Abstract
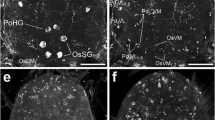
The midgut of the female mosquitoAedes aegypti was studied immunohistologically with antisera to various regulatory peptides. Endocrine cells immunoreactive with antisera to perisulfakinin, RFamide, bovine pancreatic polypeptide, urotensin 1, locustatachykinin 2 and allatostatins A1 and B2 were found in the midgut. Perisulfakinin, RFamide and bovine pancreatic polypeptide all react with the same, about 500 endocrine cells, which were evenly distributed throughout the posterior midgut, with the exception of its most frontal and caudal regions. In addition, these antisera recognized three to five neurons in each ingluvial ganglion and their axons, which ran longitudinally over the anterior midgut, as well as axons innervating the pyloric sphincter. The latter axons appear to be derived from neurons located in the abdominal ganglia. Antisera to two different allatostatins recognized about 70 endocrine cells in the most caudal area of the posterior midgut and axons in the anterior midgut whose cell bodies were probably located in either the brain or the frontal ganglion. Antiserum to locustatachykinin 2 recognized endocrine cells present in the anterior midgut and the most frontal part of the posterior midgut, as well as about 50 cells in the most caudal region of the posterior midgut. Urotensin 1 immunoreactivity was found in endocrine cells in the same region as the perisulfakinin-immunoreactive cells, but no urotensin-immunoreactive axons were found in the midgut. Double labeling experiments showed that the urotensin and perisulfakinin immunoreactivities were located in different cells. Such experiments also showed that the locustatachykinin and allatostatin immunoreactivities in the most caudal area of the posterior midgut were present in different cells. No immunoreactivity was found in the mosquito midgut when using antisera to corazonin, allatotropin or leucokinin IV. Since these peptides have either been isolated from, or can reasonably be expected to be present in mosquitoes, it was concluded that these peptides are not present in the mosquito midgut.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agricola H-J, Bräunig P (1995) Comparative aspects of peptidergic signaling pathways in the nervous systems of arthropods. In: Breidbach O, Kutsch W (eds) The nervous systems of invertebrates: an evolutionary and comparative approach. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 303–327
Andriès J-C, Beauvillain JC (1988) Ultrastructural study of cholecystokinin-like immunoreactivity in endocrine cells of the insect midgut. Cell Tissue Res 254:75–81
Andriés J-C, Tramu G (1984) Détection immunohistochimique de substances apparentées à des hormones peptidiques de mammifères dans le mésentéron d'Aesha cyanea (Insecte, Odonate). C R Acad Sc Paris 299:181–184
Andriès J-C, Tramu G (1985a) Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study of endocrine cells in the midgut of the cockroachBlaberus craniifer (Insecta, Dictyoptera). Cell Tissue Res 240:323–332
Andriès J-C, Tramu G (1985b) Distribution patterns of mammalian-like peptide immunoreactive cells in the midgut ofAeshna cyanaea (Insecta, Odonata). Experientia 41:500–503
Barillas-Mury C, Graf R, Hagedorn HH, Wells MA (1991) cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of a blood meal-induced trypsin from the mosquito,Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem 21:825–831
Barillas-Mury C, Noriega FG, Wells MA (1995) Early trypsin activity is part of the signal transduction system that activates transcription of the late trypsin gene in the midgut of the mosquito,Aedes aegypti. Insect Mol Biol 25:241–246
Bennett HPJ, Browne CA, Solomon S (1981) Purification of two major forms of rat pituitary corticotropin using only reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Biochemistry 20:4530–4538
Briegel H, Lea AO (1975) Relationship between protein and proteolytic activity in the midgut of mosquitoes. J Insect Physiol 21:1597–1609
Brown MR, Raikhel AS, Lea AO (1985) Ultrastructure of midgut endocrine cells in the adult mosquito,Aedes aegypti. Tissue Cell 17:709–721
Brown MR, Crim JW, Lea AO (1986) FMRFamide- and pancreatic polypeptide-like immunoreactivity of endocrine cells in the midgut of a mosquito. Tissue Cell 18:419–428
Brown MR, Crim JW, Lea AO (1990) Localization of Aea-HP-1 and vertebrate-like peptides in the neuroendocrine and midgut endocrine systems ofAedes aegypti. In: Hagedorn HH, Hildebrand JG, Law JH (eds) Molecular insect science. Plenum Press, New York London, p 284
