Abstract
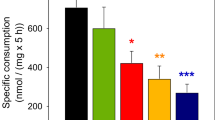
The effects of ammonium chloride (3 mM) and β-methylene-dl-aspartate (BMA; 5 mM) (an inhibitor of aspartate aminotransferase, a key enzyme of the malate-aspartate shuttle (MAS)) on the metabolism of glutamate and related amino acids were studied in primary cultures of astrocytes and neurons. Both ammonia and BMA inhibited14CO2 production from [U-14C]-and [1-14C]glutamate by astrocytes and neurons and their effects were partially additive. Acute treatment of astrocytes with ammonia (but not BMA) increased astrocytic glutamine. Acute treatment of astrocytes with ammonia or BMA decreased astrocytic glutamate and aspartate (both are key components of the MAS). Acute treatment of neurons with ammonia decreased neuronal aspartate and glutamine and did not apparently affect the efflux of aspartate from neurons. However, acute BMA treatment of neurons led to decreased neuronal glutamate and glutamine and apparently reduced the efflux of aspartate and glutamine from neurons. The data are consistent with the notion that both ammonia and BMA may inhibit the MAS although BMA may also directly inhibit cellular glutamate uptake. Additionally, these results also suggest that ammonia and BMA exert differential effects on astroglial and neuronal glutamate metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper, A. J. L., and Plum, F. 1987. Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia. Physiol. Rev. 67:440–519.
Cooper, A. J. L., and Lai, J. C. K. 1987. Cerebral ammonia metabolism in normal and hyperammonemic rats. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:67–95.
Kvamme, E. 1983. Ammonia metabolism in the CNS. Prog. Neurobiol. 20:109–132.
Sarna, G. S., Bradbury, M. W. B., Cremer, J. E., Lai, J. C. K., and Teal, H. M. 1977. Brain metabolism and specific transport at the blood-brain barrier after portocaval anastomosis in the rat. Brain Res. 160:69–83.
Hawkins, R. A., Mans, A. M., and Biebuyck, J. F. 1987. Changes in brain metabolism in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Pathol 6:35–66.
Butterworth, R. F., Giguère, J.-F., Michaud, J., Lavoie, J., and Layrargues, G. P. 1987. Ammonia: key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:1–12.
Raabe, W. 1987. Synaptic transmission in ammonia intoxication. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:145–166.
Norenberg, M. D. 1987. The role of astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:13–33.
Yu, A. C., Schousboe, A., and Hertz, L. 1984. Influence of pathological concentrations of ammonia on metabolic fate of14C-labeled glutamate in astrocytes in primary cultures. J. Neurochem. 42:594–597.
Murthy, Ch. R. K., and Hertz, L. 1988. Pyruvate decarboxylation in astrocytes and in neurons in primary cultures in the presence and the absence of ammonia. Neurochem. Res. 13:57–61.
Lai, J. C. K., and Cooper, A. J. L. 1986. Brain α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: kinetic properties, regional distribution, and effects of inhibitors. J. Neurochem. 47:1376–1386.
Jessy, J., and Murthy, Ch. R. K. 1985. Elevation of transamination of branched chain amino acids in brain in acute ammonia toxicity. Neurochem. Int. 7:1027–1031.
Murthy, Ch. R. K., and Hertz, L. 1987. Acute effect of ammonia on branched-chain amino acid oxidation and incorporation into proteins in astrocytes and in neurons in primary cultures. J. Neurochem. 49:735–741.
Murthy, C. R. K., and Hertz, L. 1987. Comparison between acute and chronic effects of ammonia on branched-chain amino acid oxidation and incorporation into protein in primary cultures of astrocytes and of neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 17:271–276.
Fitzpatrick, S. M., Cooper, A. J. L., and Hertz, L. 1988. Effects of ammonia and β-methylene-Dl-aspartate on the oxidation of glucose and pyruvate by neurons and astrocytes in primary culture. J. Neurochem. 51:1197–1203.
Hindfelt, B., Plum, F., and Duffy, T. E. 1977. Effect of acute ammonia intoxication on cerebral metabolism in rats with portacaval shunts. J. Clin. Invest. 59:386–396.
