Summary
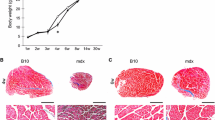
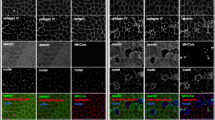
The pattern of spontaneous skeletal muscle degeneration and clinical recovery in hindlimb muscles of the mdx mutant mouse was examined for functional and metabolic confirmation of apparent structural regeneration. The contractile properties, histochemical staining and myosin light chain and parvalbumin contents of extensor digitorum longus (EDL) and soleus (Sol) muscles of mdx and age-matched control mice were studied at 3–4 and 32 weeks. Histochemical staining (myofibrillar ATPase and NADH-tetrazolium reductase) revealed no significant change in slow-twitch-oxidative (SO) or fast-twitch-oxidative-glycolytic (FOG) fibre type proportions in mdx Sol apart from the normal age-related increase in SO fibres. At 32 weeks mdx EDL, however, showed significantly smaller fast-twitch-glycolytic (FG) and larger FOG proportions than those in control EDL. These fibre type distributions were confirmed by differential staining with antibodies to myosin slow-twitch and fast-twitch heavy chain isozymes. Frequency distribution of cross-sectional area for each fibre type showed a wider than normal range of areas especially in FOG fibres of mdx Sol, and FG fibres of mdx EDL, supporting previous observations using autoradiography of myofibre regeneration. Isometric twitch and tetanic tensions in Sol were significantly less than in controls at 4 weeks, but by 32 weeks, values were not different from age-matched controls. In mdx EDL at 3 weeks, twitch and tetanus tensions were significantly less, and time-to-peak twitch tensions were significantly faster than in control EDL. By 32 weeks, mdx EDL twitch and tetanus tensions expressed relative to muscle weight continued to be significantly lower than in age-matched controls, despite normal absolute tensions. The maximum velocity of shortening in 32-week mdx EDL was significantly lower than in control EDL. Myosin light chain distribution in mdx Sol exhibited significantly less light chain 2-slow (LC2s) and more light chain 1b-slow(LC1bs) at 32 weeks than age-matched control Sol. Gels of EDL from 32-week-old mdx mice showed significantly less light chain 2-fast-phosphorylated (LC2f-P) and light chain 3-fast (LC3f) and significantly more light chain 1-fast (LC1f) and light chain 2-fast (LC2f), but normal parvalbumin content compared to age-matched controls. These observations suggest that mdx hindlimb muscles are differentially affected by the disease process as it occurs in murine models of dystrophy. However, the uniqueness of mdx Sol and to a lesser extent EDL is that they also undergo an important degree of functional regeneration which is able to compensate spontaneously for degenerative influences of genetic origin. The mdx mutant may therefore be an important model for the study of regeneration by skeletal muscle, and of the nerve-muscle interactions which enable or restrict that regeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J. E., Ovalle, W. K. &Bressler, B. H. (1987) Electron microscopic and autoradiographic characterization of hindlimb muscle regeneration in the mdx mouse.Anat. Rec. 219, 243–57.
Baumann, H., Jaggi, M., Soland, F., Howald, H. &Schaub, M. C. (1987) Exercise training Induces transitions of myosin isoform subunits within histochemically typed human muscle fibres.Pflügers Arch. 409, 349–360.
Bressler, B. H., Jasch, L. G., Ovalle, W. K. &Slonecker, C. E. (1983) Changes in isometric contractile properties of fast-twitch and slow-twitch skeletal muscle of C57BL/6J dy2J/dy2J dystrophic mice during postnatal development.Expl. Neurol. 80, 457–70.
Bridges, L. R. (1986) The association of cardiac muscle necrosis and inflammation with the degenerative and persistent myopathy of mdx mice.J. Neurol. Sci. 72, 147–57.
Bulfield, G., Siller, W. G., Wight, P. A. L. &Moore, K. J. (1984) X Chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse.Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,81, 1189–92.
Carnwath, J. W. &Shotton, D. M. (1987) Muscular Dystrophy in the mdx mouse: histopathology of the soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscles.J. Neurol. Sci. 80, 39–54.
