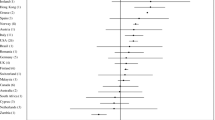
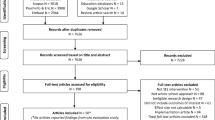
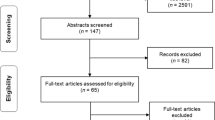
Abstract
A shorter version of SAY IT STRAIGHT (SIS) training was investigated during the 1983–84 school year with 1055 5th, 6th, 7th and 8th graders. Training was delivered in 7- and 5-day models which were compared with the 10-day model used in 1982–83 with 509 6th, 7th and 8th graders. Both shorter training models yielded significant changes toward more assertive/leveling attitudes (p<.01). Comparisons of 10, 7 and 5 day training models yielded no significant differences in such attitude changes as a function of training length. Alcohol/drug related school suspensions were not found in 1983–84 among 5th graders whether or not they were trained. However, such suspensions were significantly lower among the 1564 6th–9th graders who had received training either in the 1982–83 or the 1983–84 school year compared to the 1295 6th–9th graders who were not trained (p<.05).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandura, A. (1977).Social learning theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Botvin, G.J. & Eng, A. (1982). The efficacy of a multicomponent approach to the prevention of cigarette smoking.Preventive Medicine, 11, 199–211.
Englander-Golden, P., Elconin, J., & Miller, K.J. (1985). SAY IT STRAIGHT: Adolescent substance abuse prevention training.Academic Psychology Bulletin, 7, 65–79.
Englander-Golden, P., (1983).SAY IT STRAIGHT: Assertive/leveling refusal behavior and positive peer pressure training. Self-published.
Evans, R.I., Hansen, W.B. & Mittelmark, M.B. (1977). Increasing the validity of self-reports of smoking behavior in children.Journal of Applied Psychology, 62, 521–523.
Evans, R.I., Rozelle, R.M., Maxwell, S.E., Raines, B.E., Dill, C.A., & Guthrie, T.J. (1981). Social modeling films to deter smoking in adolescents: Results of a three-year field investigation.Journal of Applied Psychology, 66, 399–414.
Evans, R.I., Rozelle, R.M., Mittelmark, M.B., Hansen, W.B., Bane, A.L., & Havis, J. (1978). Deterring the onset of smoking in children: Knowledge of immediate physiological effects and coping with peer pressure, media pressure, and parent modeling.Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 8, 126–135.
Feshbach, N.D. (1983). Learning to care: A positive approach to child training and discipline.Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 12, 266–271.
Fry, E.B. (1969). A readability graph for librarians, part 1.School Libraries, 19, 13–16.
Horan, J.J. & Williams, J.M. (1982). Longitudinal study of assertion training as a drug abuse prevention strategy.American Educational Research Journal, 19, 341–351.
Hurd, P.D., Johnson, C.A., Pechacek, T., Bast, L.P., Jacobs, D.R., & Luepker, R.V. (1980). Prevention of cigarette smoking in seventh grade students.Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 3, 15–28.
Luepker, R.V., Pechacek, T.F., Murray, D.M., Johnson, C.A., Hurd, F., & Jacobs, D.R. (1981). Saliva thiocyanate: A chemical indication of cigarette smoking in adolescents.American Journal of Public Health, 71, 1320–24.
McAlister, A.L., Perry, C.L., Killen, J., Slinkard, L.A., & Maccoby, N. (1980). Pilot study of smoking, alcohol, and drug abuse prevention.American Journal of Public Health, 70, 719–721.
McAlister, A.L., Perry, C.L., & Maccoby, N. (1979). Adolescent smoking: Onset and prevention.Pediatrics, 63(4), 650–658.
McGuire, W.J. (1964). Inducing resistance to persuasion: Some contemporary approaches. In L. Berkow (Ed.),Advances in experimental social psychology (Vol. 1). New York: Academic Press.
Perry, C.L., Killen, J. & Slinkard, L.A. (1980). Peer teaching and smoking prevention among junior high students.Adolescence, 15, 277–281.
Prince, H.T. (1975). The effects of covert behavioral rehearsal, modeling, and vicarious consequences in assertive training. Dissertation, University of Texas at Austin.
Satir, V. (1972).Peoplemaking. CA: Science and Behavior Books, Inc.
Additional information
Paula Englander-Golden, Ph.D. is at the Department of Human Relations at the University of Oklahoma, 601 Elm, Room 730, Norman, OK 73019.
This research was supported in part by the Oklahoma Department of Mental Health, Contract #N200073.
Dr. A.B. Schwarzkopf, University of Oklahoma, Statistical Consulting Laboratory, provided statistical analysis of experimental data.
The authors thank Antoinette Bradley, Claire Germond, Lisa Hammond Denwalt, Julie Hunt, Tom Lancaster and Roxanne Moore for their help in the training of the youngsters.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Englander-Golden, P., Elconin, J., Miller, K.J. et al. Brief SAY IT STRAIGHT training and follow-up in adolescent substance abuse prevention. J Primary Prevent 6, 219–230 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01330263
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01330263