Summary
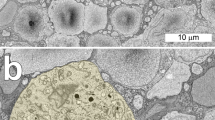
A Golgi-stained flat diffuse cone bipolar cell from a vervet monkey's retina (Cercopithecus aethiops), contacting six cones, was serially sectioned for electron microscopy (EM) to determine the types of synapses it made with the cone pedicles. All the synapses were basal (flat) contacts. Their distribution and ultrastructural type were similar at each pedicle. Approximately half the synapses were definable as triad-associated and the rest were elsewhere on the cone pedicle base. Their ultrastructure is the same regardless of those positions. About 25 synapses were made with each cone. Thus this type (DB2 of Boycott & Wässle, 1991) of flat diffuse cone bipolar cell is in contact with six cones through about 150 synapses. At the eccentricity studied each cone pedicle probably makes 90–100 basal synapses with between three and four DB2 bipolar cells. This is between two and three times the number that are made with all the types of invaginating bipolar cells. A brief review of cone photoreceptor synapses with bipolar cells shows that, for those so far examined in the primate retina, the dichotomy into two types of bipolar cell invaginating (ribbon-related), with axons ending in the b-layer of the inner plexiform layer (IPL) (hence presumptive On-bipolars) and flat (basal synapses), with axons ending in the a-layer of the inner plexiform layer (hence presumptive Off-bipolars) is the rule. But other vertebrate retinae, including that of the cat, also have bipolar cells which vary from this pattern.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balkema, G. W. (1991) A synaptic antigen (B16) is localized in retinal synaptic ribbons.Journal of Comparative Neurology 312, 573–83.
Boycott, B. B. &Dowling, J. E. (1969) Organization of the primate retina: light microscopy.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London (Biology) 255, 109–94.
Boycott, B. B. &Kolb, H. (1973) The connections between bipolar cells and photoreceptors in the retina of the domestic cat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 148, 91–114.
Boycott, B. B. &Hopkins, J. M. (1981) Microglia in the retina of monkey and other mammals; its distinction from other types of glia and horizontal cells.Neuroscience 6, 679–88.
Boycott, B. B., Hopkins, J. M. &Sperling, H. G. (1987) Cone connections of the horizontal cells of the rhesus monkey's retina.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London (Biology) 229, 345–79.
Boycott, B. B. &Hopkins, J. M. (1991) Cone bipolar cells and cone synapses in the primate retina.Visual Neuroscience 7, 49–60.
Boycott, B. B. &Wässle, H. (1991) Morphological classification of bipolar cells of the primate retina.European Journal of Neuroscience 3, 1069–88.
Cohen, E. &Sterling, P. (1990) Demonstration of cell types among cone bipolar neurons of cat retina.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B (London) 330, 305–21.
Cohen, E. &Sterling, P. (1991) Microcircuitry related to the receptive field center of the On-Beta ganglion cell.Journal of Neurophysiology 65, 352–9.
Dacheux, R. F. (1982) Connections of the small bipolar cells with the photoreceptors in the turtle. An electron microscope study of Golgi-impregnated, gold-toned retinas.Journal of Comparative Neurology 205, 55–62.
Dacheux, R. F. &Raviola, E. (1986) The rod pathway in the rabbit retina: a depolarizing bipolar and amacrine cell.Journal of Neuroscience 6, 331–45.
Dacheux, R. F. &Raviola, E. (1990) Physiology of H1 horizontal cells in primate retina.Proceeding of the Royal Society B (London) 239, 213–30.
Dolan, R. P. &Schiller, P. H. (1989) Evidence for only depolarising rod bipolar cells in the primate retina.Visual Neuroscience 2, 421–4.
Dowling, J. E. (1987)The Retina, an Approachable Part of the Brain. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
Dowling, J. E. &Boycott, B. B. (1966) Organisation of the primate retina: electron microscopy.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London (Biology) 166, 80–111.
Dowling, J. E., Brown, J. E. &Major, D. (1966) Synapses of horizontal cells in rabbit and cat retinas.Science 153, 1639–41.
Famiglietti, E. V. &Kolb, H. (1976) Structural basis for ON- and OFF-center responses in retinal ganglion cells.Science 194, 193–5.
Famiglietti, E. V., Kaneko, A. &Tachibana, M. (1977) Neuronal architecture of on and off pathways to ganglion cells in carp retina.Science 198, 1267–9.
Famiglietti, E. V. (1981) Functional architecture of cone bipolar cells in mammalian retina.Vision Research 21, 1559–63.
Fisher, S. K. &Boycott, B. B. (1974) Synaptic connexions made by horizontal cells within the outer plexiform layer of the retina of the cat and the rabbit.Proceedings of the Royal Society London (Biology) 186, 317–31.
Gray, E. G. &Guillery, R. W. (1966) Synaptic morphology in the normal and degenerating nervous system.International Review of Cytology 19, 111–82.
