Summary
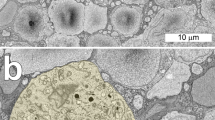
An axonless horizontal cell (AHC) of the rabbit retina was penetrated with a microelectrode and stained with horseradish peroxidase after recording its light responses. The cell was then serially sectioned and its connections examined with the electron microscope. Physiologically, the cell exhibited cone-dominated responses and a minor rod influence known as rod aftereffect. Electron microscopy showed that this AHC was only connected to cones. Therefore, the rod aftereffect could only invade the cell through the gap junctions between the synaptic endings of rod and cone photoreceptors. In the synaptic invaginations of the cone pedicles contacting the cell, only one of the lateral elements was stained. This suggests that the two lateral elements of each cone-invaginating synapse belong to two different horizontal cells. By staining intracellularly adjacent AHCs, we showed that the two lateral processes may originate from two horizontal cells belonging to the same morphological type.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J. C. (1977) Technical considerations on the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker.Neuroscience 2, 141–5.
Dacheux, R. F. &Raviola, E. (1982) Horizontal cells in the retina of the rabbit.Journal of Neuroscience 2, 1486–93.
Dacheux, R. F. &Raviola, E. (1986) The rod pathway in the rabbit retina: a depolarizing bipolar and amacrine cell.Journal of Neuroscience 6, 331–45.
Karnovsky, M. J. (1971) Use of ferrocyanide-reduced osmium tetroxide in electron microscopy. InProceedings of the 11th Annual Meeting of the American Society for Cell Biology 146A. New Orleans.
Kolb, H. (1974) The connections between horizontal cells and photoreceptors in the retina of the cat: electron microscopy of Golgi preparations.Journal of Comparative Neurology 155, 1–14.
Kolb, H. &Famiglietti, E. V. Jr (1976) Rod and cone pathways in the retina of the cat.Investigative Ophthalmology 15, 935–45.
Nelson, R. (1977) Cat cones have rod input: a comparison of the response properties of cones and horizontal cell bodies in the retina of the cat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 172, 109–36.
Nelson, R. &Kolb, H. (1983) Synaptic patterns and response properties of bipolar and ganglion cells in the cat retina.Vision Research 23, 1183–95.
Nelson, R., Kolb, H., Famiglietti, E. V. Jr &Gouras, P. (1976) Neural responses in the rod and cone systems of the cat retina: intracellular records and procion stains.Investigative Ophthalmology 15, 946–53.
Raviola, E. &Dacheux, R. F. (1983) Variations in structure and response properties of horizontal cells in the retina of the rabbit.Vision Research 23, 1221–7.
Raviola, E. &Gilula, N. B. (1973) Gap junctions between photoreceptor cells in the vertebrate retina.Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (USA) 70, 1677–81.
Raviola, E. &Gilula, N. B. (1975) Intramembrane organization of specialized contacts in the outer plexiform layer of the retina. A freeze-fracture study in monkeys and rabbits.Journal of Cell Biology 65, 192–222.
Raviola, E. &Raviola, G. (1982) Structure of the synaptic membranes in the inner plexiform layer of the retina: a freeze-fracture study in monkeys and rabbits.Journal of Comparative Neurology 209, 233–48.
Smith, R. G., Freed, M. A. &Sterling, P. (1986) Microcircuitry of the dark-adapted cat retina: functional architecture of the rod-cone network.Journal of Neuroscience 6, 3505–17.
Steinberg, R. H. (1969a) Rod and cone contributions to S-potentials from the cat retina.Vision Research 9, 1319–29.
Steinberg, R. H. (1969b) Rod-cone interaction in S- potentials from the cat retina.Vision Research 9, 1331–44.
Steinberg, R. H. (1969c) The rod after-effect in S-potentials from the cat retina.Vision Research 9, 1345–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raviola, E., Dacheux, R.F. Axonless horizontal cells of the rabbit retina: synaptic connections and origin of the rod aftereffect. J Neurocytol 19, 731–736 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01188041
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01188041