Summary
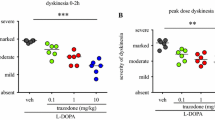
The behavioral effects of L-dopa or cabergoline alone were compared with those of the joint administration of the two drugs in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-lesioned parkinsonian cynomolgus monkeys with attention to the induction of hyperactivity and dyskinesia. Cabergoline alone at 0.2mg/kg or less improved in a dose-dependent fashion the parkinsonism without inducing hyperactivity and dyskinesia following a single subcutaneous injection. L-dopa alone improved the parkinsonism, but induced hyperactivity and dyskinesia, depending on the dose applied. Doses required for 50% amelioration by L-dopa and cabergoline were 10 and 0.038mg/kg, s.c., respectively. With low doses (50%-amelioration doses), cabergoline or L-dopa alone improved the parkinsonism without induction of hyperactivity and dyskinesia, but the duration of action was brief. Cabergoline in combination with L-dopa was highly effective in improving motor disability without induction of hyperactivity and dyskinesia. Moreover, the duration of action was more prolonged with the coadministration than with the single administration of each drug. These findings suggest that the combined therapy with low doses of L-dopa and cabergoline is beneficial for treating patients with advanced Parkinson's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlskog JE, Muenter MD, Maraganore DM, Matsumoto JY, Lieberman A, Wright KF, Wheeler K (1994) Fluctuating Parkinson's disease: treatment with the long-acting dopamine agonist cabergoline. Arch Neurol 51: 1236–1241
Akai T, Ozawa M, Yamaguchi M, Mizuta E, Kuno S (1995) Combination treatment of the partial D2 agonist terguride with the D1 agonist SKF 82958 in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-lesioned parkinsonian cynomolgus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273: 309–314
Arai N, Isaji M, Miyata H, Fukuyama J, Mizuta E, Kuno S(1995) Differential effects of three dopamine receptor agonists in MPTP-treated monkeys. J Neural Transm [P-D Sect] 10: 55–62
Benedetti MS, Dostert P, Barone D, Efthymiopoulos C, Peretti G, Roncucci R (1990) In vivo interaction of cabergoline with rat brain dopamine receptors labelled with [3H]N-n-propylnorapomorphine. Eur J Pharmacol 187: 399–408
Calne DB (1993) Treatment of Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 329: 1021–1027
Clarke CE, Sambrook MA, Mitchell IJ, Crossman AR (1987) Levodopa-induced dyskinesia and response fluctuations in primates rendered parkinsonian with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). J Neurol Sci 78: 273–280
Goodwin FK (1971) Psychiatric side effects of levodopa in man. J Am Med Assoc 218: 1915–1920
Hutton JT, Morris JL, Brewer MA (1993) Controlled study of the antiparkinsonian activity and tolerability of cabergoline. Neurology 43: 613–616
Klawans HL (1988) Psychiatric side-effects during the treatment of Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm 27 [Suppl]: 117–122
Lera G, Vaamonde J, Rodriguez M, Obeso JA (1993) Cabergoline in Parkinson's disease: long-term follow-up. Neurology 43: 2587–2590
Lieberman A, Goldstein M, Leibowitz M, Neophytides A, Kupersmith M, Pact V, Kleinberg D (1981) Treatment of advanced Parkinson's disease with pergolide. Neurology 31: 675–682
Lieberman A, Imke S, Muenter M, Wheeler K, Ahlskog JE, Matsumoto JY, Maraganore DM, Wright KF, Schoenfelder J (1993) Multicenter study of cabergoline, a long-acting dopamine receptor agonist, in Parkinson's disease patients with fluctuating response to levodopa/carbidopa. Neurology 43: 1981–1984
Marsden CD, Parkes JD (1976) “On-off” effects in patients with Parkinson's disease on chronic levodopa therapy. Lancet i: 292–296
Mayeux R, Stern Y, Mulvey K, Cote L (1985) Reappraisal of temporary levodopa withdrawal (“drug holiday”) in Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 313: 724–728
Rinne UK (1985) Combined bromocriptine-levodopa therapy early in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 35: 1196–1198
Steiger MJ, Quinn NP (1992) Levodopa-based therapy. In: Koller WC (ed) Handbook of Parkinson's disease, 2nd ed. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 391–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arai, N., Isaji, M., Kojima, M. et al. Combined effects of cabergoline and L-dopa on parkinsonism in MPTP-treated cynomolgus monkeys. J. Neural Transmission 103, 1307–1316 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271191
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271191