Abstract
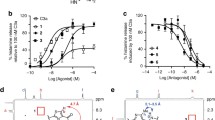
The inhibitory activity of the sodium salt of the anti-inflammatory peptide N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamic acid (NAAGA) on activation of the classical and alternative pathways of human complement was compared with that of the clinically used magnesium salt of NAAGA (NAAGA-Mg). Sodium salt of NAAGA (NAAGA-Na) inhibited both pathways of activation in a dose-dependent manner at concentration ranging from 1 to 10 mM by acting on formation and/or function of the C3 convertases as shown by the inhibitory capacity of the peptide on the release of the C3 cleavage fragment C3b and C3a. NAAGA-Na was as effective as NAAGA-Mg in inhibiting classical pathway activation at concentration above 10 mM. NAAGA-Na was more effective than NAAGA-Mg in inhibiting the alternative pathway since the sodium salt did not interfere with Mg-dependent formation of the alternative pathway C3 convertase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. M. Glovsky, T. E. Hugh, T. Ishizaka, E. M. Lichtenstein and B. N. Erickson,Anaphylatoxin-induced histamine release with human leucocytes: studies of C3a leukocyte binding and histamine release. J. Clin Invest.64, 804–808 (1979).
N. Haeffner-Cavaillon, J. M. Cavaillon, M. Laude and M. D. Kazatchkine,C3a (C3a desarg) induces production and release of interleukin-1 by cultured human monocytes. J. Immunol.139, 794–799 (1987).
S. Okusawa, C. A. Dinarello, B. Yancey et al.,C5a induction of human interleukin-1. Synergistic effect with endotoxin or interferon gamma. J. Immunol.139, 2635–2640 (1987).
H. J. Müller-Eberhard,Molecular organization and function of the complement system. Ann. Rev. Biochem.57, 321–347 (1988).
M. Etievant, B. Leluc and B. David,In vitro inhibition of the classical and alternative pathways of activation of human complement by N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamic acid (NAAGA). Agents and Actions24, 137–144 (1988).
R. A. Nelson, J. Jensen, I. Gigli and N. Tamura,Methods for the separation, purification and measurement of the nine components of hemolytic complement of guinea pig serum. Immunochemistry3, 111–135 (1986).
M. M. Mayer,Complement and complement fixation. InExperimental immunochemistry, pp. 133–241 (E. A. Kabat and M. M. Mayer, Eds.). Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, Ill., USA 1967.
T. A. E. Platts Mills and K. Ishizaka,Activation of the alternative pathway of human complement by rabbit cells. J. Immunol.113, 348–353 (1974).
M. P. Carreno, D. Labarre, M. Josefowicz and M. D. Kazatchkine,The ability of Sephadex to activate human complement is suppressed in specifically substituted functional Sephadex derivatives. Mol. Immunol.25, 165–171 (1988).
P. Garred, T. E. Mollnes and M. D. Kazatchkine,Activation dependent antigenic changes of human complement factor C3 with special reference to monoclonal anti-neoepitope antibodies. Complement and Inflammation6, 205–218 (1989).
P. Garred, T. E. Mollnes and M. D. Kazatchkine,Quantification in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of a C3 neoepitope expressed on activated human complement factor C3. Scand. J. Immunol.27, 329–335 (1988).
M. D. Kazatchkine and U. E. Nydegger,The human alternative pathway: biology and immunopathology of activation and regulation. Progr. Allergy30, 193–234 (1982).
J. Blamoutier and J. Luyckx,A double-blind cross-over study comparing N-acetyl aspartyl glutamic acid (NAAGA) with disodium cromoglycate (SDCG) in the treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis. Acta Therapeut.14, 145–157 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feuillard, J., Maillet, F., Goldschmidt, P. et al. Comparative study ofin vitro inhibition of activation of the classical and alternative pathways of human complement by the magnesium and sodium salts of the anti-inflammatory peptide N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamic acid (NAAGA). Agents and Actions 32, 343–346 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01980896
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01980896