Brown MR, Klowden MJ, Crim JW, Young L, Shrouder LA, Lea AO (1994) Endogenous regulation of mosquito host-seeking behavior by a neuropeptide. J Insect Physiol 40:399–406
Burg M, Grantham M, Abramow M, Orloff J (1966) Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol 210:1293–1298
Cantera R, Veenstra JA, Nässel DR (1994) Postembryonic development of corazonin-containing neurons in the blowfly,Phormia terranovae. J Comp Neurol 350:559–572
Chen Y, Veenstra JA, Davis NT, Hagedorn HH (1994) A comparative study of leucokinin-immunoreactive neurons in insects. Cell Tissue Res 276:69–83
Davis NT, Homberg U, Dircksen H, Levine RB, Hildebrand JG (1993) Crustacean cardioactive peptide-immunoreactive neurons in the hawkmothManduca sexta and changes in their immunoreactivity during postembryonic development. J Comp Neurol 338:612–627
Digan ME, Roberts DN, Enderlin FE, Woodworth AR, Kramer SJ (1992) Characterization of the precursor forManduca sexta diuretic hormone Mas-DH. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:11074–11078
Donly BC, Ding Q, Tobe SS, Bendena WG (1993) Molecular cloning of the gene for the allatostatin family of neuropeptides from the cockroachDiploptera punctata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8807–8811
Duve H, Thorpe A (1982) The distribution of pancreatic polypeptide in the nervous system and gut of the blowfly,Calliphora vomitoria (Diptera). Cell Tissue Res 227:67–77
Duve H, Thorpe A (1994) Distribution and functional significance of Leu-callatostatins in the blowflyCalliphora vomitoria. Cell Tissue Res 267:367–379
Duve H, Johnsen AH, Scott AG, Yu CG, Yagi KJ, Tobe SS, Thorpe A (1993) Callatostatins: neuropeptides from the blowflyCalliphora vomitoria with sequence homology to cockroach allatostatins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:2456–2460
Endo Y, Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J (1981) Gut endocrine cells in insects: the ultrastructure of the gut endocrine cells of the lepidopterous species. Biomed Res 2:270–280
Endo Y, Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J (1982) Exocytotic release of secretory granules from endocrine cells in the midgut of insects. Cell Tissue Res 222:515–522
Endo Y, Iwanaga T, Fujita T, Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J (1982a) Localization of pancreatic polypeptide (PP)-like immunoreactivity in the central and visceral nervous systems of the cockroachPeriplaneta. Cell Tissue Res 227:1–9
Endo Y, Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J, Iwanaga T, Fujita T (1982b) Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical identification of pancreatic polypeptide-immunoreactive endocrine cells in the cockroach midgut. Biomed Res 3:454–456
Fujita T, Iwanaga T, Kusumoto Y Yoshie S (1981) Paraneurons and neurosecretion. In: Farner DS, Lederis (eds) Neurosecretion. Molecules, cells, systems. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 3–13
Gaus G, Doble KE, Price DA, Greenberg MJ, Lee TD, Batelle B-A (1993) The sequences of five neuropeptides isolated fromLimulus using antisera to FMRFamide. Biol Bull 184:322–329
Glättli E, Rudin W, Hecker H (1987) Immunoelectron microscopic demonstration of pancreatic polypeptide in midgut epithelium of hematophagous Dipterans. J Histochem Cytochem 35:891–896
Graf R, Raikhel AS, Brown MR, Lea AO, Briegel H (1986) Mosquito trypsin: immunocytochemical localization in the midgut of blood-fedAedes aegypti. Cell Tissue Res 245:19–27
Harlow E, Lanc D (1988) Antibodies. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Holman GM, Cook BJ, Nachman RJ (1986) Isolation, primary structure and synthesis of leucomyosuppressin, an insect neuropeptide that inhibits spontaneous contractions of the cockroach hindgut. Comp Biochem Physiol 85C:329–333
Iwanaga T, Fujita T, Nishiitsutsujii-Uwo J, Endo Y (1981) Immunohistochemical demonstration of PP-, somatostatin-, entero-glucagon-and VIP-like immunoreactivities in the cockroach midgut. Biomed Res 2:202–207
Iwanaga T, Fujita T, Takeda N, Endo Y, Lederis K (1986) Urotensin I-like immunoreactivity in the midgut endocrine cells of the insectsGryllus bimaculatus andPeriplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 244:565–568
Jenkins AC, Brown MR, Crim JW (1989) FMRF-amide immunoreactivity and the midgut of the corn earworm (Heliothis zea). J Exp Zool 252:71–78
