Abstract
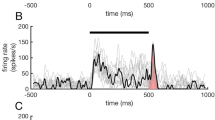
The spike responses of the motor cortex neurons (area 4) associated with forelimb movement were studied in awake cats earlier trained to perform placing motor reactions. Responses produced by the same neurons were compared in two situations: 1) when a sound-click conditioning stimulus (CS) was applied in isolation; 2) when a CS followed a preliminary warning stimulus (WS), a light flash, with a 100–1000 msec delay. During the reflex initiation by combined action of the WS and CS, response components that occurred prior to the placing movement (PM) performance under isolated CS action weakened and arrived 50–150 msec later; yet, response components that appeared in the same situation simultaneously with PM onset or later remained unchanged. PM latent periods were not changed when WS was applied. The temporal interval between WS and CS was characterized by depression of neuronal activity; depression duration was determined by the interstimulus delay. It is conceivable that the described transformations in spike responses of cortical neurons occurred due to changes in the sensory direction of the animal's attention; this direction, in all cases, is a crucial factor in the formation of neuronal activity in the cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. C. Batuev, G. P. Dem'yanenko, A. A. Orlov, and V. I. Shefer,Neuronal Mechanisms in the Awake Brain of Monkeys [in Russian], Nauka, Leningrad (1988).
B. I. Busel' and M. G. Moldavan, “Activity of the motor cortex neurons during the inhibition of conditioned reflex of postural changes,”Neurophysiology,17, No. 5, 489–500 (1985).
B. I. Busel' and M. G. Moldavan, “Effect of food motivation on responses of the somatic cortex neurons in cats during instrumental reflex,”Neurophysiology,19, No. 5, 646–653 (1987).
B. I. Busel' and M. G. Moldavan, “Effect of food motivation on the impulse activity of the somatic cortex neurons in cats,”Neurophysiology,19, No. 5, 725–735 (1987).
B. I. Busel', M. G. Moldavan, and A. P. Kniga, “Inhibitory effect of application of extra stimuli on impulse in cats during conditioned reflex,”Neurophysiology,22, No. 2, 147–155 (1990).
B. I. Busel' and A. P. Kniga, “Inhibitory effect of application of auxiliary stimuli on responses of the sensory-motor cortex neurons in cats during conditioned reflex,”Neurophysiology,23, No. 2, 174–181 (1991).
B. I. Busel' and A. P. Kniga, “Alteration in the responses of neurons in Area 7 to unconditional stimulation following the action of auxiliary stimuli,”Neurophysiology, 564–574 (1991).
B. I. Busel and A. P. Kniga, “Effect of inhibition of responses of the motor cortex neurons in cats associated with elicitation of conditioned reflex during expectation of the action of a light flash,”Neurophysiology,24, No. 3, 340–343 (1992).
A. G. Zadorozhnyi and E. F. Ryazantseva, “Inhibitory effect of extraneous stimuli on the impulse activity of the motor cortex neurons during conditioned reflex in cats,”Fiziol. Zh.,31, No. 5, 611–618 (1985).
Zh. A. Kruchenco, V. V. Sachenco, and N. N. Koval'chuk, “Responses of the somatosensory cortex neurons in cats during external and internal inhibition of instrumental conditioned reflex,”Fiziol. Zh.,30, No. 6, 641–650 (1984).
N. E. Maximova and I. O. Alexandrov, “Typology of slow potentials in the brain, neuronal activity, and the dynamics of systemic organization of behavior,” in:EEG and Neuronal Activity in Psychophysiological Investigations [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1987), pp. 44–72.
T. N. Reznikova and V. M. Smirnov, “Electrophysiological correlates of attention,” in:Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Attention, Moscow University Press, Moscow (1979), pp. 173–185.
K. V. Sudakova (ed.),Systemic Mechanisms of Behavior, Meditsina Publishing House, Moscow (1990).
V. M. Storozhuk and A. N. Tal'nov, “Responses of the somatic cortex neurons in cats during instrumental reflex of placing the paw in a support,”Neurophysiology,14, No. 4, 392–401 (1982).
A. N. Tal'nov, “The connections between responses of the somatic cortex neurons in cats during instrumental and alimentary reflexes,”Neurophysiology,17, No. 2, 212–221 (1985).
G. Tesse, “Evoked potentials in man and attention,” in:Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Attention, Moscow University Press, Moscow (1979).
G. Walter,The Living Brain [Russian translation], Mir, Moscow (1966).
K. V. Sudakova (ed.),Functional Systems of the Organism, Meditsina, Moscow (1987).
Ch. Shagas,Evoked Potentials of the Brain in Norm and Pathology, Mir, Moscow (1975).
V. B. Shvyrkov, “What are neuronal activity and EEG from the systemic and evolutionary approach,” in:EEG and Neuronal Activity in Psychophysiological Investigations, Nauka, Moscow (1987), pp. 5–23.
R. Ernandets-Peon, “Neurophysiological aspects of attention,” in:Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Attention, Moscow University Press, Moscow (1979), pp. 50–73.
E. E. Fetz, “Neuronal activity associated with conditioned limb movements,” in:Handbook of Behavioral Neurobiology, A. L. Towe (ed.), Vol. 5, Plenum Press, New York-London (1981), pp. 493–566.
E. E. Fetz and D. V. Finoccio, “Correlation between activity of motor cortex cell and arm muscles during operantly conditioned response patterns,”Exp. Brain Res.,23, No. 3, 217–234 (1975).
M. D. Low, J. D. Frost, R. L. Maulsby, and J. W. Sherry,Electroencephalographic Correlates of Preparation Set, New York (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 25, No. 1, pp. 21–27, January–February, 1993.t
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Busel', B.I., Kniga, A.P. Effect of response inhibition in cat motor cortex neurons during the expectation of conditioning stimulus. Neurophysiology 25, 16–21 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01053628
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01053628