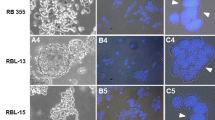
Abstract
Establishment of new tumor cell lines is an important first step for biological studies of tumor cells. High success rates in establishing retinoblastoma cell lines have been reported when feeder-layer culture but not liquid-culture techniques were used. Liquid culture is, however, essential for studies in which feeder-layer cells are undesirable. In a previous study, we formulated a medium (RB−− medium), the components of which were almost identical to those of a soft-agar medium developed for colony formation of established retinoblastoma cell lines, in which one cell line from 12 primary retinoblastoma specimens was established. In this study, another medium (RB++ medium), RB−− medium to which 20 μM 2-mercaptoethanol and 375 μM asparagine were added, was tested for its ability to grow retinoblastoma cells from clinical specimens. In the RB++ medium, 6 cell lines from 16 primary sites, 2 from 2 intraocular-recurrent and 3 from 3 metastatic retinoblastomas grew for over a year. The major reason for the apparent improvement of the RB++ medium on the RB−− medium was demonstrated to be the addition of 2-mercaptoethanol.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Rb:
-
retinoblastoma
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- HTCA:
-
human tumor clonogenic assay
- 2ME:
-
2-mercaptoethanol
References
Bogenmann E, Mark C (1983) Routine growth and differentiation of primary retinoblastoma cells in culture. J Natl Cancer Inst 70:95–104
Broome JD, Jeng MW (1973) Promotion of replication in lymphoid cells by specific thiols and disulfides in vitro. J Exp Med 138:574–592
Campbell M, Chader GJ (1988) Retinoblastoma cells in tissue culture. Opththalmic Paediatr Genet 9:171–199
Epstein AL, Kaplan HS (1979) Feeder layer and nutritional requirements for the establishment and cloning of human malignant lymphoma cell lines. Cancer Res 39:1748–1759
Gallie BL, Holmes W, Philipps RA (1982) Reproducible growth in tissue culture of retinoblastoma tumor specimens. Cancer Res 42:301–305
Griegel S, Hong C, Frötschl R, Hülser DF, Greger V, Horsthemke B, Rajewsky MF (1990) Newly established human retinoblastoma cell lines exhibit an “immortalized” but not an invasive phenotypein vitro. Int J Cancer 46:125–132
Hamburger AW, Salmon SE (1971) Primary bioassay of human tumor stem cells. Science 197:461–463
Inomata M, Kaneko A (1987) Chemosensitivity profiles of primary and cultured human retinoblastoma cells in a human tumor clonogenic assay. Jpn J Cancer Res 78:858–868
Inomata M, Kaneko A, Hoshi A (1986) Improved colony formation of cultured retinoblastoma cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 27:1423–1428
Inomata M, Sasaki SM, Hirota T, Itabashi M, Tsumuraya M, Kaneko A, Hoshi A, Koyama Y, Saijo N (1991) Establishment of a human retinoblastoma cell line: NCC-RbC-39. Cancer J 4:18–23
Ishii T, Bannai S, Sugita Y (1981 a) Mechanism of growth stimulation of L1210 cells by 2-mercaptoethanolin vitro. Role of the mixed disulfide of 2-mercaptoethanol and cysteine. J Biol Chem 256:12387–12392
Ishii T, Hishinuma I, Bannai S, Sugita Y (1981 b) Mechanism of growth promotion of mouse lymphoma L1210 cellsin vitro by feeder layer or 2-mercaptoethanol. J Cell Physiol 107:283–293
Knudson AG Jr (1971) Mutation and cancer. Statistical study of retinoblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 68:820–823
McFall RC, Sery TW, Makadon M (1977) Characterization of a new continuous cell line derived from a human retinoblastoma. Cancer Res 37:1003–1010
Pavelic K (1985)l-Ascorbic acid-induced DNA strand breaks and cross links in human neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res 342:369–373
Reid TW, Albert DM, Rabson AS, Russell P, Craft J, Chu EW, Tralka TS, Wilcox JL (1974) Characteristics of an established cell line of retinoblastoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 53:347–360
Weinberg RA (1991) Tumor supressor genes. Science 254:1138–1160
White L (1991) Chemotherapy in retinoblastoma: current status and future directions. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 13:189–201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported in part by a grant-in-aid for cancer research from the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Japan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inomata, M., Kaneko, A., Saijo, N. et al. Culture of retinoblastoma cells from clinical specimens: growth-promoting effect of 2-Mercaptoethanol. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 120, 149–155 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01202193
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01202193