Abstract
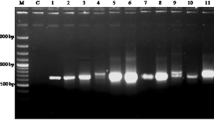
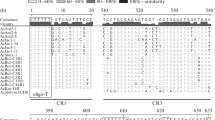
Heterogeneity of the internal transcribed spacer ITS1 of the rDNA within individuals ofTulipa gesneriana L.,T. kaufmanniana Regel, and their interspecific hybrids was analyzed by PCRRFLP, using the polymorphic restriction enzymesRsaI andHinfI, and by nucleotide sequence analysis. In most cases, the sum of the sizes of the restriction fragments was higher than the entire length of the undigested ITS fragment, indicating heterogeneity at the restriction sites within an individual. Differences in band intensities within the restriction patterns indicate the occurrence of variation in copy number of these different ITS1 variants within individuals. Automated sequencing without a visual inspection often failed to detect existing heterogeneity within sequences, resulting in a discrepancy between the sequencing and restriction analysis results. By visual interpretation of the sequences, the restriction patterns could mostly be predicted well. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) experiments in fourTulipa species revealed the occurrence of several rDNA spots. The number of rDNA loci varied from seven inT. gesneriana ‘Christmas Marvel’ to ten inT. australis Link. This might explain the occurrence of heterogeneity in ITS sequences inTulipa, as homogenization of variants has to take place over different loci.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels R., Honeycutt R. L. (1986) rDNA: evolution over a billion years. In: Dutta S. K. (ed.) DNA systematics, vol. II. Boca Raton, FL, CRC Press, pp. 81–135.
Arnheim N., Krystal M., Schmickel R., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E. (1980) Molecular evidence for genetic exchanges among ribosomal genes on nonhomologous chromosomes in man and apes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA 77: 7323–7327.
Badaeva E. D., Friebe B., Gill B. S. (1996) Genome differentiation inAegilops. 2. Physical mapping of 5S and 18–26S ribosomal RNA gene families in diploid species. Genome 39: 1150–1158.
Baldwin B. G., Sanderson M. J., Porter J. M., Wojciechowski M. F., Campbell C. S., Donoghue M. J. (1995) The ITS region of nuclear ribosomal DNA: a valuable source of evidence on angiosperm phylogeny. Ann. Missouri Bot. Garden 82: 247–277.
Bennett M. D., Smith J. B. (1976) Nuclear DNA amounts in Angiosperms. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 274: 227–274.
Bennett M. D., Smith J. B. (1991) Nuclear DNA amounts in Angiosperms. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 334: 309–345.
Bennett M. D., Leitch I. J. (1995) Nuclear DNA amounts in Angiosperms. Ann. Bot. 76: 113–176.
Brown G. R., Amarasinghe V., Kiss G., Carlson J. E. (1993) Preliminary karyotype and chromosomal localization of ribosomal DNA sites in white spruce using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genome 36: 310–316.
Buckler E. S. IV., Holtsford T. P. (1996)Zea systematics: ribosomal evidence. Mol. Biol. Evol. 13: 612–622.
Buitendijk J. H., Boon E. J., Ramanna M. S. (1997) Nuclear DNA content in twelve species ofAlstroemeria L. and some of their hybrids. Ann. Bot. 79: 343–353.
Campbell C. S., Baldwin B. G., Donoghue M. J., Wojciechowski M. F. (1993) Toward a phylogeny ofAmelanchier (Rosaceae: Maloideae): evidence from sequences of the internal transcribed spacers (ITS) of nuclear ribosomal DNA (nrDNA). Am. J. Bot. 80 (Suppl.): abstract 398.
Campbell C. S., Wojciechowski M. F., Baldwin B. G., Alice L. A., Donoghue M. J. (1997) Persistent nuclear ribosomal DNA sequence polymorphism in theAmelanchier agamic complex (Rosaceae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 14: 81–90.