Dangain, J. &Vrbova, G. (1984) Muscle development in mdx mutant mice.Muscle Nerve 7, 700–4.
Davis, H. L., Bressler, B. H. &Jasch, L. G. (1988) Myotrophic effects on denervated fast-twitch muscles of mice: correlation of physiological, biochemical and morphological findings.Expl. Neurol. 99, 474–89.
Douglas, W. B. Jr &Baskin, R. J. (1971) Contractile properties of developing mouse dystrophic muscle.Am. J. Physiol. 220, 1344–54.
Dubowitz, V. &Brooke, M. H. (1973)Muscle Biopsy: A Modern Approach. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders.
Edman, K. A. P. (1979) The velocity of unloaded shortening and its relation to sarcomere length and isometric force in vertebrate muscle fibres.J. Physiol. 291, 143–59.
Edwards, R. H. T., Chapman, S. J., Newman, D. J. &Jones D. A. (1987) Practical analysis of variability of muscle function measurements in Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Muscle Nerve 10, 6–14.
England, P. J. (1984) The significance of phosphorylation of myosin light chains in heart.J. molec. Cell Cardiol. 16, 591–5.
Fitzsimons, R. B. &Hoh, J. F. Y. (1983) Myosin isoenzymes in fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles of normal and dystrophic mice.J. Physiol. 343, 539–50.
Franks, K., Cooke, R. &Stull, J. T. (1984) Myosin phosphorylation decreases the ATPase activity of cardiac myofibrills.J. molec. Cell. Cardiol. 16, 597–604.
Harris, J. B. &Slater, C. R. (1980) Animal models: What is their relevance to the pathogenesis of human muscular dystrophy?Br. Med. Bull. 36, 193–7.
Hoffman, E. P., Kundson, C. M., Campell, K. P. &Kunkel, L. M. (1987) Subcellular fractionation of dystrophin to the triads of skeletal muscle.Nature Lond. 330, 754–7.
Houston, M. E., Green, H. J. &Stull, J. T. (1985) Myosin light chain phosphorylation and isometric twitch potentiation in intact human muscle.Pflügers Arch. 403, 348–52.
Hurko, O., McKee, L., Zuurveld, J. G. E. M., Walsh, F. S. &Swick, H. M. (1986) Proliferative capacity of Duchenne and wild-type myoblasts derived from a DMD-G6PD double heterozygote. InMolecular Biology of Muscle Development, pp. 921–8. New York: Alan R. Liss.
Jasch, L. G., Bressler, B. H., Ovalle, W. K. &Slonecker, C. E. (1982) Abnormal distribution of proteins in the soleus and extensor digitorum longus of dystrophic mice.Muscle Nerve 5, 462–70.
Jasch, L. G. &Moase, E. H. (1985) Evidence for the identities of five proteins decreased in skeletal muscle of dystrophic mice.Muscle Nerve 8, 389–401.
Jones, S. P., Ridge, R. M. A. P. &Rowlerson, A. (1987) The non-selective innervation of muscle fibres and mixed composition of motor units in a muscle of neonatal rat.J. Physiol. 386, 377–94.
Julian, F. J., Moss, R. L. &Waller, G. S. (1981) Mechanical properties and myosin light chain composition of skinned muscle fibres from adult and new born rabbits.J. Physiol. 311, 201–18.
Kerrick, W. G. L., Secrist, D., Coby, R. &Lucas, S. (1976) Development of difference between red and white muscles in sensitivity to Ca2+ in the rabbit from embryo to adult.Nature, Lond. 260, 440–1.
McComas, A. J., Sica, R. E. P. &Currie, S. (1971) An electrophysiological study of Duchenne dystrophy.J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychol. 34, 461–8.
Mascarello, F., Carpene, E., Veggetti, A., Rowlerson, A. &Jenny, E. (1982) The tensor tympani muscle of cat and dog contains IIM and slow-tonic fibres: an unusual combination of fibre types.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 3, 363–74.
Mascarello, F., Rowlerson, A. &Scapolo, P. A. (1984) The fibre type composition of the striated muscle of the oesophagus in ruminants and carnivores.Histochemistry 80, 277–88.
