Abstract
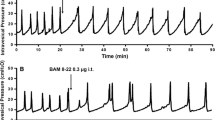
The involvement of capsaicin-sensitive primary afferent neurons has been investigated in a rat model of cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis. CYP (150 mg/kg i.p., 48 h before) was administered in both vehicle- and capsaicin-(50 mg/kg s.c., 4 days before)-treated rats. Some experiments were performed 96 h after bilateral removal of pelvic ganglia (bladder denervation). CYP produced a marked detrusor hyperreflexia which was abolished by capsaicin pretreatment. CYP produced a marked increase in bladder weight and plasma protein extravasation (PPE, measured by Evans blue leakage technique): CYP-induced PPE was reduced by bladder denervation and was aggravated by capsaicin pretreatment. PPE aggravation by capsaicin was abolished by ganglionectomy. The bladder content of calcitonin gene-related peptide, was unaffected CYP. We conclude that CYP-induced decrease in bladder capacity is entirely mediated through stimulation of capsaicin-sensitive bladder afferents. At the time chosen as end point in these experiments, capsaicin-sensitive afferents exert an antiinflammatory influence on CYP-induced cystitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. A. Maggi,The role of peptides in the regulation of micrturition feflex: An update, Gen. Pharmacol.22, 1–24 (1991).
C. A. Maggi, S. Giuliani, E. Del Bianco, P. Geppetti, E. Theodorsson and P. Santicioli,CGRP in the regulation of urinary tract motility. Ann. NY Acad. Sci.657, 328–343 (1992).
L. H. Fraiser, S. Kanekal and J. P. Kehrer,Cyclophosphamide toxicity—Characterising and avoiding the problem. Drugs42, 781–795.3, 143–201 (1991).
D. J. Grinberg-Funes, C. Sheldon and M. Weiss,The use of prostaglandin F 2α for the prophylaxis of cyclophosphamide induced cystitis in rats. J. Urol.144, 1500–1504 (1990).
C.A. Maggi, P. Santicioli, L. Abelli, M. Parlani, M. Capasso, B. Conte, S. Giuliani and A. Meli,Regional differences in the effects of capsaicin and tachykinins on motor activity and vascular permeability of the rat lower urinary tract, Naun. Schmied. Arch. Pharmacol.335, 636–645 (1978).
C. A. Maggi, P. Santicioli, R. Patacchini, P. Geppetti, S. Giuliani, M. Astolfi, E. Baldi, M. Parlani, E. Theodorsson, B. Fusco and A. Meli,Regional differences in the motor response to capsaicin in the guinea-pig urinary bladder-relative role of pre- and post-junctional factors related to neuropeptide-containing sensory nerves. Neuroscience27, 675–688 (1988).
L. Abelli, V. Somma, C.A. Maggi, D. Regoli, M. Astolfi, M. Parlani, P. Rovero, B. Conte and A. Meli,Effects of tachykinins and selective tachykinin receptor agonists on vascular permeability in the rat lower urinary tract: Evidence for the involvement of NK-1 receptors. J. Autonom. Pharmacol.9, 253–260 (1989).
A. Eglezos, S. Giuliani, G. Viti and C. A. Maggi,Direct evidence that capsaicin-induced plasma protein extravasation is mediated through tachykinin NK-1 receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol.209, 277–279 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maggi, C.A., Lecci, A., Santicioli, P. et al. Cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in rats: Involvement of capsaicin-sensitive primary afferents. Agents and Actions 38 (Suppl 2), C28–C30 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991127
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991127