Abstract
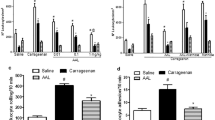
Bacterial products fmet-leu-phe (FMLP), muramyl dipeptide (MDP) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were assayed for their ability to alter the inflammatory response to λ carrageenan-induced pleurisy in Hooded Surgery rats. Continuously infused FMLP, or one initial i.v. dose of FMLP, MDP or LPS either ablated or partially suppressed the pleurisy. Total circulating leucocytes and neutrophils were suppressed by 55–65% when compared to the normal circulating leucocyte response to carrageenan pleurisy, excepting the protocol incorporating a single i.v. dose of FMLP where suppression was intermediate at 30%. There were also significant changes in the expression of FMLP receptors on circulating neutrophils. MDP and LPS induced a receptor number increase of 2 and 1.7 times initial value respectively, whilst a continuous FMLP infusion caused a receptor decrease to 0.3 times the initial value. The introduction of bacterial products at an alternative site to that of the pleurisy had an anti-inflammatory effect and the pleurisy was reduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. A. Sklar, A. J. Jesaitis and R. G. Painter,The neutrophil N-formyl peptide receptor: Dynamics of ligand-receptor interactions and their relationship to cellular responses. InContemporary Topics in Immunobiology, Vol. 14. (Ed. R. Snyderman) pp. 29–74, Plenum Press, New York 1984.
L. T. Williams, R. P. Snyderman, M. C. Re and R. J. Lefkowitz,Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA)74, 1204–1210 (1977).
D. E. Chenoweth and T. E. Hugh,Demonstration of a specific C5a receptor on intact human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA)75, 3943–3949 (1978).
C. Haslett, J. S. Savill and L. Megher,The neutrophil. InCurrent Opinion in Immunology, Vol. 2, No. 1. (Ed. I. M. Roitt) pp. 10–18, Alden Press, Oxford 1989.
L. Guthrie, L. McPhail, P. Henson and R. Johnston Jr.,Priming of neutrophils for enhanced release of oxygen metabolites by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J. Exp. Med.160, 1656–1671 (1984).
C. Jupin, M. Parant and L. Chedid,Involvement of reactive oxygen metabolites in the candidacidal activity of human neutrophils stimulated by muramyl dipeptide or tumour necrosis factor. Immunobiology180, 68–79 (1989).
G. S. Worthen, J. F. Seccombe, K. L. Clay, L. A. Guthrie and R. B. Johnston Jr.,The priming of neutrophils by lipopolysaccharide for production of intracellular platelet-activating factor: Potential role in mediation of enhanced superoxide secretion. J. Immunol.140, 3553–3559 (1988).
C. Dahinden, C. Galanos and J. Fehr,Granulocyte activation by endotoxin 1. Correlation between adherence and other granulocyte functions, and role of endotoxin structure on biologic activity. J. Immunol.130, 857–862 (1983).
C. Haslett, L. A. Guthrie, M. M. Kopaniek, R. B. Johnston and P. M. Henson,Modulation of multiple neutrophil functions by preparative methods or trace concentrations of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Am. J. Pathol.119, 101–110 (1985).
C. A. Allen, M. F. Broom and V. S. Chadwick,Flow Cytometry analysis of the expression of neutrophil FMLP receptors. J. Immunol. Methods149, 159–164 (1992).
R. B. Gilbertsen, G. W. Carter and D. J. Quinn,Effects of F-met-lue-phe and zymosan-activated serum on rat neutrophils in vivo. J. Reticuloendothelial Soc.27, 485–494 (1980).
G. S. Worthen,Lipid mediators, neutrophils and endothelial injury. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis.136, 455–458 (1987).
Z. Zidek, K. Masek and F. Sedivy,Anti-inflammatory effects of muramyl dipeptide in experimental models of acute inflammation. Agents and Actions14, 72–75 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, C.A., Ferry, D.M. & Chadwick, V.S. Anti-inflammatory effects of LPS, MDP and FMLP on carrageenan pleurisy in the rat. Agents and Actions 41, 53–56 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01986394
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01986394