Mastaglia, F. L. &Kakulas, B. A. (1969) Regeneration in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a histological and histochemical study.Brain 92, 809–18.
Mastaglia, F. L., Papadimitriou, J. M. &Kakulas, B. A. (1970) Regeneration of muscle in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: an electron microscope study.J. Neurol. Sci. 11, 425–44.
Muntener, M., Berchtold, M. W. &Heizmann, C. W. (1985) Parvalbumin in cross-reinnervated and denervated muscles.Muscle Nerve 8, 132–7.
Nonaka, I., Takagi, A. &Sugita, H. (1981) The significance of type 2c muscle fibres in Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Muscle Nerve 4, 326–33.
Ovalle, W. K., Bressler, B. H., Jasch, L. G. &Slonecker, C. E. (1983) Abnormal distribution of fiber types in the slow-twitch soleus muscle of the C57BL/6J dy2J/dy2J dystrophic mouse during postnatal development.Am. J. Anat. 168, 291–304.
Peter, J. B., Barnard, R. J., Edgerton, V. R., Gillespie, C. A. &Stempel, K. E. (1972) Metabolic profiles of three fiber types of skeletal muscle in guinea pigs and rabbits.Biochemistry 11, 2627–33.
Redenbach, D. M. &Bressler, B. H. (1988) Alterations in contractile properties of extensor digitorum longus muscle from C57BL/6J mice following neonatal denervation at one day of age.Expl Neurol. 100, 542–55.
Rowland, L. P. &Layzer, R. B. (1979) X-linked muscular dystrophies. InHandbook of Clinical Neurology. Diseases of Muscle (edited byVinken, P. J. &Bruyn, G. W.), Vol. 46, pp. 349–414. New York: North-Holland.
Rowlerson, A., Pope, B., Murray, J., Whalen, R. B. &Weeds, A. G. (1981) A novel myosin present in the cat jaw-closing muscles.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 2, 415–38.
Schaub, M. C., Jauch, A., Walzthoeny, D. &Wallimann, T. (1986) Myosin light chain functions.Biomed. Biochim. Acta 45, S39-S44.
Silverman, H. &Atwood, H. L. (1980) Increase in oxidative capacity of muscle fibres in dystrophic mice and correlation with overactivity in these fibers.Expl Neurol. 68, 97–113.
Snow, M. H. (1983) A quantitative ultrastructural analysis of satellite cells in denervated fast and slow muscles of the mouse.Anat. Rec. 207, 593–604.
Strohman, R. C. &Matsuda, R. (1983) Myosin expression during regeneration and in denervated skeletal muscle.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 182, 259–63.
Syrovy, I. (1979) Changes in light chains of myosin during animal development.Int. J. Biochem. 10, 223–7.
Tanabe, Y., Esaki, K. &Nomura, T. (1986) Skeletal muscle pathology in X-chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) mouse.Acta Neuropathol. (Berlin) 69, 91–5.
Torres, L. F. B. &Duchen, L. W. (1987) The mutantmdx: Inherited myopathy in the mouse.Brain 110, 269–99.
Wakayama, Y. (1976) Electron microscopic study on the satellite cell in the muscle of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.J. Neuropathol. Expl. Neurol. 35, 532–40.
Weeds, A. G. (1976) Light chains from slow-twitch muscle myosin.Eur. J. Biochem. 66, 157–73.
Westwood, S. A., Hudlicka, O. &Perry, S. V. (1984) Phosphorylationin vivo of the light chain of myosin in rabbit fast and slow skeletal muscles.Biochem. J. 218, 841–7.
Wood, D. S., Sorenson, M. M., Eastwood, A. B., Charash, W. E. &Reuben, J. P. (1978) Duchenne dystrophy: Abnormal generation of tension and Ca++ regulation in single skinned fibres.Neurology 28, 447–57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, J.E., Bressler, B.H. & Ovalle, W.K. Functional regeneration in the hindlimb skeletal muscle of the mdx mouse. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 9, 499–515 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738755
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738755