Abstract
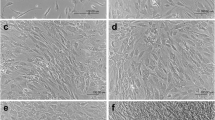
Anin vitro model was developed for the investigation of bone cell mineralization processes. Out-grown cells of explanted human nasal bone fragments were selected into three lineages and one of them, the osteoblast-enriched line, was partially characterized. A large number of cells of this line stained readily for alkaline phosphatase. They produced prostanoids, PGl2, PGF2α and PGE2, and osteocalcin in the presence of 1,25(OH)2D3. Cells synthesized collagen and mineralized the developed extracellular matrix. This latter line seems to be appropriate as a model system to find effective compounds which increase bone calcification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Feuer, P. Barát, I. Strauss and E. Kékes,Experimental studies on the cardiological effects of ipriflavone on the isolated rabbit heart, and rat and dog. Arzneimittel Forsch. Drug Res.31, 953–958 (1981).
S. Benvenuti, A. Tanini, U. Frediani, S. Bianchi, L. Masi, R. Casano, L. Bufalino, M. Serio and M. L. Brandi,Effects of ipriflavone and its metabolites on a clonal osteoblastic cell line. J. Bone Miner. Res.6, 987–996 (1991).
Y. Kakai, T. Kawase, T. Nakano, Y. Mikuni-Takagaki and S. Saito,Effect of ipriflavone and estrogen on the differentiation and proliferation of osteogenic cells, Calcif. Tissue Int.51 (Suppl. 1), S11-S15 (1992).
N. Udagawa, T. Sasaki, T. Akatsu, N. Takahashi, S. Tanaka, T. Tamura, H. Tanaka and T. Suda,Lack of bone resorption in osteosclerotic (oc/oc) mice is due to a defect in osteoclast progenitors rather than the local microenvironment provided by osteoblastic cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.184, 67–72 (1992).
J. M. Kissane and E. Robins,The fluorometric measurement of deoxyribonucleic in animal tissues with special reference to the central nervous system. J. Biol. Chem.233, 184–188 (1958).
M. Goppelt-Struebe and M. Golombek,Fluorometric determination of the DNA content of cells cultured in tissue culture plates. J. Immunol. Methods151, 245–248 (1992).
D. Mascelier, B. Herbert, N. Hauser, P. Mermillod, E. Schonne and C. Remacle,Morphologic characterization of osteoblast-like cell cultures isolated from newborn rat Calvaria. Calcif. Tissue Int.47, 92–104 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ecsedi, G.G. Model forin vitro investigation of bone mineralization. Agents and Actions 41, 84–85 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01986399
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01986399