Summary
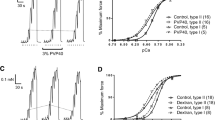
Potassium contractures and asymmetric charge movement were recorded from extensor digitorum longus (EDL) and soleus muscle from normal rats and rats that had been made thyrotoxic by daily intraperitoneal injections of triiodothyronine (150 μg kg−1) for two to three weeks. Potassium contracture tension (relative to tetanic tension) in thyrotoxic rats was greater in EDL muscles and smaller in soleus muscles than in normal rats. As the relationship between membrane potential and potassium concentration was unaltered by thyroid treatment, it was concluded that the changes in potassium contracture tension were due to changes in excitation-contraction coupling. In thyrotoxic rats there was an average negative shift of −5 mV in the voltage sensitivity of tension in EDL fibres and a positive shift of 5 mV in soleus. As a result, the tension-membrane potential curves for EDL and soleus fibres essentially coincided. There was a corresponding average negative shift of −4 mV in the voltage sensitivity of asymmetric charge in EDL fibres, and a positive shift of 4 mV in soleus fibres from thyrotoxic rats. The dependence of asymmetric charge movement on membrane potential became essentially the same in EDL and soleus fibres from thyrotoxic rats. The maximum asymmetric charge in soleus fibres increased from an average value of 6.5 nC μF−1 in normal rats (n=33) to 8.9 nC μF−1 in thyrotoxic rats (n=32;p<0.005). The increase in charge movement in EDL fibres in thyrotoxic rats was not statistically significant. The real increase was masked by an increase in linear capacity due to proliferation of T-system membrane: the density of triads where charge movement probably occurs did not increase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, R. H. &Almers, W. (1976a) The voltage dependence of membrane capacity.J. Physiol., Lond. 254, 317–38.
Adrian, R. H. &Almers, W. (1976b) Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle.J. Physiol., Lond. 254, 339–60.
Adrian, R. H., Chandler, W. K. &Hodgkin, A. L. (1970) Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres.J. Physiol., Lond. 208, 607–44.
Adrian, R. H. &Peres, A. (1979) Charge movement and membrane capacity in frog muscle.J. Physiol., Lond. 289, 83–97.
Almers, W. (1976) Differential effects of tetracaine on delayed potassium channels and displacement currents in frog skeletal muscle.J. Physiol., Lond. 262, 613–37.
Dulhunty, A. F. (1985) Excitation-contraction coupling and contractile properties of denervated rate EDL and soleus muscles.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 6, 207–25.
Dulhunty, A. F. &Gage, P. W. (1983) Asymmetrical charge movement in slow- and fast-twitch fibres in normal and paraplegic rats.J. Physiol., Lond. 341, 213–31.
Dulhunty, A. F. &Gage, P. W. (1985) Excitation-contraction coupling and charge movement in denervated rat EDL and soleus muscles.J. Physiol., Lond. 358, 75–89.
Dulhunty, A. F., Gage, P. W. &Lamb, G. D. (1986) Differential effects of thyroid hormone on T-tubules and terminal cisternae in rat muscle: an electrophysiological and morphometric analysis.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 7, 225–36.
Eisenberg, B. R. &Milton, R. L. (1984) Muscle fibre termination at the tendon of the frog's sartorius: a stereological study.Am. J. Anat. 171, 273–84.
Fitts, R. H., Brimmer, C. J., Troup, J. P. &Unsworth, B. R. (1984) Contractile and fatigue properties of thyrotoxic rat skeletal muscle.Nerve Musc. 7, 470–7.
Fitts, R. H., Winder, W. W., Brooke, M. H., Kaiser, K. K. &Hollozy, J. O. (1980) Contractile, biochemical and histochemical properties of thyrotoxic rat soleus muscle.Am. J. Physiol. 238, C15-C20.
Gage, P. W. &Dulhunty, A. F. (1981)a Excitation-contraction coupling and charge movement in skeletal muscle fibres of paraplegic rats.Proc. Aust. physiol. pharmacol. Soc. 12, 93p.
