Abstract
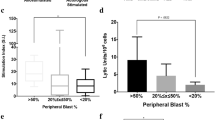
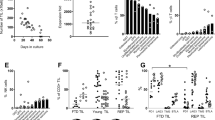
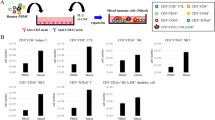
Combined CD3 and CD28 monoclonal antibodies (mAb) may initiate efficient activation and expansion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL). In this study we compared phenotypical and functional characteristics of TIL from a group of 17 solid human tumors, stimulated either by high-dose recombinant interleukin 2 (rIL-2, 1000 IU/ml) or by a combination of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies in the presence of low-dose rIL-2 (10 IU/ml). Compared to activation with high-dose rIL-2, stimulation of TIL with CD3/CD28 mAb induced significantly stronger proliferation and yielded higher levels of cell recovery on day 14. Following the CD3/CD28 protocol, expansion of an almost pure population of CD3+ cells was obtained. Whereas CD4+ cells dominated in the first week of culturing, within 4 weeks the CD8+ population increased to over 90%. The specific capacity to kill autologous tumor cells was not increased as compared to the high-dose rIL-2 protocol, but all cultures showed high cytotoxic T cell activity as measured in a CD3-mAb-mediated redirected kill assay. These studies show that combined CD3 and CD28 mAb are superior to rIL-2 with respect to the initiation of expansion of CD8+ cytolytic TIL from solid tumors. Stimulation with specific tumor antigens at a later stage of culturing may further augment the expansion of tumor-specific cytolytic T cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebersold P, Hyatt C, Johnson S, Hines K, Koreak L, Sanders M, Lotze M, Topalian S, Yang JC, Rosenberg SA (1991) Lysis of autologous melanoma cells by tumor infiltrating lymphocytosis associated with clinical response. J Natl Cancer Inst 147: 609
Barth RJ, Mulé JJ, Spiess PJ, Rosenberg SA (1991) Interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor have a role in tumor regression mediated by murine CD8+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. J Exp Med 173: 647
Belldegrun A, Muul LM, Rosenberg SA (1988) Interleukin 2 expanded tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in human renal cell cancer: isolation, characterization, and antitumor activity. Cancer Res 48: 206
Crossland KD, Lee VK, Chen W, Riddell SR, Greenberg PD, Cheever MA (1991) T cells from tumor-immune mice nonspecifically expanded in vitro with anti-CD3 plus IL-2 retain specific function in vitro and can eradicate disseminated leukaemia in vivo. J Immunol 146: 4414
Fisher B, Packard BS, Read EJ, Carrasquillo JA, Carter CS, Topalian SL, Yang JC, Yolles P, Larson SM, Rosenberg SA (1989) Tumor localization of adoptively transferred indium-111 labeled tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol 7: 250
Gillis S, Ferm MM, Ou W, Smith KA (1978) T-cell growth factors: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol 120: 2027
Gruters RA, Otto SA, Al BJM, Verhoeven AJ, Verweij CL, Lier RAW van, Miedema F (1991) Non-mitogenic T cell activation signals are sufficient for induction of human immunodeficiency virus transcription. Eur J Immunol 21: 167
Hom SS, Schwartzentruber DJ, Rosenberg SA, Topalian SL (1993) Specific release of cytokines by lymphocytes infiltrating human melanomas in response to shared melanoma antigens. J Immunol 13: 18
Hom SS, Rosenberg SA, Topalian SL (1993) Specific immune recognition of autologous tumor by lymphocytes infiltrating colon carcinomas: analysis by cytokine secretion. Cancer Immunol Immunother 36: 1
Jong R de, Brouwer M, Rebel VI, Seventer GA van, Miedema F, Lier RAW van (1990) Generation of alloreactive cytolytic T lymphocytes by immobilized anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies. Immunology 70: 357
Jong R de, Stokkers P, Lamme E, Kool JM, Borst F, Brouwer M, Miedema F, Lier RAW van (1991) Regulation of T-cell differentiation by CD2 and CD28 accessory molecules. Immunology 74: 175
Jong R de, Brouwer M, Miedema F, Lier RAW van (1991) Human CD8+ T lymphocytes can be divided into CD45RA+ and CD45RO+ cells with different requirements for activation and differentiation. Immunology 146: 2088
June CH, Ledbetter JA, Linsley PS, Thompson CB (1990) Role of the CD28 receptor in T-cell activation. Immunol Today 11: 211
Koulova L, Clark EA, Shu G, Dupont B (1991) The CD28 ligand B7/BB1 provides costimulatory signal for alloactivation of CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med 173: 759