Crane C. F., Price H. J., Stelly D. M., Czeschin D. G., Jr. (1993) Identification of a homologous chromosome pair by in situ DNA hybridization to ribosomal RNA loci in meiotic chromosomes of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Genome 36: 1015–1022.
Dover G. (1982) Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature 299: 111–117.
Dover G. (1986) Molecular drive in multigene families: how biological novelties arise, spread, and are assimilated. Trends in Genetics 2: 159–165.
Dover G. (1989) Linkage disequilibrium and molecular drive in the rDNA family. Genetics 122: 249–252.
Dvořák J. (1990) Evolution of multigene families: the ribosomal RNA loci of wheat and related species. In: Brown A. H. D., Klegg M. T., Kahler A. L., Weir B. S. (eds.) Plant population genetics, breeding, and genetic resources. Sunderland, Sinauer Associates, pp. 83–97.
Edwards K., Johnstone C., Thompson C. (1991) A simple and rapid method for the preparation of plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis. Nucl. Acids Res. 19: 1349.
Enea V., Corredor V. (1991) The evolution of plasmodial stage-specific rRNA genes is dominated by gene conversion. J. Mol. Evol. 32: 183–186.
Furata Y. (1975) Quantitative variation of nuclear DNA in genusAegilops. Jap. J. Genet. 50: 383–392.
Gasser R. B., Hoste H. (1995) Genetic markers for closely-related parasitic nematodes. Mol. Cell. Probes 9: 315–320.
Gerlach W. L., Bedbrook J. R. (1979) Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley. Nucl. Acids Res. 7: 1869–1885.
Goff L. J., Moon D. A., Coleman A. W. (1994) Molecular delineation of species and species relationships in the red algal agarophytesGracilariopsis andGracilaria (Gracilariales). J. Phycol. 30: 521–537.
Hamby R. K., Zimmer E. A. (1992) Ribosomal RNA as a phylogenetic tool in plant systematics. In: Soltis P. S., Soltis D. E., Doyle J. J. (eds.) Molecular systematics of plants. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp. 50–91.
Hanson R. E., Islam-Faridi M. N., Percival E. A., Crane C. F., Ji Y., McKnight T. D., Stelly D. M., Price H. J. (1996) Distribution of 5S and 18–28S rDNA loci in a tetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and its putative diploid ancestors. Chromosoma 105: 55–61.
Harlton C. E., Lévesque C. A., Punja Z. K. (1995) Genetic diversity inSclerotium (Athelia) rolfsii and related species. Phytopathol. 85: 1269–1281.
Hillis D. M., Dixon M. T. (1991) Ribosomal DNA: molecular evolution and phylogenetic inference. Quart. Rev. Biol. 66: 411–453.
Hoste H., Chilton N. B., Gasser R. B., Beveridge I. (1995) Differences in the second internal transcribed spacer (ribosomal DNA) between five species ofTrichostrongylus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae). Int. J. Parasitol. 25: 75–80.
Kamstra S. A., Kuipers A. G. J., De Jeu M. J., Ramanna M. S., Jacobsen E. (1997) Physical localisation of repetitive DNA sequences inAlstroemeria: karyotyping of two species with species-specific and ribosomal DNA. Genome 40: 652–658.
Karvonen P., Karjalainen M., Savolainen O. (1993) Ribosomal RNA genes in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.): chromosomal organization and structure. Genetica 88: 59–68.
Karvonen P., Szmidt A. E., Savolainen O. (1994) Length variation in the internal transcribed spacers of ribosomal DNA inPicea abies and related species. Theor. Appl. Genet. 89: 969–974.
Kim K.-J., Jansen R. K. (1994) Comparisons of phylogenetic hypotheses among different data sets in dwarf dandelions (Krigia, Asteraceae): additional information from internal transcribed spacer sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Plant Syst. Evol. 190: 157–185.
Kuipers G. J., Van Os D. P. M., De Jong J. H., Ramanna M. S. (1997) Molecular cytogenetics ofAlstroemeria: identification of parental genomes in interspecific hybrids and characterization of repetitive DNA families in constitutive heterochromatin. Chrom. Res. 5: 31–39.
