Summary
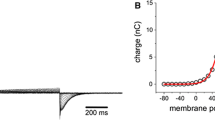
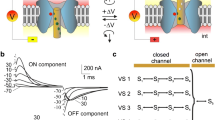
C-terminal fragments of colicin E1, ranging in mol wt from 14.5 to 20kD, form channels with voltage dependence and ion selectivity qualitatively similar to those of whole E1, placing an upper limit on the channel-forming domain. Under certain conditions, however, the gating kinetics and ion selectivity of channels formed by these different E1 peptides can be distinguished. The differences in channel behavior appear to be correlated with peptide length. Enzymatic digestion with trypsin of membrane-bound E1 peptides converts channel behavior of longer peptides to that characteristic of channels formed by shorter fragments. Apparently trypsin removes segments of protein N-terminal to the channel-forming region, since gating behavior of the shortest fragment is little affected by the enzyme. The success of this conversion depends on the side of the membrane to which trypsin is added and on the state, open or closed, of the channel. Trypsin modifies only closed channels from thecis side (the side to which protein has been added) and only open channels from thetrans side. These results suggest that regions outside the channel-forming domain affect ion selectivity and gating, and they also provide evidence that large protein segments outside the channel-forming domain are translocated across the membrane with channel gating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blobel, G., Dobberstein, B. 1975. Transfer of proteins across membranes: I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma.J. Cell. Biol. 67:835–851
Blumenthal, R., Klausner, R.D., Weinstein, J.N. 1980. Voltage-dependent translocation of the asialoglycoprotein receptor across lipid membranes.Nature (London) 288:333–338
Brunden, K.R., Cramer, W.A., Cohen, F.S. 1984. Purification of a small receptor-binding peptide from the central region of the colicin E1 molecule.J. Biol. Chem. 259:190–196
Bullock, J.O., Cohen, F.S., Dankert, J.R., Cramer, W.A. 1983. Comparison of the macroscopic and single channel conductance properties of colicin E1 and its COOOH-terminal tryptic peptide.J. Biol. Chem. 258:9908–9912
Cleveland, M.vB., Slatin, S., Finkelstein, A., Levinthal, C. 1983. Structure-function relationships for a voltage-dependent ion channel: Properties of COOH-terminal fragments of colicin E1.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:3706–3710
Dankert, J.R., Uratani, Y., Grabau, C., Cramer, W.A., Hermodson, M. 1982. On a domain structure of colicin E1.J. Biol. Chem. 257:3857–3863
Date, T., Goodman, J.M., Wickner, W.T. 1980. Procoat, the precursor of M13 coat protein, requires an electrochemical potential for membrane insertion.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:4669–4673
Davidson, V.L., Brunden, K.R., Cramer, W.A., Cohen, F.S. 1984. Studies on the mechanism of action of channel-forming colicins using artificial membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 79:105–118
Engelman, D.M., Steitz, T.A. 1981. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: The helical hairpin hypothesis.Cell 23:411–422
Goldstein, L. 1976. Kinetic behavior of immobilized enzyme systems.Methods Enzymol. 54:397–443
Guy, R.H. 1983. A model of colicin E1 membrane channel protein structure.Biophys. J. 41:363a
Hay, R., Bohni, P., Gasser, S. 1984. How mitochondria import proteins.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 779:65–87
Kagan, B.L. 1981. Voltage-dependent channels formed by colicins. Ph. D. Thesis. Albert Einstein College of Medicine. New York
Liu, Q.-R., Fine, R., Crozel, V., Levinthal, F., Levinthal, C. 1985. Molecular models andin vitro mutagenesis of colicin E1.Biophys. J. 47:430a
Ohno-Iwashita, Y., Imahori, K., 1982. Assignment of the functional loci in the colicin E1 molecule by characterization of its proteolytic fragments.J. Biol. Chem. 257:6446–6451
Raymond, L., Slatin, S.L., Finkelstein, A. 1985a. Channels formed by colicin E1 in planar lipid bilayers are large and exhibit pH-dependent ion selectivity.J. Membrane Biol. 84:173–181
Raymond, L., Slatin, S.L., Finkelstein, A. 1985b. Gating of a voltage-dependent channel (colicin E1): The role of membrane translocation of protein.Biophys. J. 47:430a
Rosenberg, P.A., Finkelstein, A. 1978. Interaction of ions and water in gramicidin A channels. Streaming potentials across lipid bilayer membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 72:327–350
Slatin, S., Finkelstein, A. 1984. Colicin E1 channels at low pH gate in milliseconds and inactivate.Biophys. J. 45:62a
Slatin, S.L., Raymond, L., Finkelstein, A. 1986. Gating of a voltage-dependent channel (colicin E1) in planar lipid bilayers: The role of protein translocation.J. Membrane Biol. 92:247–253
Wallace, R.B., Johnson, P.F., Tanaka, S., Schöld, M., Itakura, K., Abelson, J. 1980. Directed deletion of a yeast transfer RNA intervening sequence.Science 209:1396–1400
Weinstein, J.N., Blumenthal, R., Renswoude, J. van, Kempf, C., Klausner, R.D. 1982. Charge clusters and the orientation of membrane proteins.J. Membrane Biol. 66:203–212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raymond, L., Slatin, S.L., Finkelstein, A. et al. Gating of a voltage-dependent channel (colicin E1) in planar lipid bilayers: translocation of regions outside the channel-forming domain. J. Membrain Biol. 92, 255–268 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869394
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869394