Abstract
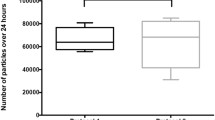
Migration of particulate matter from plastic tubing and solid plastic implants has been documented in a number of studies, including some with the use of cardiac bypass, haemodialysis, and pump-assisted intravenous infusions. In order to ascertain whether silicone embolisation occurs when children have an Ivac 560 pump-assisted IV infusion, we passed 180 ml of pumped fluid through a microfilter and compared the scanning electron micrographs of those filters with unused filters and with others through which a similar volume had been passed without using the pump. The particles on the filters were analysed for their elemental content using energy-dispersive X-ray analysis. In addition, the appearance of the silicone tubing used in the pump over 3 and 72 h was assessed and compared to that of flow-only and unused tubing. More particles were found on the microfilter when fluid had been delivered via the pump than on those through which nonpumped fluid had passed or that were unused. Elemental silicon-containing particles were only found on the filter when a pump had been attached to the IV line. The flow-only and unused tubing were found to have adherent particles on the inner surface that were not seen once the tubing had been used for 3 h in the Ivac 560 pump. Also, after 72 h use, the silicone tubing had a deformed inner layer. The clinical significance of these findings is yet to be determined, but it does appear that silicone embolisation occurs during pump-assisted infusions in children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaronson IA, Rames RA, Greene WB, Walsh LG, Hasal UA, Garen PD (1993) Endoscopic treatment of reflux: migration of teflon to the lungs and brain. Eur Urol 23: 394–399
Barrett DM, O'Sullivan DC, Malizia AA, Reiman HM, Abell-Aleff PC (1991) Particle shedding and migration from silicone genitourinary prosthetic devices. J Urol 146: 319–322
Ben-Hur N, Ballantyne DL Jr, Rees TD, Seidman I (1967) Local and systemic effects of dimethylpolysiloxane fluid in mice. Plast Reconstr Surg 39: 423–426
Benjamin E, Ahmed A, Rashid AT, Wright DH (1982) Silicone lymphadenopathy: a report of two cases, one with concomitant malignant lymphoma. Diag Histopath 5: 133–141
Boedts D, Roels H, Kluyskens P (1967) Laryngeal tissue responses to Teflon. Arch Otolaryngol 86: 562–567
Bommer J, Ritz E, Waldherr R (1981) Silicone-induced splenomegaly: treatment of pancytopenia by splenectomy in a patient on hemodialysis. New Engl J M 305: 1077–1079
Boretos JW, Wagner FR (1971) Particle fragmentation generated in pump sets. J Biomed Mater Res 5: 411–412
Bowen JH, Woodard BH, Barton TK, Ingram P, Shelburne JD (1981) Infantile pulmonary hypertension associated with foreign body vasculitis. Am J Clin Pathol 75: 609–614
Chena Y-M, Lu C-C, Perng R-P (1993) Silicone fluid-induced pulmonary embolism. Am Rev Respir Dis 147: 1299–1302
Christie AJ, Weinberger KA, Dietrich M (1977) Silicone lymphadenopathy and synovitis. Complications of silicone elastomer finger joint prostheses. JAMA 237: 1463–1464
Claes H, Stroobants D, Van Meerbeek J, Verbeken E, Knockaert D, Baert L (1989) Pulmonary migration following periurethral polytetrafluoroethylene injection for urinary incontinence. J Urol 142: 821–822
Dewan PA, Byard RW (1994) Histological response to injected Polytef and Bioplastique in a rat model. Br J Urol 73: 370–376
Dewan PA, Fraundorfer M (1995) Skin migration following periurethral polytetrafluoroethylene for urinary incontinence. Aust NZ J Surg 65: 884–886
Dewan PA, Owen AJ, Byard RW (1995) Histological response to injected Polytef and Bioplastique in the sheep brain. Br J Urol 75: 666–669
Dewan PA, Owen AJ, Byard RW (1995) Long-term histological response to subcutaneously injected Polytef and Bioplastique in a rat model. Br J Urol 76: 161–164