Kataoka H, Troetschler RG, Li JP, Kramer SJ, Carney RL, Schooley DA (1989) Isolation and identification of a diuretic hormone from the tobacco hornworm,Manduca sexta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2976–2980
Kay I, Coast GM, Cusinato O, Wheeler CH, Totty NF, Goldsworthy GJ (1991) Isolation and characterization of a diuretic peptide fromAcheta domesticus — evidence for a family of insect diuretic peptides. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 372:505–512
Kingan TG (1989) A competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: applications in the assay of peptides, steroids, and cyclic nucleotides. Anal Biochem 183:283–289
Kingan TG, Teplow DB, Philips JM, Riehm JP, Rao KR, Hildebrand JG, Homberg U, Kammer AE, Jardine I, Griffin PR, Hunt DF (1990) A new peptide in the FMRFamide family isolated from the CNS of the hawkmoth,Manduca sexta. Peptides 11:849–856
Lange AB, Chan KK, Stay B (1993) Effects of allatostatin and proctolin on antennal pulsatile organ and hindgut muscle in the cockroach,Diploptera puncata. Archiv Insect Biochem Physiol 24:79–92
Lehmberg E, Ota RB, Furuya K, King DS, Applebaum SW, Ferenz H-J, Schooley DA (1991) Identification of a diuretic hormone ofLocusta migratoria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 179:1036–1041
Lundquist CT, Clottens F, Holman GM, Riehm JP, Bonkale W, Nässel DR (1993) Locustatachykinin immunoreactivity in the blowfly central nervous system and intestine. J Comp Neurol 341:225–240
Lundquist CT, Clottens FL, Holman GM, Nichols R, Nachman RJ, Nässel DR (1994) Callitachykinins I and II, two novel myotropic peptides isolated from the blowfly,Calliphora vomitoria, that have resemblances to tachykinins. Peptides 15:761–768
Matsumoto S, Brown MR, Crim JW, Vigna SR, Lea AO (1989) Isolation and primary structure of neuropeptides from the mosquito,Aedes aegypti, immunoreactive to FMRFamide antiserum. Insect Biochem 19:277–283
Montuenga LM, Barrenechea MA, Sesma P, López, Vázquez JJ (1989) Ultrastructure and immunocytochemistry of endocrine cells in the midgut of the desert locust,Schistocerca gregaria (Forskal). Cell Tissue Res 258:577–583
Myers CM, Evans PD (1985) The distribution of bovine pancreatic polypeptide/FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in the ventral nervous system of the locust. J Comp Neurol 234:1–16
Nachman RJ, Holman GM, Haddon WF, Ling N (1986a) Leucosulfakinin, a sulfated insect neuropeptide with homology to gastrin and cholecystokinin. Science 234:71–73
Nachman RJ, Holman GM, Cook BJ, Haddon WF, Ling N (1986b) Leucosulfakinin II, a blocked sulfated insect neuropeptide with homology to cholecystokinin and gastrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 140:357–364
Nambu JR, Murphy-Erdosh C, Andrews PC, Gottfried J, Feistner GJ, Scheller RH (1988) Isolation and characterization of aDrosophila neuropeptide gene. Neuron 1:55–61
Nichols R (1992) Isolation and expression of theDrosophila drosulfakinin neural peptide gene product, DSK-I. Mol Cell Neurosci 3:342–347
Nichols R, Schneuwly SA, Dixon JE (1988) Identification and characterization of aDrosophila homologue to the vertebrate neuropeptide cholecystokinin. J Biol Chem 263:12167–12170
Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J, Endo Y (1981) Gut endocrine cells in insects: the ultrastructure of the endocrine cells in the cockroach midgut. Biomed Res 2:30–44
O'Brien MA, Schneider LE, Taghert PH (1991) In situ hybridization analysis of the FMRFamide neuropeptide gene inDrosophila. II. Constancy in the cellular pattern of expression during metamorphosis. J Comp Neurol 304:623–638
Petzel DH, Hagedorn HH, Beyenbach KW (1985) Preliminary isolation of mosquito natriuretic factor. Am J Physiol 249:R701-R711
Pratt GE, Farnsworth DE, Siegel NR, Fok KF, Feyereisen RE (1989) Identification of an allatostatin from adultDiploptera punctata. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:1243–1247
Pratt GE, Farnsworth DE, Fok KF, Siegel NR, McCormack AL, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Feyereisen R (1991) Identity of a second type of allatostatin from cockroach brains: an octadecapeptide amide with a tyrosine-rich address sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2412–2416
Reichwald K, Unnithan GC, Davis NT, Agricola H, Feyereisen R (1994) Expression of the allatostatin gene in endocrine cells of the cockroach midgut. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11894–11898
