Summary
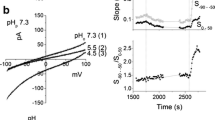
Patch-clamp measurements were made on osteoblast-like cells isolated from embryonic chick calvaria. Cell-attachedpatch measurements revealed two types of high conductance (100–250 pS) channels, which rapidly activated upon 50–100 mV depolarization. One type showed sustained and the other transient activation over a 10-sec period of depolarization. The single-channel conductances of these channel types were about 100 or 250 pS, depending on whether the pipettes were filled with a low K+ (3mm) or high K+ (143mm) saline, respectively. The different reversal potentials under these conditions were consistent with at least K+ conduction. Whole-cell measurements revealed the existence of two types of outward rectifying conductances. The first type conducts K+ ions and activates within 20–200 msec (depending on the stimulus) upon depolarizing voltage steps from <−60 mV to >−30 mV. It inactivates almost completely with a time constant of 2–3 sec. Recovery from inactivation is biphasic with an initial rapid phase (1–2 sec) followed by a slow phase (>20 sec). The second whole-cell conductance activates at positive membrane potentials of >+50 mV. It also rapidly turns on upon depolarizing voltage steps. Activation may partly disappear at the higher voltages. Its single channels of 140 pS conductance were identified in the whole cell and did conduct K+ ions but were not highly Cl− or Na+ selective. The results show that osteoblasts may express various types of voltage controlled ionic channels. We predict a role for such channels in mineral metabolism of bone tissue and its control by osteoblasts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashcroft, F.M., Harrison, D.E., Ashcroft, S.J.H. 1984. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells.Nature (London) 312:446–448
Bevan, S., Raff, M. 1985. Voltage-dependent potassium currents in cultured astrocytes.Nature (London) 315:229–232
Choquet, D., Sarthou, P., Primi, D., Cazenave, P., Korn, H. 1987. Cyclic AMP-modulated, potassium channels in murine B cells and their precursors.Science 235:1211–1214
Connor, J.A., Stevens, C.F. 1971. Prediction of repetitive firing behaviour from voltage clamp data on an isolated neurone soma.J. Physiol. (London) 213:31–51
DeCoursey, T.E., Chandy, K.G., Gupta, S., Cahalan, M.D. 1984. Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: A role in mitogenesis.Nature (London) 307:465–468
Dixon, S.J., Aubin, J.E., Dainty, J. 1984. Electrophysiology of a clonal osteoblast-like cell line: Evidence for the existence of a Ca2+ activated K+ conductance.J. Membrane Biol. 80:49–58
Edelman, A., Fritsch, J., Balsan, S. 1986. Short-term, effects of PTH on cultured rat osteoblasts: Changes in membrane potential.Am. J. Physiol. 251:C483-C490
Ferrier, J., Ward, A. 1986. Electrophysiological differences between bone cell clones: Membrane potential responses to parathyroid hormone and correlation with the cAMP response.J. Cell. Physiol. 126:237–242
Ferrier, J., Ward-Kesthely, A., Homble, F., Ross, R. 1987. Further analysis of spontaneous membrane potential activity and the hyperpolarizing response to parathyroid hormone in osteoblastlike cells.J. Cell. Physiol. 130:344–351
Giles, W. R., Van Ginneken, A.C.G. 1985. A transient outward current in isolated cells from the crista terminalis of rabbit heart.J. Physiol. (London) 368:243–264
Grega, D.S., Werz, M.A., MacDonald, R.L. 1987. Forskolin and phorbol esters reduce the same potassium conductance of mouse neurons in culture.Science 235:345–348
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches.Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Hille, B. 1984. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer Associates. Sunderland, Mass.
Ince, C., Dissel, J.T. van, Diesselhoff, M.M.C. 1985. A Teflon culture dish for high-magnification microscopy and measurements in single cells.Pfluegers Arch. 403:240–244
Ince, C., VanBavel, E., VanDuijn, B., Donkersloot, K., Coremans, A., Ypey, D.L., Verveen, A.A. 1986. Intracellular microelectrode measurements in small cells evaluated with the patch-clamp technique.Biophys. J. 50:1203–1209
Maruyama, Y., Petersen, O.H., Flanagan, P., Pearson, G.T. 1983. Quantification of Ca2+ activated K+ channels under hormonal control in pig pancreas acinar cells.Nature (London) 305:228–232
Nelson, D.J., Jacobs, E.R., Tong, J.M., Zeller, J.M., Bone, R.C. 1985. Immunoglobulin-G induced single ionic channels in human alveolar macrophage membranes.J. Clin. Invest. 76:500–507
Nijweide, P.J., Burger, E.H., Feyen, J.H.M. 1986. Cells of bone: Proliferation, differentiation and hormonal regulation.Physiol. Rev. 66:855–886
Nijweide, P.J., Plas, A. van der, Scherft, J.P. 1981. Biochemical and histological studies on various bone cell preparations.Calcif. Tissue Int. 33:529–540
Petersen, O.H., Maruyama, Y. 1984. Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion.Nature (London) 307:693–696
Ypey, D.L., Clapham, D.E. 1984. Development of a delayed outward-rectifying K− conductance in cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:3083–3087
Ypey, D.L., Ravesloot, J.H., Nijweide, P.J., Buisman, H.P. 1987. Voltage activated ionic channels and conductances in cultured osteoblasts.Calcif. Tissue Int. (Suppl. 2):41:78 (abstr.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ypey, D.L., Ravesloot, J.H., Buisman, H.P. et al. Voltage-activated ionic channels and conductances in embryonic chick osteoblast cultures. J. Membrain Biol. 101, 141–150 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872829
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872829