Abstract
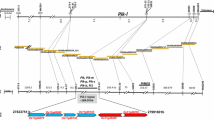
Rice blast, caused byPyricularia grisea, is a major production constraint in many parts of the world. The Korean rice variety Tongil showed high levels of resistance for about six years when widely planted under highly disease-conducive conditions, before becoming susceptible. Tongil was found to carry a single dominant gene, designatedPi-10t, conferring resistance to isolate 106 of the blast pathogen from the Philippines. We report here the use of bulked segregant RAPD analysis for rapid identification of DNA markers linked toPi-10t. Pooled DNA extracts from five homozygous blast-resistant (RR) and five susceptible (rr) BC3F2 plants, derived from a CO39 × Tongil cross, were analyzed by RFLP using 83 polymorphic probes and by RAPD using 468 random oligomers. We identified two RAPD markers linked to thePi-10t locus: RRF6 (3.8 ± 1.2 cM) and RRH18 (2.9 ± 0.9 cM). Linkage of these markers withPi-10t was verified using an F2 population segregating forPi-10t. The two linked RAPD markers mapped 7 cM apart on chromosome 5. Chromosomal regions surrounding thePi-10t gene were examined with additional RFLP markers to define the segment introgressed from the donor genome.Pi-10t is likely to be a new blast-resistance locus, because no other known resistance gene has been mapped on chromosome 5. These tightly linked RAPD markers could facilitate early selection of thePi-10t locus in rice breeding programmes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard RW: Formulas and tables to facilitate the calculation of recombination values in heredity. Hilgardia 24: 235–278 (1956).
Birnboim HC, Doly J: A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucl Acids Res 7: 1513–1525 (1986).
Bonman JM, Vergel de Dios TI, Khin MM: Physiologic specialisation ofPyricularia oryzae in the Philippines. Plant Dis 70: 767–769 (1986).
Bonman JM, Khush GS, Nelson RJ: Breeding rice for resistance to pests. Annu Rev Phytopath 30: 507–528 (1992).
Choi HO, Bae SJ, Chung GS, Cho JY, Heu MH, Beachell HM: A new short statured rice variety ‘Tongil’. Res Rep Off Rural Dev (Crop) 16: 1–12 (1974).
Chung CT, Niemala SL, Miller RH: One-step preparation of competentEscherichia coli: transformation and storage of bacterial cells in the same solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 2172–2175 (1989).
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB: Maize DNA miniprep. In: Molecular Biology of Plants, pp. 36–37. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbour, NY (1985).
Ellingboe AH: Segregation of avirulence/virulence on three rice cultivars in 16 crosses ofMagnaporthe grisea. Phytopathology 82: 597–601 (1992).
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B: A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132: 6–13 (1984).
Fischer M, Azpiroz S, Hoisington D: Comparison of RFLP and RAPD technologies for analysing genetic diversity in open-pollinated maize varieties. In: Hallick RB (ed) Program and Abstracts, Third International Congress of Plant Molecular Biology, Molecular Biology of Plant Growth and Development, Tucson, AZ (1991).
Flor HH: Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu Rev Phytopath 9: 275–296 (1971).
Kiyosawa S: Genetics of blast resistance. In: Rice Breeding, pp. 203–225. International Rice Research Institute, P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines (1972).
Kiyosawa S, Cho CI: Identification of blast resistance genes in Korean rice variety, Tongil. Japan J Breed 30: 73–82 (1980).
Kiyosawa S: Gene analysis for blast resistance. Oryza 18: 196–203 (1981).
Kosambi DD: The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12: 172–175 (1944).
Kozaka T: The nature of the blast fungus and varietal resistance in Japan. In: Proceedings of the Rice Blast Workshop, pp. 3–25. International Rice Research Institute, P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines (1979).
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newberg L: MAPMAKER: An interactive computer program for constructing primary genetic maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1: 174–181 (1987).
Lee EJ, Cho SY: Variation in races of rice blast disease and varietal resistance in Korea. Proceedings of the IRRC (1990).
Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Suh HS, Srilingam R: Genes for resistance to Philippine isolates of the rice blast pathogen. Rice Genet Newsl 2: 80–81 (1985).
Mackill DJ, Bonman JM: Inheritance of blast resistance in near-isogenic lines of rice. Phytopathology 82: 746–749 (1992).
Martin GB, Williams JGK, Tanksley SD: Rapid identification of markers linked to aPseudomonas resistance gene in tomato by using random primers and nearly isogenic lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 2336–2340 (1991).
Martin GB, Brommonschenkel SH, Chunwongse J, Frary A, Ganal MW, Spivey R, Wu T, Earle ED, Tanksley SD: Map-based cloning of a Protein Kinase gene conferring disease resistance in plants. Science 262: 1432–1436 (1993).
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD: Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76: 815–829 (1988).
Mendenhall W, Scheaffer RL: Mathematical Statistics with Applications, pp. 63–67. Duxbury Press, UK (1973).
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV: Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 9828–9832 (1991).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: In: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Tai TH, Tanksley SD: A rapid and inexpensive method for isolation of total DNA from dehydrated plant tissue. Plant Mol Biol Rep 8: 297–303 (1990).
Tanksley SD: Pooled sample mapping: a rapid method for determining the order of tightly linked DNA markers relative to a target gene with a visible phenotype. Tomato Genet Coop 41: 59 (1991).
Tohme J, Montenegro M, Correa F, Martinez C, Zeigler RS, Roca W: Tagging resistance genes to Rice Hoja Blanca Virus and Colombia isolates of rice blast with RFLP and RAPD markers. (Abstract.) Fifth Annual Meeting of the Rockefeller Foundation's International Program on Rice Biotechnology, Tucson, AZ, p. 5 (1991).
Valent B, Farrall L, Chumley FG:Magnaporthe grisea genes for pathogenicity and virulence identified through a series of backcrosses. Genetics 127: 87–101 (1991).
Wang GL, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, McCouch SR, Champoux MC, Nelson RJ: RFLP mapping of genes conferring complete and partial resistance to blast in a durably resistant rice cultivar. Genetics 136: 1421–1434 (1994).
Welsh J, McClelland M: Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucl Acids Res 24: 7213–7218 (1990).
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV: DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl Acids Res 18: 6531–6535 (1990).
Yu ZH, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM: Inheritance of resistance to blast in some traditional and improved rice cultivars. Phytopathology 77: 323–326 (1987).
Yu ZH, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Tanksley SD: Tagging genes for blast resistance in rice via linkage to RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 81: 471–476 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naqvi, N.I., Bonman, J.M., Mackill, D.J. et al. Identification of RAPD markers linked to a major blast resistance gene in rice. Mol Breeding 1, 341–348 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01248411
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01248411