Ratna Kumari, L., Subballakshmi, G. Y. C. Y., and Murthy, C. R. K. 1986. Acute effects of ammonia on the enzymes of the citric acid cycle in rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 8:115–120.
Brand, M. D., and Chappell, J. B. 1974. Glutamate and aspartate transport in rat brain mitochondria. Biochem. J. 140:205–210.
Dennis, S. C., Land, J. M., and Clark, J. B. 1976. Glutamate metabolism and transport in rat brain mitochondria. Biochem. J. 156:323–331.
Dennis, S. C., Lai, J. C. K., and Clark, J. B. 1977. Comparative studies on glutamate metabolism in synaptic and non-synaptic rat brain mitochondria. Biochem. J. 164:727–736.
Minn, A., and Gayet, J. 1977. Kinetic study of glutamate transport in rat brain mitochondria. J. Neurochem. 29:873–881.
Dennis, S. C., and Clark, J. B. 1978. The regulation of glutamate metabolism by tricarboxylic acid-cycle activity in rat brain mitochondria. Biochem. J. 172:155–162.
Cooper, A. J. L., Fitzpatrick, S. M., Ginos, J.-Z., Kaufman, C., and Dowd, P. 1983. Inhibition of glutamate-aspartate transaminase by β-methylene-DL-aspartate. Biochem. Pharmacol. 32:679–689.
Fitzpatrick, S. M., Cooper, A. J. L., and Duffy, T. E. 1983. Use of β-methylene-D,L-aspartate to assess the role of aspartate aminotransferase in cerebral oxidative metabolism. J. Neurochem. 41:1370–1383.
Hertz, L., Murthy, Ch. R. K., Lai, J. C. K., Fitzpatrick, S. M., and Cooper, A. J. L. 1987. Some metabolic effects of ammonia on astrocytes and neurons in primary cultures. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:97–129.
Lai, J. C. K., Murthy, Ch. R. K., Hertz, L., and Cooper, A. J. L. 1986. NH3 & β-methyleneaspartate inhibit neuronal & glial glutamate oxidation. Trans. Am. Soc. Neurochem. 17:217.
Lai, J. C. K., Murthy, Ch. R. K., Cooper, A. J. L., Hertz, E., and Hertz, L. 1988. βMA alters neuronal and astroglial amino acid metabolism. Trans. Am. Soc. Neurochem. 19:112.
Yu, A. C. H., Hertz, E., and Hertz, L. 1984. Alterations in uptake and release rates for GABA, glutamate and glutamine during biochemical maturation of highly purified cultures of cerebral cortical neurons of a GABAergic preparation. J. Neurochem. 42:951–960.
Hertz, L., Juurlink, B. H. J., and Szuchet, S. 1985. Cell cultures. Pages 603–661,in Lajtha, A. (ed.) Handbook of Neurochemistry (2nd Ed.) Vol. 8, Plenum Press, New York.
Hertz, L., Juurlink, B. H. J., Fosmark, H., and Schousboe, A. 1982. Methodological appendix: astrocytes in primary cultures. Pages 175–186,in Pfeiffer, S. E. (ed.), Neuroscience Approached through Cell Culture, Vol. I, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Hertz, L., Murthy, Ch. R. K., and Schousboe, A. 1988. Metabolism of glutamate and related amino acids. Pages 395–406,in Norenberg, M. D., Hertz, L., and Schousboe, A. (eds.), The Biochemical Pathology of Astrocytes, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
Yu, A. C., Schousboe, A., and Hertz, L. 1982. Metabolic fate of14C-labeled glutamate in astrocytes in primary cultures. J. Neurochem. 39:954–960.
Gregorios, J. B., Mozes, L. W., Norenberg, L.-O. B., and Norenberg, M. D. 1985. Effect of cyclic AMP on ammonia-treated astrocyte cultures. Neurology 35 (Suppl. 1):250.
Lindroth, P., and Mopper, L. 1979. High performance liquid chromatographic determination of subpicomole amounts of amino acids by precolumn fluorescence derivatization with o-phthaldialdehyde. Anal. Chem. 51:1667–1674.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Schousboe, A., Larsson, O. M., Drejer, J., Krogsgaad-Larsen, P., and Hertz, L. 1983. Uptake and release processes for glutamine, glutamate and GABA in cultured neurons and astrocytes. Pages 297–315,in Hertz, L., Kvamme, E., McGeer, E. G., and Schousboe, A. (eds.), Glutamine, Glutamate, and GABA in the Central Nervous System, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
Cheeseman, A. J., and Clark, J. B. 1988. Influence of the malateaspartate shuttle on oxidative metabolism in synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 50:1559–1565.
