Summary
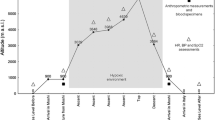
Effects of high altitude exposure on plasma lipids and lipoprotein cholesterol were studied in 8 mountaineers who spent 3 weeks at the Annapurna IV base camp (4800 m) after a 12 day trek. In spite of the moderate physical exertion at the camp, the loss of body weight was more pronounced during the stay at high altitude than during the trekking period. Compared with baseline values observed at sea level, marked reductions in plasma cholesterol (−27%) and phospholipids (−19%) were found 3 days after arrival at the camp and persisted during the next 17 days. A less marked fall in plasma triglycerides occurred, weakly significant at the end of the stay. Because there were no relevant changes in very low density lipoproteins or in high density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol, the low plasma cholesterol levels at the high altitude resulted mainly from the reduction in low density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol: the mean HDL/LDL cholesterol ratio changed from 0.39 at sea level to 0.63 at the end of the stay at 4800 m. Fluctuations in LDL-cholesterol were not concomitant with those in body weight and were independent of the exercise training during the expedition. This study shows moreover that the early drop in LDL-cholesterol was associated with an opposite change in plasma levels of catecholamines and thyroid hormones. Taking into account that such hormonal responses are classically observed at high altitude, the concomitant decrease in LDL-cholesterol might be interpreted as being a relevant adaptative response to hypoxic conditions at high altitude.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- VLDL:
-
very low density lipoproteins
- LDL:
-
low density lipoproteins
- HDL:
-
high density lipoproteins
References
ARPE (1982) Expédition Médicale Française au Numbur Peak. Doc. ARPE 82-1
Bason R, Billings CE (1969) Effects of high altitude on lipid components of human serum. Arch Environ Health 19:183–185
Bauch HJ, Grünwald J, Visher P, Gerlach U, Hauss WH (1987) A possible role of catecholamines in atherogenesis and subsequent complications of atherosclerosis. Exp Pathol 31:193–204
Belfiore F (1980) in Enzyme regulation and metabolic diseases. Karger, Basel, pp 104–106
Boyer SJ, Blume FD (1984) Weight loss and changes in body composition at high altitude. J Appl Physiol 57:1580–1585
Brotherhood JR, Budd GM, Regnard J, Hendrie AL, Jeffery SE, Lincoln GJ (1986) The physical characteristics of the members during the international biomedical expedition to the Antartic. Eur J Appl Physiol 55:517–523
Brown MJ, Jenner DA (1981) Novel double-isotope technique for enzymatic assay of catecholamines, permitting high precision, sensitivity and plasma sample activity. Clin Sci 61:591–598
Chapman MJ, Goldstein S, Lagrange D, Laplaud PM (1981) A density gradient ultracentrifugal procedure for the isolation of the major lipoproteins classes from human serum. J Lip Res 22:339–358
Demacker PN, Van Sommeren-Zontag DF, Stalenhoef AF, Stuyt PM, Van't Laar A (1983) Ultracentrifugation in swinging-bucket and fixed-angle rotors evaluated for isolation and determination of high density lipoproteins subfractions HDL2 and HDL3. Clin Chem 29:656–663
De Mendoza S, Nucete H, Ineichen E, Salazar E, Zerpa A, Glueck CJ (1979) Lipids and lipoproteins in subjects at 1000 and 3500 meter altitudes. Arch Environmental Health 5:308–311
Durning VGA, Vomerly G (1974) Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurement on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. Br J Nutr 32:77–97
Enger S, Herjornsen K, Erikssen J, Fretland A (1977) High density lipoprotein (HDL) and physical activity: the importance of physical exercise, age and smoking on HDL-cholesterol and the HDL/total cholesterol ratio. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 37:251–255
Escourrou P, Johnson DG, Rowell LB (1984) Hypoxemia increases plasma catecholamines concentrations in exercising humans. J Appl Physiol 57:1507–1511
Goldenberg F, Richalet JP, Keromes A, Rathat C, Dantlo B (1985) Poor sleep induced by high altitude hypoxia. Effects of thienodiazepine, Brotizolam. In: Koella WP, Rüther E, Schultz H (eds) Sleep '84. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, New York, pp 316–318
Heimberg M, Olubavedo JO, Wilcox HG (1985) Plasma lipoprotein and regulation of hepatic metabolism of fatty acids in altered thyroid states. Endoc Rev 6:590–607
Hietanen E (1982) Regulation of serum lipids by physical exercise, Hietanen E (ed) CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 35–54
Klain GJ, Hannon JP (1968) Effects of high altitude on lipid components of human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 129:646–649
Langer T, Strober W, Levy RI (1972) The metabolism of low density lipoprotein in familial type II hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest 51:1528–1536
Lehtonen A, Viikari J (1978) Serum triglycerides and cholesterol and serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol, in highly physically active men. Acta Med Scand 204:111–114
Mortimer EA, Monson RR, MacMahon B (1977) Reduction of mortality from coronary heart disease in men residing at high altitude. New Eng J Med 296:581–585
Nestel PJ, Podkolinski M, Fidge NH (1979) Marked increase in high density lipoproteins in mountaineers. Atherosclerosis 34:193–196
Richalet JP, Rathat C, Keromes A, Herry JP, Larmignat P, Garnier M, Pillardeau P (1983) Plasma volume, body weight and acute mountain sickness. Lancet 1 (8323):525
Richalet JP, Vignon P, Rathat C, Keromes A, Sabatier C, Lhoste F (1985) Catecholamines and histamine at exercise in acute hypoxia (3823 and 4350 m). Effects of atropine. (Abstr) Proceedings of the 3rd Hypoxia Symposium, Lake Louise
Roschlau P, Bernt E, Gruber W (1974) Enzymatische Bestimmung des Gesamtcholesterins im Serum. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 12:403–407
Ruiz L, Penazola D (1977) Altitude and hypertension. Mayo Clin Proc 52:442–445
Shivastava KK, Malhotra MS (1974) Effect of adaptation of high altitude on components of blood and urine of lowlanders compared to high altitude natives. Int J Biometeorol 13:279–287
Stock MJ, Chapman C, Stirling JL (1978) Effects of exercise, altitude and food on blood hormones and metabolic levels. J Appl Physiol 45:350–354
Sutton JR (1982) Sleep disturbances at high altitude. Phys Sport Med 10:79–84
Thompson GR, Soutar AK, Spengel FA, Jadhav A, Gavogam SJP, Myant NB (1981) Defects of receptors-mediated low density lipoprotein catabolism in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and hypothyroïdism. Proc Soc Natl Acad Sc USA 78:2591–2595
Vondra K, Brodan V, Dobrasova M, Vitek V, Kopecka J (1986) Effect of sleep deprivation on cholesterol metabolism and triglyceridaemia in male volunteers. Eur J Appl Physiol 55:83–87
Wood PD, Haskell WL (1979) The effect of exercise on plasma high density lipoproteins. Lipids 14:417–427
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Férézou, J., Richalet, J.P., Coste, T. et al. Changes in plasma lipids and lipoprotein cholesterol during a high altitude mountaineering expedition (4800 m). Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 57, 740–745 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01075997
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01075997