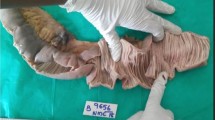
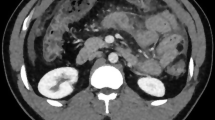
Summary
A 58-year-old male from Puerto Rico who was taking orally administered cortisone analogs for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease presented with fever, absolute eosinophilia, right lower quadrant pain, and rebound tenderness associated withStrongyloides stercoralis infection of the appendix. A 37-year-old alcoholic male developed fever, right lower quadrant abdominal pain, and rebound tenderness because of infection of the appendix withEntamoeba histolytica. These are the seventh reported case of isolated amebic appendicitis and the ninth reported case of appendiceal involvement withStrongyloides. In all these cases the diagnosis was made only after surgery. Patients with unexplained right lower quadrant pain, particularly if immunosuppressed or with an appropriate travel history, should have stool examinations for ova and parasites. Early diagnosis and treatment may prevent life-threatening complications such as perforation and peritonitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang AR: An analysis of the pathology of 3003 appendices. Aust NZ J Surg 51:169–178, 1981
Collins DC: 71,000 human appendix specimens—a final report, summarizing forty years' study. Am J Proct 14:365–381, 1963
Kean BH, Gilmore HR, Vanstone W: Fatal amebiasis: Report of 148 fatal cases from the Armed Forces Institutes of Pathology. Ann Intern Med 44:831–842, 1956
Variyam EP, Gogate P, Hassan M, Costerton WJ, Pillai S, Ward H, Jalan K: Nondysenteric intestinal amebiasis: co-Ionic morphology and search forEntamoeba histolytica adherence and invasion. Dig Dis Sci 34:732–740, 1989
Hawe P: The surgical aspect of intestinal amebiasis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 81:387–392, 1945
Kapoor OP, Joshi VR, Sabnis AM: Amoebic appendicitis. J Trop Med Hyg 75:1–3, 1972
Kleitsch WP, Kisner P: Amebic appendicitis, peritonitis and wound infection. Ann Surg 133:139–142, 1951
Gulati SM, Grover NK, Iyenger B, Taneja OP: Amebic appendicitis with fulminating peritonitis: Report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum 15:308–310, 1972
Peison B: Acute localized amebic appendicitis: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum 16:532–536, 1973
Judy KL: Amebiasis presenting as an acute abdomen. Am J Surg 127:275–279, 1974
Robinson AS, Levinson M: Amebic appendicitis associated with hepatic abscess. South Med J 77:1047–1048, 1984
Drugs for parasitic diseases. Med Lett 28:9–18, 1986
Adams EB, MacLeod IN: Invasive amebiasis I—amebic dysentery and its complications. Medicine 56:315–323, 1977
Adams EB, MacLeod IN: Invasive amebiasis II—amebic liver abscess and its complications. Medicine 56:325–334, 1977
Greenstein AJ, Barth J, Dicker A, Bottone EJ, Aufses AH: Amebic liver abscess: a study of 11 cases compared with a series of 38 patients with pyogenic liver abscess. Am J Gastroenterol 80:472–478, 1985
Sarda AK, Bal S, Sharma AK, Kapur MM: Intraperitoneal rupture of amoebic liver abscess. Br J Surg 76:202–203, 1989
Davidson RA: Strongyloidiasis—a presentation of 63 cases. NC Med J 43:23–25, 1982
Kane MG, Luby JP, Krejs GJ: Intestinal secretion as a cause of hypokalemia and cardiac arrest in a patient with strongyloidiasis. Dig Dis Sci 29:768–772, 1984
Milder JE, Walzer PD, Kilgore G, Rutherford I, Klein M: Clinical features ofStrongyloides stercoralis infection in an endemic area of the United States. Gastroenterology 80:1481–1488, 1981
Morse JMD, Laurain AR, Thomas E: Spurious pseudomembranous enteritis in strongyloidiasis. Am J Gastroenterol 79:109–112, 1984
Pelletier LL: Colonic strongyloidiasis in World War II Far East ex-prisoners of war. Am J Trop Med Hyg 33:55–61, 1984
Powell RW, Moss JP, Nagar D, Melo JC, Boram LH, Anderson WH, Cheng SH: Strongyloidiasis in immunosuppressed hosts. Arch Intern Med 140:1061–1063, 1980
Armignacco O, Capecchi A, DeMori P, Grillo LR:Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med 86:258, 1989 (letter)
Davidson RA, Fletcher RH, Chapman LE: Risk factors for strongyloides: A case control study. Arch Intern Med 144:321–324, 1984
Genta RM, Miles P, Fields K: OpportunisticStrongyloides stercoralis infection in lymphoma patients: Report of a case and review of the literature. Cancer 63:1407–1411, 1989
Ingra-Siegman Y, Kapila R, Sen P, Kaminski ZC, Louria DB: Syndrome of hyperinfection withStrongyloides stercoralis. Rev Infect Dis 3:397–407, 1981
Maayan S, Wormser GP, Widerhorn J, Sy ER, Kim YH, Ernst JA:Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection in a patient with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med 83:945–948, 1987
Pagliuca A, Layton DM, Allen S, Mufti GJ: Hyperinfection with strongyloides after treatment for adult T cell leukaemia-lymphoma in an African immigrant. Br Med J 297:1456–1457, 1988
Stemmerman GN: Eosinophilic granuloma of the appendix: A study of its relation to Strongyloides infestation. Am J Clin Pathol 36:524–531, 1961
Stemmerman GN: Strongyloides in migrants: Pathological and clinical considerations. Gastroenterology 53:59–70, 1967
Scowden EB, Schaffner W, Stone WJ: Overwhelming strongyloidiasis—an unappreciated opportunistic infection. Medicine 57:527–544, 1978
Noodleman JS: Eosinophilic appendicitis: Demonstration ofStrongyloides stercoralis as a causative agent. Arch Pathol Lab Med 105:148–149, 1981
Shakir AA, Youngberg G, Alvarez S: Strongyloides infestation as a cause of acute appendicitis. J Tenn Med Assoc 79:543–544, 1986
von Kuster LC, Genta RM: Cutaneous manifestations of strongyloidiasis. Arch Dermatol 124:1826–1830, 1988
Carp NZ, Nejman JH, Kelly JJ: Strongyloidiasis: An unusual cause of colonic polyps and gastrointestinal bleeding. Surg Endosc 1:175–177, 1987
Kane MG, Luby J, Krejs G: Intestinal secretion as a cause of hypokalemia and cardiac arrest in a patient with strongyloidiasis. Dig Dis Sci 29:768–772, 1984
Maayam S, Wormser GP, Widerhorn J, Sy ER, Kim YH, Ernst JA:Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection in a patient with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med 83:945–948, 1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadler, S., Cappell, M.S., Bhatt, B. et al. Appendiceal infection byEntamoeba histolytica andStrongyloides stercoralis presenting like acute appendicitis. Digest Dis Sci 35, 603–608 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01540408
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01540408