Summary
-
1.
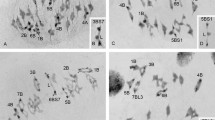
An experiment usingScilla sibirica endosperm with a synchronized mitosis for X-ray breakage studies is described.
-
2.
So-called point error aberrations arise through treatment of prophase. They lead through intercalary and terminal union of chromatids to bridge formation at anaphase.
-
3.
The bridges break mechanically at anaphase to produce fragments. Breakage, however, is seldom at the point of union.
-
4.
After a dose of 54 r and temperature maintained at 18° C point errors appear in anaphases from 2–6 1/4 hours following irradiation. They increase in frequency with time.
-
5.
Point errors are assumed to arise through breakage and reunion of sub-chromatids to give structures resembling meiotic chiasmata.
-
6.
Associations at non-homologous loci arise through coiled and overlapping prophase chromatids. Thus, loop structures occur through intrachromatid union; whilst interchromatid union, between sisters or non-sisters, gives configurations with unequal arms distal to the point of union.
-
7.
There is evidence of interference by the centromere, point errors therefore rarely occur in its vicinity.
-
8.
The interpretation of sub-chromatid breakage in relation to chromosome structure and reproduction is briefly discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avanzi, M. G.: Frequenza e tipi di aberrazioni cromosomiche indotte da alcuni derivati dell'α-naftalene. Caryologia (Pisa)3, 165–180 (1950)
Crouse, H. V.: X-ray breakage of lily chromosomes at first meiotic metaphase. Science (Lancaster, Pa.)119, 485–487 (1954).
D'Amato, F.: The chromosome breaking activity of chemicals as studied by theAllium cepa test. Pubbl. Staz. Zool. Napoli Suppl.22, 1–16 (1950).
—: Further investigations on the mutagenic activity of acridines. Caryologia (Pisa)4, 388–413 (1952).
Darlington, C. D.: The working units of heredity. Hereditas (Lund) Suppl.1949, 189–200.
Darlington, C. D., andP. C. Koller: The chemical breakage of chromosomes. Heredity (Lond.)1, 187–221 (1947).
Darlington, C. D., andL. F. La Cour: Nucleic acid starvation of chromosomes inTrillium. J. Genet.11, 185–213 (1940).
—: Chromosome breakage and the nucleic acid cycle. J. Genet.46, 180–267 (1945).
—: The Handling of Chromosomes. London: Allen & Unwin 1947.
—: The classification of radiation effects at meiosis. Heredity (Lond.) Suppl.6, 41–55 (1952).
Haque, H.: The irradiation of meiosis inTradescantia. Heredity (Lond.) Suppl.6, 57–75 (1952).
La Cour, L. F.: The physiology of chromosome breakage and reunion inHyacinthus. Heredity (Lond.) Suppl.6, 163–179 (1952).
La Cour, L. F., andA. Rutishauser: Chromosome breakage experiments with endosperm: sub-chromatid breakage. Nature (Lond.)172, 501 (1953).
Levan, A.: The influence on chromosomes and mitosis of chemicals, as studied by theAllium test. Proc. 8. Internat. Congr. Genet., Stockholm. Hereditas (Lund) Suppl.1949, 325–333.
Levan, A., andJ. H. Tjio: Induction of chromosome fragmentation by phenols. Hereditas (Lund)34, 453–484 (1948).
Lewis, D., andL. K. Crowe: Theory of revertible mutations. Nature (Lond.)172, 501 (1953).
Marshak, A.: The nature of chromosome division and the duration of the nuclear cycle. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.25, 502–510 (1939).
Nebel, B. R.: Chromosome Structure. XII. Further radiation experiments withTradescantia. Amer. J. Bot.24, 365–372 (1937).
Östergren, G.: Chromosome bridges and breaks by coumarin. Bot. Not. (Lund)4, 376–380 (1948).
Östergren, G., andT. Wakonig: A sensitive period at the chromosome break ng activity of coumarin. Proc. 9. Internat. Congr. Genet. Bellagio (in the press).
Rees, H.: Centromere control of chromosome splitting and breakage. Heredity (Lond.) Suppl.6, 235–245 (1952).
Rutishauser, A., u.H. R. Hunziker: Untersuchungen über die Zytologie des Endosperms. Arch. Klaus-Stiftg25, 477–483 (1950).
Slizynski, B. M.: Partial breakage of salivary gland chromosomes. Genetics35, 279–287 (1950).
Sparrow, A. H.: Radiation sensitivity of cells during mitotic and meiotic cycles with emphasis on possible cytochemical changes. Ann. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.51, 1508–1540 (1951).
Swanson, C. P.: X-ray and ultraviolet studies on pollen tube chromosomes. II. The quadripartite structure of the prophase chromosomes ofTradescantia. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.33, 229–232 (1947).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
La Cour, L.F., Rutishauser, A. X-ray breakage experiments with endosperm I. Sub-chromatid breakage. Chromosoma 6, 696–709 (1953). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01259956
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01259956