Abstract
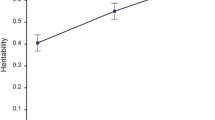
Three recent studies have used twin data to explore the possibility of differential contributions of heritability and environmentality to individual differences in cognitive ability as a function of ability level (Detterman, D. K.,et al., Behav. Genet. 20:369–384; 1990; Bailey, M. J. amd Revelle, W.,Behav. Genet. 21:397–404, 1991; Cherny, S. S.,et al., Behav. Genet. 22:153–162, 1992). All arrived at different conclusions: higher heritability at the low end, higher heritability at the high end, and no differential influence, respectively. The current report involves a sample of 148 identical and 135 fraternal twin pairs from the Western Twin Project who were tested on a battery of intelligence and achievement tests to further explore the issue. The results suggest no significant differences in heritability at either the high or the low end, although a trend toward higher heritability for children of higher ability is evident. Individual differences for a composite ability/achievement score showed significantly greater influence of shared family environment at the low end than the rest of the distribution. In general, results for cognitive ability and academic achievement were highly similar.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, M. J., and Revelle, W. (1991). Increased heritability for lower IQ levels?Behav. Genet. 21:397–404.
Cherny, S. S., Cardon, L. R., Fulker, D. W., and DeFries, J. C. (1992). Differential heritability across levels of cognitive ability?Behav. Genet. 22:153–162.
Cohen, J. (1988).Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd. ed. Academic Press, New York.
DeFries, J. C., and Fulker, D. W. (1985). Multiple regression analysis of twin data.Behav. Genet. 15:467–473.
DeFries, J. C., and Fulker, D. W. (1988). Etiology of deviant scores versus individual differences.Acta Genet. Med. Gemellol. Twin Res. 37:205–216.
DeFries, J. C., and Gillis, J. J. (1991). Etiology of reading deficits in learning disabilities: Quantitative genetic analysis. In (Ed.)Neurophychological Foundations of Learning Disabilities, Academic Press, Academic Press, New Jersey, pp. 29–47.
Detterman, D. K., and Daniel, M. H. (1989). Correlations of mental tests with each other and with cognitive variables are highest for low IQ groups.Intelligenece 13:349–359.
Detterman, D. K., Thompson, L. A., and Plomin, R. (1990). Differences in heritability across groups differing in ability.Behav. Genet. 20:369–384.
Jensen, A. R. (1987). Twins: The puzzle of non-genetic varance. Paper presented at the 17th Annual Meeting of the Behavior Genetics Association, Minneapolis.
LaBuda, M. C., and DeFries, J. C. (1990). Genetic etiology of reading disability: Evidence from a twin study. In Pavlidis, G. Th. (ed.),Perspectives on Dyslexia: Vol. 1., Neurology, Neuropsychology and Genetics, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, England, pp. 47–76.
LaBuda, M. C., DeFries, J. C., and Fulker, D. W. (1986). Multiple regression analysis of twin data obtained from selected samples.Genet. Epidemiol. 3:425–433.
Nichols, P. L. (1984). Familial mental retardation.Behav. Genet. 14:161–170.
Plomin, R., and Neiderhiser, J. M. (1992). Quantitative genetics, molecular genetics, and intelligence.Intelligence 15:369–387.
Plomin, R., DeFries, J. C., and McClearn, G. E. (1990).Behavioral Genetics: A Primer, 2nd Ed., Freeman, New York.
Thompson, L. A., Detterman, D. K., and Plomin, R. (1991). Associations between cognitive abilities and scholastic achievement: Genetic overlap but environmental differences.Psychol. Sci. 2:158–165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, L.A., Detterman, D.K. & Plomin, R. Differences in heritability across groups differing in ability, revisited. Behav Genet 23, 331–336 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067433
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067433