Summary
Purpose
The effect of endovascular treatment for vasospasm was investigated by analysing the results of patients treated in Wakayama City in 1994.
Materials and Methods
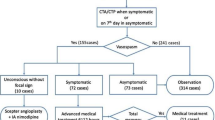
Ninty nine patients with ruptured cerebral aneurysms, who survived more than one week and were treated in Wakayama City in 1994, were studied. Twenty five patients caused symptomatic vasospasm and 25 were treated by endovascular therapy, percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) and/or intra-arterial papaverine infusion (IAP). PTA was performed for proximal vasospasm which located in the main arterial trunk, such as ICA, M1, BA (n = 3). IAP was chosen for distal vasospasm which located mainly in the M2, A1, A2 (n = 12). PTA and/or IAP was performed for diffuse vasospasm which located in proximal and distal arteries (n = 10).
Results
In the proximal vasospasm group, all patients were good to moderately disabled on the Glasgow outcome scale (GOS). In the distal vasospasm group, 8 patients were good to moderately disabled, and 4 patients were severely disabled. The overall results were as follows: 17 (68%), good to moderately disabled, 4 (16%), severely disabled, 4 (16%), dead. The morbidity and mortality rate was 8/25 (32%) in symptomatic spasm group.
Conclusion
PTA was very effective especially for proximal vasospasm, but IAP was not always effective for distal or diffuse vasospasm. Diffuse vasospasm revealed a high mortality rate in spite of the endovascular therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodman Gilman (1980) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 6th Ed. Macmillan, New York, pp 830
Barr JD, Mathis JM, Horton JA (1994) Transient severe brain stem depression during intraarterial papaverine infusion for cerebral vasospasm. AJNR 11: 239–247
Brothers MF, Holgate RC (1990) Intracranial angioplasty for treatment of vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: technique and modifications to improve branch access. AJNR 11: 239–247
Findlay JM, Weir BKA, Kanamara Ket al (1990) The effect of timing of intrathecal fibrinolytic therapy on cerebral vasospasm in a primate model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 26: 201–206
Haley EC Jr, Kassel NF, Torner JCet al (1993) A randomized controlled trial of high-dose intravenous nicardipine in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. A report of the Cooperative Aneurysm Study. J Neurosurg 78: 537–547
Hendrix LE, Dion JE, Jensen ME, Phillips CD, Newman SA (1994) Papaverine-induced mydriasis. AJNR 15: 716–718
Heros RC, Zervas NT, Varsos VG (1983) Cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: an update. Ann Neurol 14: 599–608
Higashida RT, Halbach VV, Dormandy B, Bell J, Branzawadzki M, Hieshima GB (1990) New microballoon device for transluminal angioplasty of intracranial arterial vasospasm. AJNR 11: 233–238
Higashida RT, Halbach VV, Cahan LD, Branzawadzki M, Barnwell S, Dowd C, Hieshima GB (1989) Transluminal angioplasty for treatment of intracranial arterial vasospasm. J Neurosurg 71: 648–653
Jan M, Buchheit F, Tremoulet M (1988) Therapeutic trial of intravenous nimodipine in patients with established cerebral vasospasm after rupture of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 23: 154–157
Jin Y, Sagher O, Thai Q, Kassell NF, Lee KS (1994) The effects of papaverine on phorbol dibutyrate-induced vasoconstriction in brain slice microvessels. J Neurosurg 81: 574–578
Kaku Y, Yonekawa Y, Tsukahara T, Kazekawa K (1992) Superselective intra-arterial infusion of papaverine for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 77: 842–847
Kassell NF, Helm G, Simmons N, Philips CD, Cail WS (1992) Treatment of cerebral vasospasm with intra-arterial papaverine. J Neurosurg 77: 848–852
Kassell NF, Torner JC, Haley EC, Jane JA, Adams HP, Kongable GL (1990) The international cooperative study on the timing of aneurysm surgery. Part 1: overall managment results. J Neurosurg 73: 18–36
Kassell NF, Torner JC, Jane JA, Haley EC, Adams JP, Participants (1990) The international cooperative study on timing of aneurysm surgery. Part 2: surgical results. J Neurosurg 73: 37–47
Kimberly L, Hopkins LN (1993) Intraarterial papaverine as an adjunct to transluminal angioplasty for vasospasm induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage. AJNR 14: 346–347
Kuwayama A, Zervas NT, Shintani A, Pickren KS (1972) Papaverine hydrochloride and experimental hemorrhagic cerebral arterial spasm. Stroke 3: 27–33
Linskey ME, Horton JA, Rao GR, Yonas H (1991) Fatal rupture of the intracranial carotid artery during transluminal angioplasty for vasospasm induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 74: 985–990
Marks MP, Steinberg GK, Lane B (1993) Intraarterial papaverine for the treatment of vasospasm. AJNR 14: 822–826
Mathis JM, Denardo AJ, Thibault L, Jensen ME, Savory J, Dion JE (1994) In vitro evaluation of papaverine hydrochloride incompatibilities: a simulation of intraarterial infusion of cerebral vasospasm. AJNR 15: 1665–1670
Mathis JM, Denardo A, Jensen ME, Scott J, Dion JE (1994) Transient neurologic events associated with intraarterial papaverine infusion for subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced vasospasm. AJNR 15: 1671–1674
Matsui T, Kaizu H, Itoh S, Asano T (1994) The role of active smooth-muscle contraction in the occurrence of chronic vasospasm in the canine two-hemorrhage model. J Neurosurg 80: 276–282
Newell DW, Eskridge JM, Mayberg MR, Grady MS, Winn HR (1989) Angioplasty for the treatment of symptomatic vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 71: 654–660
Ohman J, Servo A, Heiskanen O (1991) Long-term effects of nimodipine on cerebral infarcts and outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage and surgery. J Neurosurg 74: 8–13
Soloman RA, Fink ME, Lennitan L (1988) Early aneurysm surgery and prophylactic hypervolemic hypertensive therapy for the treatment of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 23: 699–704
Terada T, Nakamura Y, Yoshida N, Kuriyama T, Isozaki S, Nakai K, Itakura T, Hayashi S, Komai N (1993) Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for the M2 portion vasospasm following SAH: development of the new microballoon and report of cases. Surg Neurol 39: 13–17
Varsos VG (1983) Delayed cerebral vasospasm is not reversible by aminophyline, nifedipine, or papaverine in a “two-hemorrhage” canine model. J Neurosurg 58: 11–17
Vorkapic P (1991) Two indices of functional damage of the artery wall parallel the time course of irreversible narrowing in experimental vasospasm in the rabbit. Blood Vessels 28: 179–182
Zubkov YM, Nikiforov BM, Shustin VA (1984) Balloon catheter technique for dilatation of constricted cerebral arteries after aneurysmal SAH. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 70: 65–79
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terada, T., Kinoshita, Y., Yokote, H. et al. The effect of endovascular therapy for cerebral arterial spasm, its limitation and pitfalls. Acta neurochir 139, 227–234 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01844756
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01844756