Summary
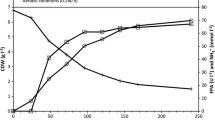
A novel approach of aerobic growth followed by anaerobic growth was used to identify the anaerobic end products of the facultative organismCellulomonas sp. (ATCC 21399) utilizing cellulose as the substrate. The organism was found to produce an equimolar mixture of ethanol and acetic acid as the two carbon end products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clemmer, J.E. (1984), Winter National Meeting of the AIChE, Atlanta, GA.
Callihan, C.D. and Irwin, G.H., Jr. (1974), National Meeting of the ACS, Atlantic City, NJ.
Goodfellow, G.I. and Webber, H.M. (1972),Chemistry and Industry, 5 February (1972), 119–20.
Keddie, R.M. (1974),Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, Buchanan, R. E. and Gibbons, N. E. eds.), the Williams and Wilkens Co., Baltimore, MD
Miller, G.L. (1959),Anal. Chem. 31, 426–28.
Miller, G.L., Blum, R., Glennon, W.E. and Burton, A.L. (1960),Anal. Biochem., 2, 127–132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clemmer, J.E., Tseng, CL. Identification of the major anaerobic end products ofCellulomonas sp. (ATCC 21399). Biotechnol Lett 8, 823–826 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01020832
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01020832