Kradin RL, Lazarus DS, Dubinett SM, Gifford J, Grove B, Kurnick JT, Preffer FI, Pinto CE, Davidson E, Callahan RJ, Strauss HW (1989) Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and interleukin-2 in treatment of advanced cancer. Lancet I: 577
Lier RAW van, Brouwer M, Aarden LA (1988) Signals involved in T-cell activation: T-cell proliferation induced through the synergistic action of anti-CD2 and anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol 18: 167
Lier RAW van, Brouwer M, Jong R de, Groot M, Groot E de, Aarden LA (1989) Functional properties of the human T-cell differentiation antigen CD28. In: Knapp W, Dorken B, Gilks WR, Rieber EP, Schmidt RE, Stein H, Borne AEGKr von dem (eds) Leukocyte typing. IV. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 353
Lier RAW van, Brouwer M, Rebel VI, Noesel CJM van, Aarden LA (1989) Immobilized anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies induce accessory cell independent lymphokine production, proliferation and helper activity in human T lymphocytes. Immunology 68: 45
Lier RAW van, Brouwer M, Groot E de, Kramer I, Aarden LA, Verhoeven AJ (1991) T cell receptor/CD3 and CD28 use distinct intracellular signalling pathways. Eur J Immunol 21: 1775
Lindsten T, June CH, Ledbetter JA, Stella G, Thompson GB (1989) Regulation of lymphokine messenger RNA stability by a surface-mediated T-cell activation pathway. Science 244: 339
Massaro AF, Schoof DD, Rubinstein A, Zuber M, Leonard-Vidal FJ, Eberlein TJ (1990) Solid-phase anti-CD3 antibody activation of murine tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. Cancer Res 50: 2587
Muul LM, Spiess P, Director EP, Rosenberg SA (1987) Identification of specific cytolytic immune responses against autologous tumor in humans bearing malignant melanoma. J Immunol 138: 989
Nijhuis EWP, Wiel-van Kemenade E van de, Figdor CG, Lier RAW van (1990) Activation and expansion of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes by anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Immunol Immunother 32: 245
Radrizzani M, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Parmiani G, Fossati G (1989) Lysis by interleukin 2-stimulated tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes of autologous and allogenic tumor cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 28: 67
Rosenberg SA, Packard BS, Aebersold PM, Solomon D, Topalian SL, Toy ST, Simon P, Lotze MT, Yang JC, Seipp CA, Simpson C, Carter C, Bock S, Schwartzentruber D, Wei JP, White DE (1988) Use of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and interleukin-2 in the immunotherapy of patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 319: 1676
Schoof DD, Jung S-E, Eberlein TJ (1989) Human tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) cytotoxicity facilitated by anti-T-cell receptor antibody. Int J Cancer 44: 219
Schoof DD, Selleck CM, Massaro AF, Jung S-E, Eberlein TJ (1990) Activation of human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes by monoclonal antibodies directed to the CD3 complex. Cancer Res 50: 1138
Schwartzentruber DJ, Topalian SL, Mancini M, Rosenberg SA (1991) Specific release of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, tumor necrosis factor-α, and IFNγ by human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes after autologous tumor stimulation. J Immunol 146: 3674
Verweij CL, Geerts M, Aarden LA (1991) Activation of interleukin-2 gene transcription via the T-cell surface molecule CD28 is mediated through an NF-kB-like response element. J Biol Chem 266: 14179
Whiteside ThL, Jost LM, Herberman RB (1992) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Potential and limitations to their use for cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol/Haematol 12: 25
Yanelli JR, Crumpacker DB, Good RW, Friddell CD, Poston R, Horton S, Maleckar JR, Oldham RK (1990) Use of anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody in the generation of effector cells from solid tumors for use in cancer biotherapy. J Immunol Methods 1: 91
Yoshizawa H, Sakai K, Chang AE, Shu S (1991) Activation by anti-CD3 tumor-draining lymph node cells for specific adoptive immunotherapy. Cell Immunol 134: 473
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flens, M.J., Mulder, W.M.C., Bril, H. et al. Efficient expansion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from solid tumors by stimulation with combined CD3 and CD28 monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Immunol Immunother 37, 323–328 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01518455
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01518455