Summary
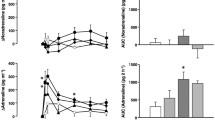
Intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.) administered dopamine (50–400 μg/ kg, 30 min; 400 μg/kg, 2 and 4 h) did not induce statistically significant changes in heart adrenaline (presumed to represent the adrenaline release from the adrenals). Only the highest dose (400 μg/kg, 30 min) brought about significant increase in adrenal dopamine (reflecting the catecholamine synthesis), accompanied by increase in heart dopamine, indicating leakage of dopamine into the peripheral circulation.
The results did not support involvement of the central dopamine receptors in the short-term control of the adrenomedullary function in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlsson M, Carlsson A (1989) Effects of mild stress on adrenal and heart catecholamines in male and female rats. J Neural Transm 77: 217–226
Kujacic M, Carlsson A (1993a) Evidence for an increased catecholamine synthesis in rat adrenal glands following stimulation of peripheral dopamine receptors. J Neural Transm [GenSect] 92: 73–79
Kujacic M, Carlsson A (1993b) Acute effects of dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists on adrenaline levels in the plasma and heart of rat (in preparation)
Kujacic M, Carlsson A (1993c) Influence of GBR 12909 and d-amphetamine on catecholamine synthesis and release in rat adrenal glands (in preparation)
Kujacic M, Svensson K, Löfberg L, Carlsson A (1990) Acute changes in dopamine levels in rat adrenal glands after administration of dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 177: 163–170
Kujacic M, Svensson K, Löfberg L, Carlsson A (1991) Dopamine receptors, controlling dopamine levels in rat adrenal glands — comparison with central dopaminergic auto-receptors. J Neural Transm [GenSect] 84: 195–204
Milliken GA, Johnson DE (1984) Analysis of messy data, vol I. Designed experiments. Lifetime Learning Publications, Belmont, California, p 33
Montastruc J-L, Gaillard G, Rascol O, Tran MA, Montastruc P (1989) Effect of apomorphine on adrenal medullary catecholamine levels. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 3: 665–670
Regunathan S, Missala K, Sourkes TL (1989) Central regulation of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase: effect of induction on catecholamine levels in the adrenal medulla and plasma. J Neurochem 53: 1706–1710
Sourkes TL (1985) Neurotransmitters and central regulation of adrenal functions. Biol Psychiatry 20: 182–191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kujacic, M., Carlsson, A. I. c. v. dopamine fails to alter adrenomedullary function in rats. J. Neural Transmission 95, 235–240 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271569
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271569