Summary
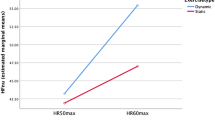
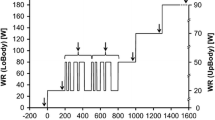
A characteristic notch in the heart rate (f c) on-response at the beginning of square-wave exercise is described in 7 very fit marathon runners and 12 sedentary young men, during cycle tests at 30% and 60% of maximal oxygen consumption (VO2max). The (f c) notch revealed af c overshoot with respect to the (f c) values predicted from exponential beat-by-beat fitted models. While at 30% of (VO2max). all subjects showed af c over-shoot, at 60% of (VO2max). it occurred in the marathon runners but not in the sedentary subjects. The mean time of occurrence of thef c overshoot from the onset of the exercise was 16.7 (SD 4.7) s and 12.2 (SD 3.2) s at 30% of (VO2max). in the runners and the sedentary subjects respectively, and 23.8 (SD 8.8) s at 60% of (VO2max). in the runners. The amplitude of the overshoot, with respect to rest, was 41 (SD 12) beats·min−1and 31 (SD 4) beats·min−1 at 30% of (VO2max). in the runners and the sedentary subjects respectively, and 46 (SD 19) beats·min−1 at 60% of (VO2max). in the runners. The existence and the amplitude of thef c overshoot may have been related to central command and muscle heart reflex mechanisms and thus may have been indicators of changes in the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic activity occurring in fit and unfit subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage P (1971) Statistical methods in medical research. Blackwell, Oxford
Åstrand PO, Rodahl K (1986) Textbook of work physiology. McGraw Hill, New York
Blomqvist CG, Saltin B (1983) Cardiovascular adaptations to physical training. Annu Rev Physiol 45:169–189
Dixon WJ (1983) BMDP Statistical software. University of California Press, Berkeley, Calif., pp 672
Fagraeus L, Linnarson D (1974) Autonomic origin of heart rate fluctuation at the onset of exercise. Report of the Laboratory Aviation Naval Medicine, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm
Galbo H (1983) Hormonal and metabolic adaptation to exercise. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 2–27
Hollander AP, Bouman LN (1975) Cardiac acceleration in man elicited by a muscle-heart reflex. J Appl Physiol 38:272–278
Jacquez JA (1972) Compartmental analysis in biology and medicine. Elsevier, North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 102–110
Kendall M, Stuart A, Ord JK (1983) The advanced theory of statistics. Griffin, London
Kniffky KD, Mense S, Schmidt RF (1981) Muscle receptors with fine afferent fibers which may evoke circulatory reflexes. Circ Res [Suppl 1] 48:25–31
Linnarson D (1974) Dynamics of pulmonary gas exchange and heart rate changes at start and end of exercise. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 415:1–68
Mense S, Stahnke M (1983) Response in muscle afferent fibers of slow conduction velocity to contractions and ischaemia in the cat. J Physiol 324:383–397
Mitchell JH (1990) Neural control of the circulation during exercise. Med Sci 22:141–154
Mitchell JH, Kaufman ML, Iwamoto GA (1983) The exercise pressor reflex: its cardiovascular effects, afferent mechanism, and central pathways. Annu Rev Physiol 45:229–242
Orizio C, Comandè A, Margonato V, Veicsteinas A (1983) Kinetics of heart rate increase with exercise in different athletes. IRCS Med Sci 11: 329–330
Orizio C, Perini R, Comandè A, Castellano M, Beschi M, Veicsteinas A (1988) Plasma catecholamines and heart rate at the beginning of exercise in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:644–651
Rowell LB, O'Leary DS (1990) Reflex control of the circulation during exercise: chemoreflexes and mechanoreflexes. J Appl Physiol 69:407–418
Victor RD, Seals DR, Mark AL (1987) Differential control of heart rate and sympathetic nerve activity during dynamic exercise. J Clin Invest 79:508–516
Wigertz O (1971) Dynamics of respiratory and circulatory adaptation to muscular exercise in man. Acta Physiol Scand 363:531
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feroldi, P., Belleri, M., Ferretti, G. et al. Heart rate overshoot at the beginning of muscle exercise. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 65, 8–12 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01466267
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01466267