Abstract
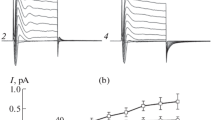
The effects of three K+-channel blockers, quinine, quinidine and sparteine on K+-evoked histamine (HA) release have been investigated. KCl (150 mM) initiated 40–55% release of HA from rat peritoneal mast cells in the absence of extracellular Ca++, and this could be suppressed by pretreating the cells with K+-channel blockers. In the concentration range of 0.05–2 mM, reductions were dose-dependent and the IC50-s (in mM) obtained were 0.15 and 0.25 for quinine and quinidine and 0.20 for sparteine. The light microscopic studies showed close parallelism between the KCl-evoked HA-release and mast cell degranulation in the absence and also in the presence of K+-channel blockers. Present results strenghthened the involvement of K+-channels in the KCl-evoked HA release and showed that these channels are sensitive to quinine/quinidine and also to sparteine. These data appeared, however, insufficient to clarify fully the mechanism of K+-induced HA secretion or to classify the K+-channels involved in this mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Németh, P. Magyar, R. Herceg and Z. Huszti,Potassium-induced release of histamine from mast cells and its inhibition by ketotifen. Agents and Actions20, 149–152, 1987.
A. Németh, P. Magyar and Z. Huszti,Inhibition of potassium-induced release of histamine from mast cells by tetraethylammonium and tetramethylammonium. Agents and Actions30, 143–145, 1990.
O. P. Hamil,Membrane ion channels: (in Burgen, Roberts, eds) Topics in molecular pharmacology, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1983, pp. 182–205.
I. Findlay, M. Dunne, S. Ulrich, C. B. Wollheim and O. H. Petersen,Quinine inhibits Ca ++-independent K +-channels whereas tetraethylammonium inhibits Ca ++-activated K +-channels in insulin-secreting cells. FEBS Letters185, 4–7, 1985.
A. L. Kleinhaus,Segregation of leech neurones by the effect of sparteine on action potential duration. J. Physiol.299, 309–321, 1980.
P. Shore, A. Burkhalter and V. H. Cohn,A method for fluorimetric assay of histamine in tissues. J. Pharm. exp. Ther.127, 182–186, 1959.
G. Paolisso, M. Nenquin, W. Schmeer, F. Mathot, H. P. Meissner and C. Henquin,Sparteine increases insulin release by decreasing the K +-permeability of the B-cell membrane. Biochem. Pharmacol.34, 2355–2361, 1985.
E. A. Newman,Distribution of potassium conductance in mammalian Muller (glial) cells: a comparative study. J. Neurosci.7, 2423–2432, 1987.
M. Armando-Hardy, J. C. Ellory, H. G. Ferreira, S. Fleminger,Inhibition of calcium-induced increase in the potassium permeability of human red blood cells by quinine, Proc. Phys. Soc.250, 32–33P, 1975.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Németh, A., Huszti, Z. Characterization of potassium channels in mast cell plasma membranes: Their possible existence and involvement in potassium-evoked histamine release. Agents and Actions 36 (Suppl 2), C308–C310 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01997359
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01997359