Summary
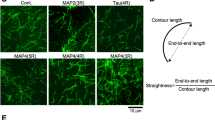
Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) are prominent components of the neuronal cytoskeleton that can promote microtubule formation and whose expression is under strong developmental regulation. They are thought to be involved in organizing the structure of microtubule fascicles in axons and dendrites, although whether they form active cross-links between microtubules or serve as strut-like spacer elements has yet to be resolved. In the experiments reported here we explored their influence on microtubules by expressing them in non-neuronal cells using DNA transfection techniques. We confirm earlier reports that microtubule-associated proteins of the MAP2/tau class can induce bundling of microtubules. In addition we find that MAP2 causes the rearrangement of microtubules in the cytoplasm in a manner that is dependent on the length of the microtubule bundles. Short bundles are straight and run across the cytoplasm whereas long bundles form a marginal band-like array at the periphery. We suggest that the latter arrangement is produced when microtubule bundles that are too long to fit inside the diameter of the cell bend under the restraining influence of the cortical cytoskeleton. In confirmation of this, we show that when the cortical actin network is depolymerized by cytochalasin B the MAP2-containing microtubule bundles push out cylindrical extensions from the cell surface. These results suggest that the induction of stiff microtubules bundles by MAP2, coupled with a breach in the cortical actin network, can confer two of the properties characteristic of neuronal processes; their cylindrical form and the presence of fasciculated microtubules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizawa, H., Emori, Y., Mori, A., Murofushi, H., Sakai, H. &Suzuki, K. (1991) Functional analyses of the domain structure of microtubule-associated protein-4 (MAP-U).Journal of Biological Chemistry 266, 9841–6.
Bernhardt, R. &Matus, A. (1984) Light and electron microscopic studies of the distribution of microtubule-associated protein 2 in rat brain: a difference between dendritic and axonal cytoskeletons.Journal of Comparative Neurology 226, 203–21.
Bray, D., Thomas, C. &Shaw, G. (1978) Growth cone formation in cultures of sensory neurons.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 75, 5226–9.
Brion, J. P., Guilleminot, J., Couchie, D., FlamentDurand, J. &Nunez, J. (1988) Both adult and juvenile tau microtubule-associated proteins are axon specific in the developing and adult rat cerebellum.Neuroscience 25, 139–46.
Brown, P. A. &Berlin, R. D. (1985) Packing volume of sedimented microtubules: regulation and potential relationship to an intracellular matrix.Journal of Cell Biology 101, 1492–1500.
Burgoyne, R. D. (1986) Microtubule proteins in neuronal differentiation.Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology (B) 83, 1–8.
Centonze, V. E., Ruben, G. C. &Sloboda, R. D. (1986) Structure and composition of the cytoskeleton of nucleated erythrocytes: III organization of the cytoskeleton of bufo marinus erythrocytes as revealed by freeze-dried platinum-carbon replicas and immunofluorescence microscopy.Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 6, 376–88.
Chapin, S. J., Bulinski, J. C. &Gundersen, G. G. (1991) Microtubule bundling in cells.Nature 349, 24.
Chen, C. &Okayama, H. (1987) High efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA.Molecular and Cellular Biology 7, 2745–52.
De Brabander, M., Geuens, G., Nuydens, R., Willebrords, R. &De Mey, J. (1981) Taxol induces the assembly of free microtubules in living cells and blocks the organizing capacity of the centrosomes and kinetochores.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 78, 5608–12.
Doll, T., Papandrikopoulou, A. &Matus, A. (1990) Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of embryonic rat MAP2c.Nucleic Acids Research 18, 361.
Friden, B., Nordh, J., Wallin, M., Deinum, J. &Norden, B. (1988) Effects of proteolysis of the extending parts of high-molecular-weight microtubule-associated proteins on interactions between microtubules.Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 955, 135–42.
Garner, C. C. &Matus, A. (1988) Different forms of microtubule-associated protein 2 are encoded by separate mRNA transcripts.Journal of Cell Biology 106, 779–83.
Gordon-Weeks, P. R. (1993) Organization of microtubules in axonal growth cones: a role for aucrotubule-associated protein MAP 1B.Journal of Neurocytology 22, 717–725.
Gottlieb, R. A. &Murphy, D. B. (1983) The pattern of MAP-2 binding on microtubules: visual enhancement of MAP attachment sites by antibody labelling and electron microscopy.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 85, 175–85.
Hernandez, M. A., Wandosell, F. &Avila, J. (1987) Localization of the phosphorylation sites for different kinases in the microtubule-associated protein MAP2.Journal of Neurochemistry 48, 84–93.
Himmler, A. (1989) Structure of the bovine tau gene: alternatively spliced transcripts generate a protein family.Molecular and Cellular Biology 9, 1389–96.
Kanai, Y., Takemura, R. &Oshima, T. (1989) Expression of multiple tau isoforms and microtubule bundle formation in fibroblasts transfected with a single tau cDNA.Journal of Cell Biology 109, 1173–84.
Kim, H., Binder, L. I. &Rosenbaum, J. L. (1979) The periodic association of MAP2 with brain microtubulesin vitro.Journal of Cell Biology 80, 266–76.
Kindler, S., Schulz, B., Goedert, M. &Garner, C. C. (1991) Molecular structure of microtubule-associated protein 2b and 2c from rat brain.Journal of Biological Chemistry 265, 19679–84.
Knopps, J., Kosik, K. S., Lee, G., Pardee, J. D., Cohen-gould, L. &McConlogue, L. (1991) Overexpression of tau in a nonneuronal cell induces long cellular processes.Journal of Cell Biology 114, 725–33.