Robb S, Packman LC, Evans PD (1989) Isolation, primary structure and bioactivity of SchistoFLRF-amide, a FMRF-amide-like neuropeptide from the locust,Schistocerca gregaria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 160:850–856
Rosewicz S, Dubar Lewis L, Wang X-Y, Liddle RA, Logsdon CD (1989) Pancreatic digestive enzyme gene expression: effects of CCK and soybean trypsin inhibitor. Am J Physiol 256:G733-G738
Rothman SS, Wells H (1967) Enhancement of pancreatic enzyme synthesis by pancreozymin. Am J Physiol 213:215–218
Schneider LE, Taghert PH (1988) Isolation and characterization of aDrosophila gene that encodes multiple neuropeptides related to Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 (FMR Famide). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1993–1997
Schneider LE, O'Brien MA, Taghert PH (1991) In situ hybridization analysis of the FMRFamide neuropeptide gene inDrosophila. I. Restricted expression in embryonic and larval stages. J Comp Neurol 304:608–622
Schols D, Verhaert P, Huybrechts R, Vaudry H, Jégou S, de Loof A (1987) Immunocytochemical demonstration of proopiomelanocortin-and other opioid-related substances and a CRF-like peptide in the gut of the American cockroach,Periplaneta americana L. Histochemistry 86:345–351
Schoofs L, Holman GM, Hayes TK, Nachman RJ, Loof A de (1990a) Locustatachykinin I and II, two novel insect neuropeptides with homology to peptides of the vertebrate tachykinin family. FEBS Lett 261:397–401
Schoofs L, Holman GM, Hayes TK, Kochansky JP, Nachman RJ, Loof A de (1990b) Locustatachykinin III and IV. Two additional insect neuropeptides with homology to peptides of the vertebrate tachykinin family. Regul Pept 31:199–212
Shapiro JP, Hagedorn HH (1982) Juvenile hormone and the development of ovarian responsiveness to a brain hormone in the mosquito,Aedes aegypti. Gen Comp Endocrinol 46:176–183
Tibbetts MF, Nichols R (1993) Immunocytochemistry of sequence-related neuropeptides inDrosophila. Neuropeptides 24:321–325
Veenstra JA (1984) Immunocytochemical demonstration of a homology in peptidergic neurosecretory cells in the suboesophageal ganglion of a beetle and a locust with antisera to bovine pancreatic polypeptide, FMRFamide, vasopressin and α-MSH. Neurosci Lett 48:185–190
Veenstra JA (1988) Effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on the Malpighian tubules ofAedes aegypti. J Insect Physiol 34:299–304
Veenstra JA (1989) Isolation and structure of two gastrin/CCK-like neuropeptides from the American cockroach homologous to the leucosulfakinins. Neuropeptides 14:145–149
Veenstra JA (1991) Presence of corazonin in three insect species, and isolation and identification of [His7]corazonin fromSchistocerca americana. Peptides 12:1285–1289
Veenstra JA (1994) Isolation and identification of three leucokinins from the mosquitoAedes aegypti. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 202:715–719
Veenstra JA, Davis NT (1993) Localization of corazonin in the nervous system of the cockroachPeriplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 274:57–64
Veenstra JA, Lambrou G (1995) Isolation of a novel RFamide peptide from the midgut of the American cockroach,Periplaneta americana. Biochem Biophys Res Commun (in press)
Veenstra JA, Schooneveld H (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of neurons in the nervous system of the Colorado potato beetle with antisera against FMRFamide and bovine pancreatic polypeptide. Cell Tissue Res 235:303–308
Veenstra JA, Lehman HK, Davis NT (1994) Allatotropin is a cardioacceleratory peptide inManduca sexta. J Exp Biol 188:347–354
Verhaert P, Downer RGH, Huybrechts R, Loof A de (1989) A substance resembling somatomedin C in the American cockroach. Regul Pept 25:99–110
Woodhead AP, Stay B, Seidel SL, Khan MA, Tobe SS (1989) Primary structure of four allatostatins: neuropeptide inhibitors of juvenile hormone synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:5997–6001
Zitnan D, Sauman I, Sehnal F (1993) Peptidergic innervation and endocrine cells of insect midgut. Archiv Insect Biochem Physiol 22:113–132
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veenstra, J.A., Lau, G.W., Agricola, HJ. et al. Immunohistological localization of regulatory peptides in the midgut of the female mosquitoAedes aegypti . Histochem Cell Biol 104, 337–347 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01458127
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01458127