Gray, E. G. &Pease, H. L. (1971) On understanding the organisation of the retinal receptor synapses.Brain Research 35, 1–15.
Gray, E. G. (1974) Synaptic morphology with special reference to microneurons. InEssays on the Nervous System (edited byBellairs, R. &Gray, E. G.). Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Greengard, P., Valtorta, F., Czernik, A. J. &Benfenati, F. (1993) Synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins and regulation of synaptic function.Science 259, 780–5.
Grünert, U. &Wässle, H. (1990) GABA-like immunoreactivity in the macaque monkey retina: a light and electron microscope study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 297, 509–24.
Grünert, U. &Martin, P. R. (1991) Rod bipolar cells in the macaque monkey retina: immunoreactivity and connectivity.Journal of Neuroscience 11, 2742–58.
Hare, W. A., Lowe, J. S. &Owen, G. (1986) Morphology of physiologically identified bipolar cells in the retina of the tiger salamander,Ambystoma tigrinum.Journal of Comparative Neurology 252, 130–8.
Hopkins, J. M. &Boycott, B. B. (1992) Synaptic contacts of a two cone flat bipolar cell in a primate retina.Visual Neuroscience 8, 379–84.
Kim, H. G. &Miller, R. F. (1993) Properties of synaptic transmission from photoreceptors to bipolar cells in mud puppy retina.Journal of Neurophysiology 69, 352–360.
Klug, K., Tsukamoto, Y., Sterling, P. &Schein, S. J. (1993) Blue cone off-midget ganglion cells in macaque.Investigative Ophthalmology Visual Science 34 ARVO. Abstract, 1398.
Kolb, H. (1970) Organization of the outer plexiform layer of the primate retina: electron microscopy of Golgi-impregnated cells.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London (Biology) 258, 261–83.
Kolb, H. &Nelson, R. (1984) Neural architecture of the cat retina.Progress in Retinal Research 21–60.
Kolb, H., Wang, H. H. &Jones, J. (1986) Cone synapses with Golgi-stained bipolar cells that are morphologically similar to a center-hyperpolarising and a center-depolarising bipolar cell type in the turtle retina.Journal of Comparative Neurology 250, 510–20.
Kolb, H., Linberg, K. A. &Fisher, S. K. (1992) Neurons of the human retina: a Golgi study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 318, 147–87.
Kouyama, N. &Marshak, D. (1992) Bipolar cells specific for blue cones in macaque retina.Journal of Neuroscience 12, 1233–52.
Lasansky, A. (1972) Cell junctions at the outer synaptic layer of the retina.Investigative Ophthalmology 11, 265–74.
Lasansky, A. (1978) Contacts between receptors and electrophysiologically identified neurones in the retina of the larval tiger salamander.Journal of Physiology 285, 531–42.
Linberg, K. A. &Fisher, S. K. (1986) An ultrastructural study of interplexiform cell synapses in the human retina.Journal of Comparative Neurology 243, 561–76.
Linberg, K. A. &Fisher, S. K. (1988) Ultrastructural evidence that horizontal cell axon terminals are presynaptic in the human retina.Journal of Comparative Neurology 268, 281–97.
Mandell, J. W., Townes-anderson, E., Czernik, A. J., Cameron, R., Greengard, P. &De Camilli, P. (1990) Synapsins in the vertebrate retina: absence from ribbon synapses and heterogeneous distribution among conventional synapses.Neuron 5, 19–33.
Marchiafava, P. L. &Weiler, R. (1980) Intracellular analysis and structural correlates of the organization of inputs to ganglion cells in the retina of the turtle.Proceedings of the Royal Society (Biology) 208, 103–13.
Mariani, A. P. (1981) A diffuse, invaginating cone bipolar cell in primate retina.Journal of Comparative Neurology 197, 661–71.
Mariani, A. P. (1984a) The neuronal organization of the outer plexiform layer of the primate retina.International Review of Cytology 86, 285–320.
Mariani, A. P. (1984b) Bipolar cells in monkey retina selective for the cones likely to be blue-sensitive.Nature 308, 184–6.
Marshak, D. W., Aldrich, L. B., Del Valle, J. &Yamada, T. (1990) Localization of immunoreactive cholecystokinin precursor to amacrine cells and bipolar cells of the macaque monkey retina.Journal of Neuroscience 10, 3045–55.
Massey, S. C. &Redburn, D. A. (1987) Transmitter circuits in the vertebrate retina.Progress in Neurobiology 28, 55–96.
Martin, P. R. &Grünert, U. (1992) Spatial density and immunoreactivity of bipolar cells in the macaque monkey retina.Journal of Comparative Neurology 323, 269–87.