Lee, G., Cowan, N. &Kirschner, M. (1988) The primary structure and heterogeneity of tau protein from mouse brain.Science 239, 285–8.
Letourneau, P. C., Shattuck, T. A. &Ressler, A. H. (1987) “Pull” and “push” in neurite elongation: observations on the effects of different concentrations of cytochalasin B and taxol.Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 8, 193–209.
Lewis, S. A., Wang, D. &Cowan, N. J. (1988) Microtubule-associated protein MAP-2 shares a microtubule binding motif with tau protein.Science 242, 936–9.
Lewis, S. A., Ivanov, I. E., Lee, G. H. &Cowan, N. J. (1989) Organization of microtubules in dendrites and axons is determined by a short hydrophobic zipper in microtubule-associated and tau.Nature 342, 498–505.
Marsh, L. &Letourneau, P. C. (1984) Growth of neurites without filopodial or lamellipodial activity in the presence of cytochalasin B.Journal of Cell Biology 99, 2041–7.
Matus, A., Bernhardt, R., Boomer, R. &Alaimo, D. (1986) Microtubule-associated protein 2 and tubulin are differently distributed in the dendrites of developing neurons.Neuroscience 17, 371–89.
Matus, A., Riederer, B. &Huber, G. (1987) Influence of monoclonal antibodies on microtubule assembly.Journal of Neurochemistry 49, 714–20.
Matus, A. (1988) Microtubule-associated proteins: their potential role in determining neuronal morphology.Annual Review of Neuroscience 11, 29–44.
Matus, A. (1991) Microtubule-associated proteins and neuronal morphogenesis.Journal of Cell Science supp.15, 61–7.
Murphy, D. B., Grasser, W. A. &Wallis, K. T. (1986) Immunofluorescence examination of beta tubulin expression and marginal band formation in developing chicken erythroblasts.Journal of Cell Biology 102, 628–35.
Murphy, D. B. &Borisy, G. G. (1975) Association of high-molecular-weight proteins with microtubules and their role in microtubule assembly in vitro.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 72, 2696–700.
Nunez, J. (1986) Differential expression of microtubule components during brain development.Developmental Neuroscience 8, 125–41.
Olmsted, J. B. (1991) Non-motor microtubule-associated proteins.Current Opinions in Cell Biology 3, 52–8.
Papandrikopoulou, A., Doll, T., Tucker, R. P., Garner, C. C. &Matus, A. (1989) Embryonic MAP2 lacks the cross-linking sidearm sequences and dendritic targeting signal of adult MAP2.Nature 340, 650–2.
Peters, A., Palay, S. L. &Webster, H. Def. (1976)The Fine Structure of the Nervous System. Philadelphia, PA: W. B. Saunders.
Sandoval, I. V., Macdonald, E., Jameson, J. L. &Cuatrecasas, P. (1977) Role of nucleotides in tubulin polymerization: effect of guanylyl 5′-methylenediphosphonate.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 74, 4881–5.
Sato, M., Schwartz, W. H., Selden, S. C. &Pollard, T. D. (1988) Mechanical properties of brain tubulin and microtubules.Journal of Cell Biology 106, 1205–11.
Schiff, P. B. &Horwitz, S. B. (1980) Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 77, 1561–5.
Seeds, N. W., Gilman, A., Amano, T. &Nirenberg, M. W. (1970) Regulation of axon formation by clonal lines of a neural tumor.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 66, 160–7.
Sloboda, R. D. &Rosenbaum, J. L. (1979) Decoration and stabilization of intact, smooth-walled microtubules with microtubule-associated proteins.Biochemistry 18, 48–55.
Tanaka, E. M. &Kirschner, M. (1991) Microtubule behaviour in the growth cones of living cells during axon elongation.Journal of Cell Biology 115, 345–63.
Tucker, R. P. (1990) The roles of microtubule-associated proteins in brain morphogenesis: a review.Brain Research Reviews 15, 101–20.
Viereck, C., Tucker, R. P. &Matus, A. (1989) The adult rat olfactory system expresses microtubule-associated proteins found in the developing brain.Journal of Neuroscience 9, 3547–57.
Voter, W. A. &Erickson, H. P. (1982) Electron microscopy of MAP2 (microtubule-associated protein 2).Journal of Ultrastructure Research 80, 374–82.
Weingarten, M., Lockwood, A., Hwo, S. -Y. &Kirschner, M. (1975) A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 72, 1858–62.
Weisshaar, B., Doll, T. &Matus, A. (1992) Reorganisation of the microtubular cytoskeleton by embryonic microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2c).Development 116, 1151–61.
West, R. R., Tenbarge, K. M. &Olmsted, J. B. (1991) A model for microtubule-associated protein 4 structure. Domains defined by comparisons of human, mouse, and bovine sequences.Journal of Biological Chemistry 266, 21886–96.
Wille, H., Mandelkow, E. M., Dingus, J., Vallee, R. B., Binder, L. I. &Mandelkow, E. (1992) Domain structure and antiparallel dimers of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2).Journal of Structural Biology 108, 49–61.
Winkler, B. &Solomon, F. (1991) A role for microtubule bundles in the morphogenesis of chicken erythrocytes.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 88, 6033–37.
Yamada, K. M., Spooner, B. S. &Wessels, N. K. (1970) Axon growth: roles of microfilaments and microtubules.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 66, 1206–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weisshaar, B., Matus, A. Microtubule-associated protein 2 and the organization of cellular microtubules. J Neurocytol 22, 727–734 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01181318
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01181318