Yudkoff, M., Nissim, I., Hummeler, K., Medow, M., and Pleasure, D. 1986. Utilization of [15N]glutamate by cultured astrocytes. Biochem. J. 234:185–192.
Nicklas, W. J., and Browning, E. T. 1978. Amino acid metabolism in glial cells: homeostatic regulation of intra- and extracellular milieu by C-6 glioma cells. J. Neurochem. 30:955–963.
Cooper, A. J. L., Lai, J. C. K., and Gelbard, A. S. 1988. Ammonia and energy metabolism in normal and hyperammonemic rat brain. Pages 419–434,in Norenberg, M. D., Hertz, L., and Schousboe, A. (eds.), The Biochemical Pathology of Astrocytes, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
Duffy, T. E., Nelson, S. R., and Lowry, O. H. 1972. Cerebral carbohydrate metabolism during acute hypoxia and recovery. J. Neurochem. 19:959–977.
Duffy, T. E., Plum, F., and Cooper, A. J. L. 1983. Cerebral ammonia metabolism in vivo. Pages 371–388,in Hertz, L., Kvamme, E., McGeer, E. G., and Schousboe, A. (eds.), Glutamine, Glutamate, and GABA in the Central Nervous System, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
Hogstad, S., Svenneby, G., Torgner, I. Aa., Kvamme, E., Hertz, L., and Schousboe, A. 1988. Glutaminase in neurons and astrocytes cultured from mouse brain: kinetic properties and effects of phosphate, glutamate, and ammonia. Neurochem. Res. 13:383–388.
Norenberg, M. D. 1983. Immunohistochemistry of glutamine synthetase. Pages 95–111,in Hertz, L., Kvamme, E., McGeer, E. G., and Schousboe, A. (eds.), Glutamine, Glutamate, and GABA in the Central Nervous System, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
Weiler, C. T., Nystrom, B., and Hamberger, A. 1979. Glutaminase and glutamine synthetase activity in synaptosomes, bulkisolated glial and neurons. Brain Res. 160:539–543.
Dennis, S. C., Lai, J. C. K., and Clark, J. B. 1980. The distribution of glutamine synthetase in subcellular fractions of rat brain. Brain Res. 197:469–475.
Patel, A. J., Hunt, A., Gordon, R. D., and Balázs, R. 1982. The activities in different neural cell types of certain enzymes associated with the metabolic compartmentation glutamate. Develop. Brain Res. 4:3–11.
Subbalakshmi, G. Y. C. V., and Murthy, Ch. R. K. 1985. Isolation of astrocytes, neurons, and synaptosomes of rat brain: distribution of enzymes of glutamate metabolism. Neurochem. Res. 10:239–250.
Parli, J. A., Godfrey, D. A., and Ross, C. D. 1987. Separate enzymatic microassays for aspartate aminotransferase isoenzymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 925:175–184.
Kimelberg, H. K., and Pang, S. 1987. Effect ofL-glutamate on ion transport processes and swelling in primary astrocyte cultures. Soc. Neurosci. Abstracts 13:195.
Kimelberg, H. K., Pang, S., and Treble, D. H. 1989. Excitatory amino acid-stimulated uptake of22Na in primary astrocyte cultures. J. Neurosci. (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to Professor E. Kvamme. Dr. Kvamme has conducted numerous pioneering studies on the regulation of the metabolism of glutamine, glutamate and ammonia in nervous and other tissues (see Refs. 1 and 3 for a complete discussion and citation of his many papers). Many important ideas in this exciting field of research have emerged from the work carried out in his laboratory.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, J.C.K., Murthy, C.R.K., Cooper, A.J.L. et al. Differential effects of ammonia and β-methylene-dl-aspartate on metabolism of glutamate and related amino acids by astrocytes and neurons in primary culture. Neurochem Res 14, 377–389 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000042
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01000042