Lubaretz O., Fuchs J., Ahne R., Meister A., Schubert I. (1996) Karyotyping of three Pinaceae species via fluorescent in situ hybridization and computer-aided chromosome analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 92: 411–416.
Nagylaki T. (1984) Evolution of multigene families under interchromosomal gene conversion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA 81: 3796–3800.
Nagylaki T., Petes T. D. (1982) Intrachromosomal gene conversion and the maintenance of sequence homogeneity among repeated genes. Genetics 100: 315–337.
O'Kane S. L., Schaal B. A., Al-Shehbaz I. A. (1996) The origins ofArabidopsis suecica (Brassicaceae) as indicated by nuclear rDNA sequences. Syst. Bot. 21: 559–566.
Perelson A. S., Bell G. I. (1977) Mathematical models for the evolution of multigene families by unequal crossing over. Nature 265: 304–310.
Petes T. D. (1980) Unequal meiotic recombination within tandem arrays of yeast ribosomal DNA genes. Cell 19: 765–774.
Rogers S. O., Bendich A. J. (1987) Ribosomal RNA genes in plants: variability in copy number and in the intergenic spacer. Plant Mol. Biol. 9: 509–520.
Sambrook J., Fritsch E. F., Maniatis T. (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, second edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York.
Sanders I. R., Alt M., Groppe K., Boller T., Wiemken A. (1995) Identification of ribosomal DNA polymorphisms among and within spores of the Glomales: application to studies on the genetic diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities. New Phytol. 130: 419–427.
Sang T., Crawford D. J., Stuessy T. F. (1995) Documentation of reticulate evolution in peonies (Paeonia) using internal transcribed spacer sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA: implications for biogeography and concerted evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA 92: 6813–6817.
Smith G. P. (1976) Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science 191: 528–534.
Suh Y., Thien L. B., Reeve H. E., Zimmer E. A. (1993) Molecular evolution and phylogenetic implications of internal transcribed spacer sequences of ribosomal DNA in Winteraceae. Am. J. Bot. 80: 1042–1055.
Szostak J. W., Wu R. (1980) Unequal crossing over in the ribosomal DNA ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 284: 426–430.
Teoh S. B., Rees H. (1976) Nuclear DNA amounts in populations ofPicea andPinus species. Heredity 36: 123–137.
Torres R. A., Ganal M., Hemleben V. (1990) GC balance in the internal transcribed spacers ITS1 and ITS2 of nuclear ribosomal RNA genes. J. Mol. Evol. 30: 170–181.
Wakamiya I., Newton R. J., Johnston J. S., Price H. J. (1993) Genome size and environmental factors in the genusPinus. Am. J. Bot. 80: 1235–1241.
Wendel J. F., Schnabel A., Seelanan T. (1995) Bidirectional interlocus concerted evolution following allopolyploid speciation in cotton (Gossypium). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA 92: 280–284.
Wesson D. M., Porter C. H., Collins F. H. (1992) Sequence and secondary structure comparisons of ITS rDNA in mosquitoes (Diptera:Culicidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1: 253–269.
White T. J., Bruns T., Lee S., Taylor J. (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis M. A., Gelfand D. H., Sninsky J. J., White T. J. (eds.) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 315–322.
Zhuo L., Sajdak S. L., Phillips R. B. (1994) Minimal intraspecific variation in the sequence of the transcribed spacer regions of the ribosomal DNA of lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush). Genome 37: 664–671.
Zijlstra C., Lever A. E. M., Uenk B. J., Van Silfhout C. H. (1995) Differences between ITS regions of isolates of root-knot nematodesMeloidogyne hapla andM. chitwoodi. Phytopathol. 85: 1231–1237.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Booy, G., Van der Schoot, J. & Vosman, B. Heterogeneity of the internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) inTulipa (Liliaceae). Pl Syst Evol 225, 29–41 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00985457
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00985457