Abstract
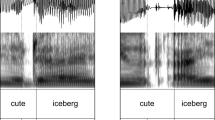
The influence of linguistic and paralinguistic structure on speech motor programming was investigated for 5-year-olds, 8-year-olds, and adults. Subjects repeated verbal stimuli, each at maximum rate on numerous consecutive trials. It was hypothesized that structure in an utterance would allow a speaker to organize its motor program more efficiently than would be possible for an otherwise identical utterance that lacked such structure, although the types of structure employed might change with age. Differences in the efficiency of motor program organization were expected to be evidenced in the syllable duration and the relative variability of the syllable duration of subjects' repetitions. At all ages, repetition durations were shorter for stimuli with a sentencelike rhythm than for unstructured stimuli. Stimuli that were syntactically structured and contained a sentencelike rhythm were spoken with shorter durations than nonsyntactic stimuli with sentential rhythm but only by 8-year-olds and adults. Meaningful stimuli were produced with shorter durations than were nonmeaningful stimuli at all ages, but there were developmental differences as regards the types of sentence meaning that affected repetition duration and the role of practice in producing an effect of sentence meaning. Thus, there is a shift from a semantically and rhythmically based motor programming system at age 5 to a system that also utilizes syntax at age 8. The variability of repetition durations was minimally influenced by utterance structure. The implications of these cross-measure differences for models of motor programming are briefly considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbeduto, L. (1982).Syntactic and semantic influences on the motor programming of speech: Developmental differences and similarities. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Illinois at Chicago.
Abbeduto, L. (1985). The effects of linguistic complexity on children's and adults' motor programming of speech.Language and Speech, 28, 361–375.
Bassett, M.R., O'Connell, D.C., & Monahan, W.J. (1977). Pausological aspects of children's narratives.Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society, 9, 166–168.
Boomer, D.S. (1965). Hesitation and grammatical encoding.Language and Speech, 8, 148–158.
Clark, H.H., & Clark, E.V. (1977).Psychology and language: An introduction to psycholinguistics. New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich.
Cohen, J.A. (1960). A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales.Educational and Psychological Measurement, 20, 37–46.
Daniel, W.W. (1978).Applied nonparametric statistics Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
Gilbert, J.H.V. (1977). A voice onset time analysis of apical stop production in 3-year-olds.Journal of Child Language, 3, 103–110.
Gilbert, J.H.V., & Purves, B.A. (1977). Temporal constraints on consonant clusters in child speech production.Journal of Child Language, 4, 417–432.
Hawkins, P.R. (1971). The syntactic location of hesitation pauses.Language and Speech, 14, 277–288.
Jarvella, R.J., & Herman, S.J. (1973). Speed and accuracy of sentence recall: Effects of ear of presentation, semantics, and grammar.Journal of Experimental Psychology, 97, 108–110.
Jones, P.A., & McMillan, W.B. (1973). Speech characteristics as a function of social class and situational factors.Child Development, 44, 119–121.
Kent, R.D., & Forner, L.L. (1980). Speech segment durations in sentence recitations by children and adults.Journal of Phonetics, 8, 157–168.
Kowal, S., O'Connell, D.C. & Sabin, E.J. (1975). Development of temporal patterning and vocal hesitations in spontaneous narratives.Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 4, 195–207.
Kozhevnikov, V.A., & Chistovich, L.A. (1965).Speech: Articulation and perception. Washington, D.C.: Joint Publication Research Service.
Kucera, H., & Francis, W.N. (1967).Computational analysis of present-day American English. Providence: Brown University Press.
Lackner, J.R., & Levine, K.B. (1975). Speech production: Evidence for syntactically and phonologically determined units.Perception and Psychophysics 17, 107–113.
Leeper, H.A., & Woodward, R.E. (1978). Temporal characteristics of topic- and picture-elicited speech of children.Perceptual and Motor Skills, 47, 496–498.
Levin, H., & Silverman, I. (1965). Hesitation phenomena in children's speech.Language and Speech, 8, 67–85.
Levin, H., Silverman, I., & Ford, B.L. (1967). Hesitations in children's speech during explanations and descriptions.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 6, 560–564.
MacKay, D.G. (1982). The problems of flexibility, fluency, and speed-accuracy trade-off in skilled behavior.Psychological Review, 89, 483–506.
MacKay, D.G., & Bowman, R.W. (1969). On producing the meaning in sentences.American Journal of Psychology, 82, 23–37.
Martin, J.G. (1972). Rhythmic (hierarchical) versus serial structure in speech and other behavior.Psychological Review, 79, 487–509.
Quirk, R. & Greenbaum, S. (1973).A concise grammar of contemporary English. New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich.
Rosenberg, S. (1968). Association and phrase structure in sentence recall.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 7, 1077–1081.
Rosenberg, S. (1969). The recall of verbal material accompanying semantically well-integrated and semantically poorly integrated sentences.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 8, 732–736.
Rosenberg, S. (1977a, November).Semantic integration in sentence memory and perception: A selected overview. Paper presented at the Psychonomic Society Meetings, Washington, D.C.
Rosenberg, S. (1977b). Semantic constraints on sentence production: An experimental approach. In S. Rosenberg (Ed.),Sentence developments in research and theory. Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum.
Rosenberg, S. & Jarvella, R.J. (1970). Semantic integration as a variable in sentence perception, memory, and production. In G.B. Flores d'Arcais & W.J.M. Levelt (Eds.),Advances in psycholinguistics. Amsterdam: North-Holland.
Rosenberg, S., Jarvella, R.J., & Cross, M. (1971). Semantic integration, age, and the recall of sentences.Child Development 42, 1959–1966.
Rosenberg, S., & Koen, M.J. (1968). Norms of sequential associative dependencies in active declarative sentences. In C. Catford (Ed.),Studies in language and language behavior, supplement to progress report VI. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan, Center for Research on Language and Language Behavior.
Sabin, E.J., Clemmer, E.J., O'Connell, D.C., & Kowal, S. (1979). A pausological approach to speech development. In A.W. Siegman & S. Feldstein (Eds.),Of speech and time: Temporal speech patterns in interpersonal contexts. Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum.
Shattuck, S., & Lackner, J.R. (1975). Speech production: Contributions of syntactic structure.Perceptual and Motor Skills, 40, 931–936.
Sternberg, S., Monsell, S., Knoll, R.L., & Wright, C.E. (1978). The latency and duration of rapid movement sequences: Comparisons of speech and typewriting. In G.E. Stelmach (Ed.),Information processing in motor control and learning. New York: Academic Press.
Tingley, B.M., & Allen, G.D. (1975). Development of speech timing control in children.Child Development, 46, 186–194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbeduto, L. Syntactic, semantic, and rhythmic influences on children's and adults' motor programming of speech. J Psycholinguist Res 16, 201–221 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067542
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067542