow velocity using color flow Doppler in neonates and infants. Pediatr Radiol 25, 175–179 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02021526
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02021526