Gage, P. W. &Dulhunty, A. F. (1981a) Upper motor neurone modulation of charge movement and mechanical activation in rat skeletal muscle fibres.Neurosci. Lett. 27, 271–6.
Gold, H. K., Spann, J. F. Jr. &Braunwald, E. (1970) Effect of alterations in the thyroid state on the intrinsic contractile properties of isolated rat skeletal muscle.J. Clin. Invest. 49, 849–54.
Hall-Craggs, E. C. B., Wines, M. M. &Max, S. R. (1983) Fibre-type changes in denervated soleus muscles of the hyperthyroid rat.Exp. Neurol. 80, 252–7.
Hollingworth, S. &Marshall, M. W. (1981) A comparative study of charge movement in mammalian skeletal muscle fibres.J. Physiol., Lond. 321, 583–602.
Horowicz, P. &Schneider, M. F. (1981) Membrane charge movement in contracting and non-contracting skeletal muscle fibres.J. Physiol., Lond. 314, 565–93.
Huang, C. L. -H. (1982) Pharmacological separation of charge movement components in frog skeletal muscle.J. Physiol., Lond. 324, 1–24.
Hui, C. S. (1983) Pharmacological studies of charge movement in frog skeletal muscle.J. Physiol., Lond. 337, 509–29.
Hui, G. G., Milton, R. L. &Eisenberg, R. S. (1984) Charge movement in skeletal muscle fibres paralyzed by the calcium-entry blocker D600Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 2582–5.
Lamb, G. D. (1986a) Generalization of the three microelectrode voltage clamp technique to allow unequal electrode spacings.J. electrophysiol. Tech. 13, 255–64.
Lamb, G. D. (1986b) Asymmetric charge movement in contracting muscle fibres in the rabbit.J. Physiol., Lond. 376, 63–83.
Lamb, G. D. (1986c) Components of charge movement in rabbit skeletal muscle: the effect of tetracaine and nifedipine.J. Physiol., Lond. 376, 85–100.
Lamb, G. D. (1987) Asymmetric charge movement in polarized and depolarized muscle fibres of the rabbit.J. Physiol., Lond. 383, 349–367.
Melzer, W., Schneider, M. F., Simon, B. J. &Szucs, G. (1986) Intramembrane charge movement and calcium release in frog skeletal muscle.J. Physiol., Lond. 373, 481–511.
Montgomery, A. (1984) Isotonic responses of hypo- and hyperthyroid rat skeletal muscles.J. Physiol., Lond. 354, 101p.
Nicol, C. N. J. &Bruce, D. S. (1981) Effect of hyperthyroidism on the contractile and histochemical properties of fast and slow twitch skeletal muscle from the rat.Pflügers Arch. 390, 73–9.
Nicol, C. J. M. &Maybee, S. H. (1982) Contractile properties and fibre composition of rat skeletal muscle: effect of mild hyperthyroidism.Qt. J. exp. Physiol. 67, 467–72.
Nwoye, L., Mommaerts, W. F. H. M., Simpson, D. R., Seraydarian, K. &Marusich, M. (1982) Evidence for a direct action of thyroid hormone in specifying muscle properties.Am. J. Physiol. 242, 12401–8.
Rakowski, R. F., Best, P. M. &James-Kracke, M. R. (1985) Voltage dependence of membrane charge movement and calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 6, 403–33.
Schneider, M. F. &Chandler, W. K. (1973) Voltage dependent charge movement in skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling.Nature, Lond. 242, 244–6.
Vergara, J. &Caputo, C. (1983) Effects of tetracaine on charge movements and calcium signals in frog skeletal muscle fibers.Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,80, 1477–81.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dulhunty, A.F., Gage, P.W. & Lamb, G.D. Potassium contractures and asymmetric charge movement in extensor digitorum longus and soleus muscles from thyrotoxic rats. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 8, 289–296 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01568885
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01568885