Mcguire, B. A., Stevens, J. K. &Sterling, P. (1984) Microcircuitry of bipolar cells in cat retina.Journal of Neuroscience 4, 2920–38.
McGuire, B. A., Stevens, J. K. &Sterling, P. (1986) Microcircuitry of Beta ganglion cells in cat retina.Journal of Neuroscience 6, 907–18.
Meinertzhagen, I. A. (1993) The synaptic populations in the fly's optic neuropil and their dynamic regulation: parallels with the vertebrate retina.Progress in Retinal Research 12, 13–39.
Merighi, A., Dacheux, R. F. &Raviola, E. (1993) Synaptic connections between cones and DAP1-labeled bipolar cells in rabbit retina.Investigative Ophthalmology Visual Science 34 ARVO abstract, 1385.
Milam, A. H., Dacey, D. M. &Dizhoor, A. M. (1993) Recoverin immunoreactivity in mammalian cone bipolar cells.Visual Neuroscience 10, 1–12.
Miller, R. F. &Slaughter, M. M. (1986) Excitatory amino acid receptors of the retina: diversity of subtypes and conductance mechanisms.Trends in Neurosciences 9, 211–18.
Missotten, L., Appelmans, M. &Michiels, J. (1963) L'ultra-structure des synapses des cellules visuelles de la rétine humaine.Bulletins et Memories de la Société Française d'Ophthalmologie 76, 59–82.
Missotten, L. (1965)The Ultrastructure of the Human Retina. Brussels: Arscia. Uitgaven N. V.
Mollon, J. D. &Bowmaker, J. K. (1992) The spatial arrangement of cones in the primate fovea.Nature 360, 677–9.
Nelson, R., Famiglietti, E. V. &Kolb, H. (1978) Intracellular staining reveals different levels of stratification for On- and Off-center ganglion cells in cat retina.Journal of Neurophysiology 41, 472–83.
Nelson, R. &Kolb, H. (1983) Synaptic patterns and response properties of bipolar and ganglion cells in the cat retina.Vision Research,23, 1183–95.
Polyak, S. L. (1941)The Retina. Chicago: University Press.
Raviola, G. &Raviola, E. (1967) Light and electron microscopic observations on the inner plexiform layer of the rabbit retina.American Journal of Anatomy 120, 403–26.
Raviola, E. &Gilula, N. B. (1975) Intramembraneorganization of specialised contacts in the outer plexiform layer of the retina.Journal of Cell Biology 65, 192–222.
Rodieck, R. W. (1988) The Primate Retina. InComparative Primate Biology 4, Neurosciences (edited bySteklis, H. D.) pp. 203–78. New York: Alan Liss.
Saito, T., Kujiraoka, T., Yonaka, T. &Chino, Y. (1985) Re-examination of photoreceptor-bipolar connectivity patterns in carp retina: HRP-EM and Golgi-EM studies.Journal of Comparative Neurology 236, 141–60.
Saito, T. (1987) Physiological and morphological differences between on- and off-center bipolar cells in the vertebrate retina.Vision Research 27, 135–42.
Schaeffer, S. F., Raviola, E. &Heuser, J. E. (1982) Membrane specializations in the outer plexiform layer of the turtle retina.Journal of Comparative Neurology 204, 253–67.
Schwartz, E. A. (1987) Depolarization without Calcium can release γ-Aminobutyric acid from a retinal neuron.Science 238, 350–5.
Smiley, J. F. &Yazulla, S. (1990) Glycinergic contacts in the outer plexiform layer of theXenopus laevis retina characterised by antibodies to glycine, GABA and glycine receptors.Journal of Comparative Neurology 299, 375–88.
Stell, W. K. (1972) The morphological organization of the vertebrate retina. InPhysiology of Photoreceptor Organs Handbook of Sensory Physiology. Vol. VII No. 2. (edited byFuortes, M. G. F.) pp. 111–213. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Stell, W. K., Ishida, A. T. &Lightfoot, D. O. (1977) Structural basis for On- and Off-center responses in retinal bipolar cells.Science 198, 1269–71.
Sterling, P. (1990) Retina. InThe Synaptic Organisation of the Brain, 3rd ed. (edited byShepherd, G. M.) pp. 170–213. New York: Oxford University Press.
Wagner, H. -J. (1990) Retinal structure of fishes. InThe Visual System of Fish (edited byDouglas, R. &Djamgoz, M. B. A.) London: Chapman & Hall.
Wässle, H. &Boycott, B. B. (1991) Functional architecture of the mammalian retina.Physiological Reviews 71, 447–80.
West, R. W. (1978) Bipolar and horizontal cells of the gray squirrel retina: Golgi morphology and receptor connections.Vision Research 18, 129–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boycott, B.B., Hopkins, J.M. Cone synapses of a flat diffuse cone bipolar cell in the primate retina. J Neurocytol 22, 765–778 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01181322
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01181322