Abstract
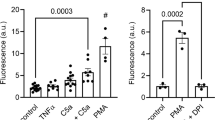
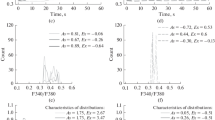
The neutrophil chemotaxins, complement fragment C5a (C5a) and GROα, induced the mobilization of Ca2+ from intracellular stores and the polymerization of actin in human neutrophils as assayed by flow cytometric measurements. [Ca2+]i-transients developed as an “all-or-none” response. Individual neutrophils required different threshold concentrations of added ligand to induce [Ca2+]i-transients which were then always maximal. In contrast, chemotaxin-induced formation of actin filaments in single neutrophils occurred in a dose-dependent manner. Pertussis toxin blocked chemotaxin-induced actin polymerization and [Ca2+]i-transients indicating that both cell responses shared initial activation steps such as ligand binding and activation of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G-proteins).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- [Ca2+]i :
-
Cytosolic free Ca2+
- C5a:
-
Complement fragment C5a
- PtdlnsP2 :
-
Phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate
- IP3 :
-
Inositol-trisphosphate
- fluo-3:
-
fluo-3-acethoxymethyl ester
- NBD-phallacidin:
-
7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-phallacidin
- EGTA:
-
[(2-(aminoethyl-glycolether-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacidic acid]
- f-actin:
-
filament actin
- PT:
-
pertussis toxin
References
D. J. Kelvin, D. F. Michiel, J. A. Johnston, A. R. Lloyd, H. Sprenger, J. J. Oppenheim and J.-M. Wang,Ohemokines and serpentines: The molecular biology of chemokine receptors. J. Leuk. Biol.54, 604–612 (1993).
M. Baggiolini, F. Boulay, J. A. Badwey and J. T. Curnutte,Activation of neutrophil leukocytes: Chemoattractant receptors and respiratory burst. Faseb J.7, 1004–1010 (1993).
M. Camps, A. Carozzi, P. Schnabel, A. Scheer, P. J. Parker and P. Gierschik,Isoenzyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-β2 by G protein βγ-subunit. Nature360 684–686 (1992).
C. D. Ferris and S. H. Snyder,IP3 receptors. Ligand-activated calcium channels in multiple forms. Ann. Rev. Physiol.54, 469–488 (1992).
G. J. Dobos, J. Norgauer, M. Eberle, P. J. Schollmeyer and A. E. Traynor-Kaplan,Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5) trisphosphate formation, but not phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bisphosphate hydrolysis and superoxide production, in human neutrophils. J. Immunol.149, 609–614 (1992).
M. Eberle, A. E. Traynor-Kaplan, L. A. Sklar and J. Norgauer,Is there a relationship between phosphatidylinositol trisphosphate and F-actin polymerization in human neutrophils? J. Biol. Chem.265, 16725–16728 (1990).
T. P. Stossel,From signal to pseudopod. How cells control cytoplasmic actin assembly. J. Biol. Chem.264, 18261–18264 (1989).
J. Elsner, J. Norgauer, G. J. Dobos, A. Emmendörffer, E. Schöpf, A. Kapp and J. Roesler,Flow cytometry reveals different lag times in rapid cytoplasmic calcium elevations in human neutrophils in response to N-formyl peptide. J. Cell. Physiol.157 637–643 (1993).
J. Norgauer, M. Eberle, S. P. Fay, H. D. Lemke and L. A. Sklar,Kinetics of N-formyl peptide receptor up-regulation during stimulation in human neutrophils. J. Immunol.146, 975–980 (1991).
J. Norgauer, G. Dobos, E. Kownatzki, C. Dahinden, R. Bunger, R. Kupper and P. Gierschik,Complement fragment Crustimulates Ca 2+ influx in neutrophils via a pertussis-toxin-sensitive G-protein. Eur. J. Biochem.217, 289–294 (1993).
J. Norgauer, E. Kownatzki, R. Seifert and K. Aktories,Botulinum C2 toxin ADP-ribosylates actin and enhances O −2 production and secretion but inhibits migration of activated human neutrophils. J. Clin. Invest.82, 1376–1382 (1988).
P. E. Nasmith and S. Grinstein,Are Ca 2+ channels in neutrophils activated by a rise in cytosolic free Ca 2+? FEBS Lett.221, 95–100 (1987).
P. Gierschik, D. Sidiropoulos and K. H. Jakobs,Two distinct G i-proteins mediate formyl peptide receptor signal transduction in human leukemia (HL-60) cells. J. Biol.264, 21470–21473 (1989).
B. Alberts, D. Bray, J. Lewis, M. Raff K. Roberts and J. D. Watson,The nervous system. InMolecular Biology of the Cell. pp. 1059–1136, Garland, New York 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metzner, B., Elsner, J., Dobos, G. et al. [Ca2+]i-transients and actin polymerization in human neutrophils under stimulation with GROα and complement fragment C5a. Agents and Actions 42, 101–106 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01983473
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01983473