Abstract
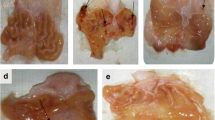
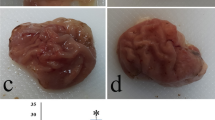
To elucidate the possible role of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in the pathogenesis of acute gastric mucosal damage, rats were treated intragastrically with 1.0 ml 96% ethanol with or without intravenous or intraperitoneal coadministration of VIP (1 nmol/liter to 1 μmol/liter/100 g). VIP was found to double the mean lesion area when compared with that induced by ethanol alone (P<0.05), an effect that was prevented by VIP antagonist (1 μmol/liter/100 g). A substance P antagonist (1 μmol/liter/100 g) also reduced the extent of gastric damage induced by coadministration of VIP and ethanol. VIP antagonist or substance P antagonist significantly reduced ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage. Gastric mucosal levels of LTB4, LTC4, VIP, and substance P were significantly increased in ethanol-treated rats as compared with saline-treated animals (P<0.05). The augmentation of ethanol-induced damage by VIP was associated with increased gastric mucosal levels of LTB4. In VIP-treated rats, gastric mucosal levels of substance P were found to be significantly increased compared with control rats (P<0.05). Administration of VIP to pyloric-ligated rats significantly increased gastric acid output and blood pepsinogen A levels as compared with saline treated rats (P<0.05). Ketotifen, a mast cell stabilizer (100 μg/100 g), administered orally 30 min before damage induction by ethanol, with or without VIP, totally abolished the damage of the surface epithelium of the entire gastric mucosa and significantly reduced the mucosal levels of LTC4 and LTB4 (P<0.05). It is suggested that VIP is involved in the pathogenesis of acute ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage. The effective mucosal protection by ketotifen suggests a role for mast cells and their mediators in the pathogenesis of acute gastric mucosal damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Said S, Mutt V: Isolation from porcine intestinal wall of vasoactive octasapeptide related to secretin and glucagon. Eur J Biochem 28:199–204, 1972
Shanahan F, Denburg JA, Fox J, Bienenstock J, Befus D: Mast cell heterogenity: Effects of neuroenteric peptides on histamine release. J Immunol 135:1331–1337, 1985
Lowman MA, Benyon RC, Church MK: Characterization of neuropeptide-induced histamine release from human dispersed skin mast cells. Br J Pharmacol 95(1):121–130, 1988
Piotrowski W, Foreman JC: On the actions of substance P, somatostatin and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide on rat peritoneal mast cells and in human skin. Naunym-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 331:364–368, 1985
Khalil Z, Andrews PV, Helme RD: VIP modulates substance P-induced plasma extravasationin vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 151(2): 281–287, 1988
Williams J: Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide is more potent than prostaglandin E2 as a vasodilator and oedema potentiator in rabbit skin. Br J Pharmacol 77:505–509, 1982
Raufman JP, Kasbeker DK, Jensen RT, Gardner JD: Potentiation of pepsinogen secretion from dispersed glands from rat stomach. Am J Physiol 245:G525–530, 1983
Raufman JP, Cosowsky L: Differential actions of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on secretin and vasoactive intestinal peptide-induced increases in chief cell cAMP. Biochim Biophys Acta 970(3):318–323, 1988
Chiba T, Taminato T, Kadowaki S, Abe H, Chihara K, Seino Y, Matsukura S, Fujita T: Effects of glucagon secretin and vasoactive intestinal peptide on gastric somatostatin and gastrin release from isolated perfused rat stomach. Gastroenterology 79:67–71, 1980
Schmid R, Schusdiazirra V, Classen M: Modulatory effect of glucose on VIP-induced gastric somatostatin release. Am J Physiol 254:E756-E759, 1988
Domschke S, Bloom SR, Adrian TE, Lux G, Bryant MG, Domschke W: Gastroduodenal mucosal hormone content in duodenal ulcer disease. Hepatogastroenterology 32:198–201, 1985
Pandal SJ, Dharmsathaphorn K, Schoeffied MS, Vale W, Rivier J: Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor antagonist (4Cl-d-Phe8,Leu17) VIP. Am J Physiol 250:G553-G557, 1986
Goetzl EJ, Chernov T, Reynold F, Payan DG: Neuropeptide regulation of the expression of immediate hypersensitivity. J Immunol 135:802S-805S, 1985
Cutz E, Chan W, Track NS: Release of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in mast cells by histamine liberators. Nature 275:661–662, 1978
Szabo S, Trier JS, Brown A, Schnoor J: Early vascular injury and increased vascular permeability in gastric mucosal injury caused by ethanol in the rat. Gastroenterology 88:228–236, 1985
Karmeli F, Eliakim R, Okon E, Rachmilewitz D: Gastric mucosal damage by ethanol is mediated by substance P and prevented by ketotifen, a mast cell stabilizer. Gastroenterology 100:1206–1216, 1991
Oates PJ, Hakkinen JP: Studies on the mechanism of ethanol-induced gastric damage in rats. Gastroenterology 94:10–21, 1988
Sabhani I, Denizot Y, Bourgeois M, Cheret AM, Leroux S, Mignon M, Lewin MJM: cAMP-independent PAF release by histamine and VIP from human gastric cell line HGT1. Gastroenterology 100:A166, 1991
Hartung HP, Walters K, Toyka KV: Substance P: Binding properties and studies on cellular response in guinea pig macrophages. J Immunol 136:3856–3863, 1986
Vagne M, Konturek SJ, Chayvialle JA: Effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on gastric secretion in the cat. Gastroenterology 83:250–255, 1982
Makhlouf GM, Zfass AM, Said SI, Schebalin M: Effects of synthesis vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), secretin and their partial sequences on gastric secretion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 157:565–568, 1978
Holm-Bentzen M, Christiansen J, Kirkegaard P, Olsen PS, Petersen B, Fahrenkrug J: The effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide on meal-stimulated gastric acid secretion in man. Scand J Gastroenterol 18:659–661, 1983
Schubert ML: The effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide on gastric secretion is predominantly mediated by somatostatin. Gastroenterology 100:1195–1200, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karmeli, F., Eliakim, R., Okon, E. et al. Role of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in pathogenesis of ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. Digest Dis Sci 38, 1210–1219 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296069
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296069