Dewan PA, Stefanek W, Byard RW (1995) Long-term response to intravenously injected Teflon and Silicone in a rat model. Pediatr Surg Int 10: 129–133
Digby JM (1982) Malignant lymphoma with intranodal silicone rubber particles following metacarpophalangeal arthroplasty. J Hand Surg 14: 326–328
Digby JM, Wells AL (1981) Malignant lymphoma with intranodal refractile particles after insertion of silicone prosthesis (letter). Lancet II: 580
Ellenbogen R, Ellenbogen R, Rubin L (1975) Injectable fluid silicone therapy: human morbidity and mortality. JAMA 234: 308–309
Groff GD, Schned AR, Taylor TH (1981) Silicone induced adenopathy eight years after metacarpophalangeal arthroplasty. Arthritis Rheum 24: 1578–1581
Kircher T (1980) Silicone lymphadenopathy. A complication of silicone elastomer finger joint prostheses. Hum Pathol 11: 240–244
Kossovsky N, Cole P, Zackson DA (1990) Giant cell myocarditis associated with silicone. An unusual case of biomaterials pathology discovered at autopsy using X-ray energy spectroscopy. Am J Clin Pathol 93: 148–152
Kurusz M, Christman EW, Williams EH, Tyers GFO (1980) Roller pump induced tubing wear: another argument in favour of arterial line filtration. J Extracorp Tech 12: 49–59
Leong AS-Y (1983) Pathological findings in silicone spallation in vitro studies. Pathology 15: 189–192
Leong AS-Y, Disney APS, Gove DW (1982) Spallation and migration of silicone from blood-pump tubing in patients on hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 306: 135–140
Malizia AA, Reiman HM, Myers RP, Sande JR, Barham SS, Benson RC, Dewanjee MK, Utz WJ (1984) Migration and granulomatous reaction after periurethral injection of Polytef (Teflon). JAMA 251: 3277–3281
Mittleman RE, Marraccini JV (1983) Pulmonary Teflon granulomas following periurethral Teflon injection for urinary incontinence. Arch Pathol Lab Med 107: 611–612
Miyakita H, Puri P (1994) Particles found in lung and brain following subureteral injection of polytetrafluoroethylene paste are not teflon particles. J Urol 152: 636–640
Murakata LA, Rangwala AF (1989) Silicone lymphadenopathy with concomitant malignant lymphoma. J Rheumatol 16: 1480–1483
Rees TD, Ballantyne DL Jr, Seidman I, Hawthorne GA (1967) Visceral response to subcutaneous and intraperitoneal injections of silicone in mice. Plast Reconstr Surg 39: 402–410
Reinberg Y, Manivel JC, Gonzalez R (1993) Silicone shedding from artificial urinary sphincter in children. J Urol 150: 694–696
Rodriquez MA, Martinez MC, Lopez-Artiguez M, Soria ML, Bernier F, Repetto M (1989) Lung embolism with liquid silicone. J Forensic Sci 34: 504–510
Savage P, Geiss S, Saussine C, Laustrait S, Becmur F, Bientz J, Christmann D, Roy E, Marcellin L (1990) Analysis and perspectives of endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux in children with a 20-month follow-up. Eur Urol 17: 310–313
Tabatowski K, Elson CE, Johnston WW (1990) Silicone lymphadenopathy in a patient with a mammary prosthesis. Fine needle aspiration cytology, histology and analytical electron microscopy. Acta Cytol 34: 10–14
Van Wagenen R, Coleman DL, Andrade JD (1975) Adsorbent hemoperfusion: non-biological particulate matter. Kidney Int 7 (Suppl): 397–400
Vandenbossche M, Delhove O, Dumortier P, Deneft F, Schulman CC (1993) Endoscopic treatment of reflux: experimental study and review of Teflon and collagen. Eur Urol 23: 386–393
Weingarten J, Kauffman SL (1977) Teflon embolization to pulmonary arteries. Ann Thor Surg 23: 371–373
Williams IM, Stephens JF, Richardson EP Jr, Stirling G (1991) Brain and retinal microemboli during cardiac surgery. Ann Neurol 30: 736–737
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dewan, P.A., Owen, A.J., Ashwood, P.J. et al. An in vitro study of silicone migration from intravenous fluid tubing. Pediatr Surg Int 12, 49–53 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01194802
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01194802