Summary
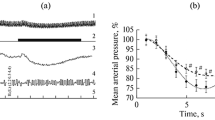
Long experiments were performed on 5 dogs. Changes in the blood supply of the brain and extremity during natural sleep and that induced by morphine were recorded by plethysmography. Coordinated changes were found in the blood supply of the brain and the extremity in the process of falling asleep, i.e., the blood supply of the brain was increased while the blood supply of the extremity reduced. It was demonstrated that such redistribution of the blood depended on the activity of the vasomotor center. Short experiments were performed on dogs with electric stimulation of the vasomotor center in the area of the fourth ventricle. Coordinated changes in the blood supply of the brain (increased pressure in the circle of Willis) and in the extremity (decrease of the plethysmogram) were recorded. Besides, data were obtained that the nervous mechanism of redistribution of the blood during sleep is influenced by carbon dioxide. In long experiments on dogs which were kept in the atmosphere, containing 4–5% of carbon dioxide, the same coordinated changes were found in the blood supply of the brain and extremity as during the process of falling asleep.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
V. P. Avrorov, Byull. Eksptl. Biol. i Med., 1954, Vol 38, No. 2, p. 66.
A. M. Bentelev, Fiziol. Zhur. SSSR, 1956, Vol. 42, No. 5, p. 363.
L. V. Blyumenau, Concerning Pressure on the Brain, In Russian Dissertation, 1889.
S. O. Istmanov, On the Effect of Stimulating the Sensory Nerves on the Human Vascular System, In Russian. Disscrtation, 1889.
A. A. Kedrov and A. I. Naumenko, Physiological Problems of Intracranial Circulation and Their Clinical Illumination, In Russian. Moscow, 1954.
G. B. Levchenko, On Changes in Cerebral Circulation During Sleep Caused by Morphine and Chloral Hydrate, In Russian. Dissertation, 1889.
Manasseina, Sleep as One Third of a Man's Life, or the Physiology, Pathology, Hygiene and Psychology of Sleep, In Russian. Moscow, 1872.
A. V. Mezhera, Vysshel Nerv. Deyatel., 1954, Vol. 4, No. 2, p. 258.
G. Ya. Pryma, Fiziol. Zhur. SSSR, 1954, Vol. 15, No. 3, p. 351.
V. A. Sklyarsky, Fiziol. Zhur. SSSR. 1940, Vol. 28, No. 2–3, p. 12.
I. R. Tarkhanov, Foster, Physiology, In Russian. Vol. II, 1882.
M. A. Ukolova, Sleep and Dreams, In Russian. Rostov-on-Don. 1955.
P. P. Dumke and C. F. Schmidt Amer. Physiol., 1941, Vol. 133, No. 2, p. 266.
Dürham, The Physiology of Sleep. Guy's hospital Reports, Vol. 6, 1860. (cited according to Manasseina).
A. Frederic and Harry Maxwell Gibbs, Arch. Nervol. Psychiatr., 1947, Bd. 57, No. 2, p. 137.
Laurence Irving, Amer. J. Physiol., 1938, Vol. 122, No. 1, p. 207.
S. Kety and J. Schmidt, J. Clin. Invest. 1948, Vol. 27, No. 4, p. 484.
A. Mosso, Uber den Kreislauf des Beutes in menschlichen Gehirn Leipzig, 1881.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ukolova, M.A., Bordyushkov, Y.N. On the coordinated changes in the blood supply of the brain and extremity which occur during the process of falling asleep. Bull Exp Biol Med 44, 1047–1050 (1957). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01306825
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01306825