Abstract
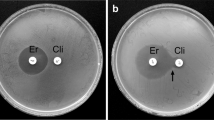
The aim of this study was to determine the evolution of resistance to macrolides and other antibiotics in strains ofStreptococcus pyogenes isolated in the province of Gipuzkoa, Spain. During the period 1984–1996, all 2561 strains ofStreptococcus pyogenes studied showed full susceptibility to penicillin. Until 1990, only 1.2% ofStreptococcus pyogenes isolates were resistant to erythromycin. Since then, resistance to erythromycin increased every year until 1995, when 34.8% (87/250) ofStreptococcus pyogenes strains were found to be resistant. In 1996 the rate of resistance to erythromycin was 17.8% (75/422). During the study period, 96.1% (246/256) of theStreptococcus pyogenes isolates resistant to erythromycin were susceptible to clindamycin. Of the remaining erythromycin-resistantStreptococcus pyogenes strains, resistance to clindamycin was constitutive in seven strains and inducible in three. When investigated by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), allStreptococcus pyogenes strains resistant to erythromycin and susceptible to clindamycin showed the 1.4 kb fragment of themefA gene, recently described as the novel macrolide-efflux-resistance determinant. The most frequent T-agglutination patterns amongStreptococcus pyogenes resistant to erythromycin were T4 and T8,25. The emergence and rapid spread of erythromycin-resistantStreptococcus pyogenes in Gipuzkoa and its relationship to the presence of themefA gene are described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisno A:Streptococcus pyogenes: In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R (eds): Principles and practice of infectious diseases. Churchill Livingstone, New York, 1995, p. 1786–1799.
Stingemore N, Francis GJR, Toohey M, McGechie DB: The emergence of erythromycin resistance inStreptococcus pyogenes in Fremantle, Western Australia. Medical Journal of Australia 1989, 150: 626–631.
Holmstrom L, Nyman B, Rosengren M, Wallander S, Ripa T: Outbreaks of infections with erythromycin-resistant group A streptococci in child day care centres. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1990, 22: 179–185.
Philipps G, Parratt D, Orange GV, Harper I, McEwan H, Young N: Erythromycin-resistantStreptococcus pyogenes. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1990, 25: 723–724.
Seppala H, Nissinen A, Jarvinen H, Huovinen S, Henriksoon T, Herva E, Holm SE, Jahkola M, Katila ML, Klaukka T, Kontiainen S, Liimatainen O, Olinonen S, Passi-Metsomaa L, Huovinen P: Resistance to erythromycin in group A streptococci. New England Journal of Medicine 1992, 326: 292–297.
Lowbury EJL, Hurst L: The sensitivity of staphylococci and other wound bacteria to erythromycin, oleandomycin and spiramycin. Journal of Clinical Pathology 1959, 12: 163–169.
Dixon JMS, Lipinski AE: Infections with beta-hemolyticStreptococcus resistant to lincomycin and erythromycin and observations on zonal-pattern resistance to lincomycin. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1974, 130: 351–356.
Maruyama S, Yoshioka H, Fujita K, Takimoto M, Satake Y: Sensitivity of group A streptococci to antibiotics: prevalence of resistance to erythromycin in Japan. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1979, 133: 1143–1145.
Sanders E, Foster MT, Scott D: Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci resistant to erythromycin and lincomycin. New England Journal of Medicine 1968, 278: 538–540.
Leclercq R, Courvalin P: Intrinsic and unusual resistance to macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin antibiotics in bacteria. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1991, 35: 1273–1276.
Weisblum B: Inducible resistance to macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramin type B antibiotics: the resistance phenotype, its biological diversity, and structural elements that regulate expression—a review. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1985, 16, Supplement A. 63–90.
Seppala H, Nissinen A, Yu Q, Huovinen P: Three different phenotypes of erythromycin-resistantStreptococcus pyogenes in Finland. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1993, 32: 885–891.
