Abstract
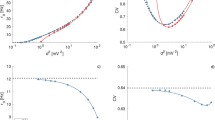
Single unit responses of the cat midbrain tectum to stimuli applied through a microelectrode 500µ rostrally to the recording electrode were recorded extracellularly. The mean latency of both direct and monosynaptic responses was 0.3 msec greater than that for local microstimulation. The responses were identified from their latent and refractory periods, the presence of summation, and the dependence of the firing index on sodium glutamate application to the recorded neuron. Thresholds of synaptic responses were measured during vertical displacement of the stimulating electrode. The experimental relationships can be approximated by parabolic functions. The results indicate that rostrocaudal projections in the midbrain tegmentum are arranged horizontally.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
M. L. Shik and A. S. Yagodnitsyn, "Investigation of neuronal connections in the dorsocaudal tegmentum of the cat by a microstimulation method," Neirofiziologiya,5, 593 (1973).
J. C. Eccles, The Physiology of Synapses, Springer, Berlin (1964).
H. Asanuma and I. Rosen, "Spread of mono- and polysynaptic connections within cat's motor cortex," Exp. Brain Res.,16, 507 (1973).
H. Asanuma and H. Sakata, "Functional organization of a cortical efferent system examined with focal depth stimulation in cats," J. Neurophysiol.,30, 35 (1967).
S. L. BeMent and J. B. Ranck, Jr., "A quantitative study of electrical stimulation of central myelinated fibers," Exper. Neurol.,24, 147 (1969).
A. L. Berman, The Brain Stem of the Cat, University of Wisconsin Press, Madison (1968).
D. R. Curtis, A. W. Duggan, D. Felix, et al., "Excitation of mammalian central neurones by acidic amino acids," Brain Res.,41, 283 (1972).
E. Jankowska and W. J. Roberts, "An electrophysiological demonstration of the axonal projections of single spinal interneurones in the cat," J. Physiol. (London),222, 597 (1972).
E. Jankowska and W. J. Robersts, "Synaptic actions of single interneurones mediating reciprocal 1a inhibition of motoneurones," J. Physiol. (London),222, 623 (1972).
A. R. Martin, W. O. Wickelgran, and R. Beránek, "Effects of iontophoretically applied drugs on spinal interneurones of the lamprey," J. Physiol. (London),207, 653 (1970).
S. Nishi, H. Soeda, and K. Koketsu, "Effect of alkali-earth cations on frog spinal ganglion cells," J. Neurophysiol.,28, 457 (1965).
E. T. Rolls, "Involvement of brain stem units in medial forebrain bundle self-stimulation," Physiol. Behav.,7, 297 (1971).
S. D. Stoney, Jr., W. D. Thompson, and H. Asanuma, "Excitation of pyramidal tract cells by intracortical microstimulation: effective extent of stimulating current," J. Neurophysiol.,31, 659 (1968).
W. Zieglgänsberger and E. A. Puil, "Actions of glutamic acid on spinal neurons," Exp. Brain Res.,17, 35 (1973).
Additional information
Institute of Problems in Information Transmission, Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Moscow. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 6, No. 6, pp. 602–609, November–December, 1974.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yagodnitsyn, A.S., Shik, M.L. Anisotropic connections in the cat midbrain tegmentum. Neurophysiology 6, 475–481 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01065223
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01065223