Sutcliffe J, Tait-Kamradt A, Wondrack L:Streptococcus pneumoniae andStreptococcus pyogenes resistant to macrolides but sensitive to clindamycin: a common resistance pattern mediated by an efflux system. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1996, 40: 1817–1824.
Clancy J, Petitpas J, Dib-Hajj F, Yuan W, Cronan M, Kamath AV, Bergeron J, Retsema JA: Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a novel macrolide-resistance determinant,mefA, formStreptococcus pyogenes. Molecular Microbiology 1996, 22: 867–879.
EUSTAT (Euskal Estatistika-Erakundea—Instituto Vasco de Estadística): Anuario Estadístico Vasco 1995. Habitantes, Movimiento Natural y Migraciones. Gobierno Vasco, Vitoria, Spain, 1996, p. 35–81.
Johnson DR, Kaplan EL, Sramek J, Bicova R, Havlicek J, Havlickova H, Motlova J, Kriz P: Determination of T-protein agglutination paterns. In: Laboratory diagnosis of group A streptococcal infections. World Health Organisation, Geneva, 1996, p. 37–41.
Perez-Trallero E, Garcia-Arenzana JM, Urbieta-Egaña M: Erythromycin resistance in streptococci. Lancet 1989, ii: 444–445.
Istre GR, Welch DF, Marks MI, Moyer N: Susceptibility of group A beta-hemolyticStreptococcus isolates to penicillin and erythromycin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1981, 20: 244–246.
Zackrisson G, Lind L, Roos K, Larsson P: Erythromycin-resistant beta-hemolytic streptococci group A in Goteborg, Sweden. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1988, 20: 419–420.
Borzani M, Varotto F, Garlaschi L, Conio F, Dell'Olio M, Careddu P: Clinical and microbiological evaluation of miocamycin activity against group A beta-hemolytic streptococci in pediatric patients. Journal of Chemotherapy 1989, 1: 35–38.
Scott RJD, Naidoo J, Lightfoot NF, George RC: A community outbreak of group A beta-haemolytic streptococci with transferable resistance to erythromycin. Epidemiology and Infection 1989, 102: 85–91.
Spencer RC, Wheat PF, Magee JT, Brown EH: Erythromycin resistance in streptococci. Lancet 1989, i: 168.
Wittler RR, Yamada SM, Bass JW, Hamill R, Wiebe RA, Ascher DP: Penicillin tolerance and erythromycin resistance of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci in Hawaii and the Philippines. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1990, 144: 587–589.
Betriu C, Sanchez A, Gomez M, Cruceyra A, Picazo JJ: Antibiotic susceptibility of group A streptococci: a 6-year follow-up study. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1993, 37: 1717–1719.
Hsueh PR, Chen HM, Huang AH, Wu JJ: Decreased activity of erythromycin againstStreptococcus pyogenes in Taiwan. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1995, 39: 2239–2242.
Cornaglia G, Ligozzi M, Mazzariol A, Valentini M, Orefici G, Fontana R, and the Italian Surveillance Group for Antimicrobial Resistance: Rapid increase of resistance to erythromycin and clindamycin inStreptococcus pyogenes in Italy, 1993–1995. Emerging Infectious Diseases 1996, 2: 339–342.
Fujita J, Murono K, Yoshikawa M, Murai T: Decline of erythromycin resistance of group A streptococci in Japan. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1994, 13: 1075–1078.
Seppala H, Klaukka T, Vuopio-Varkila J, Muotiala A, Helenius H, Lager K, Huovinen P, and the Finnish Study Group for Antimicrobial Resistance: The effect of changes in the consumption of macrolide antibiotics on erythromycin resistance in group A streptococci in Finland. New England Journal of Medicine 1997, 337: 441–446.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perez-Trallero, E., Urbieta, M., Montes, M. et al. Emergence ofStreptococcus pyogenes strains resistant to erythromycin in Gipuzkoa, Spain. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 17, 25–31 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01584359
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01584359