Abstract
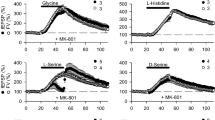
The effects of structural analogues, excitatory amino acids and certain drugs on spontaneous and potassium-stimulated exogenous taurine and GABA release were investigated in mouse cerebral cortex slices using a superfusion system. Spontaneous efflux of both amino acids was rather slow but could be enhanced by their uptake inhibitors. Taurine efflux was facilitated by exogenous taurine, hypotaurine, β-alanine and GABA, whereas GABA, nipecotic acid and homotaurine effectively enhanced GABA release. The stimulatory potency of the analogues closely corresponded to their ability to inhibit taurine and GABA uptake, respectively, indicating that these efflux processes could be mediated by the carriers operating outwards. Glutamate induced GABA release, whereas taurine efflux was potentiated by aspartate, glutamate, cysteate, homocysteate and kainate. The centrally acting drugs, including GABA agonists and antagonists, as well as the proposed taurine antagonist TAG (6-aminomethyl-3-methyl-4H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide), had no marked effects on spontaneous taurine and GABA release. Potassium ions stimulated dosedependently both taurine and GABA release from the slices, the responses of taurine being strikingly slow but sustained. Exogenous GABA and nipecotic acid accelerated the potassium-stimulated GABA release, whereas picrotoxin and bicuculline were ineffective. The potassium-stimulated taurine release was unaltered or suppressed by exogenous taurine and analogues, differing in this respect from GABA release. The apparent magnitude of the depolarization-induced GABA release is thus influenced by the function of membrane transport sites, but the same conclusion cannot be drawn with regard to taurine. Haloperidol and imipramine were able to affect the evoked release of both taurine and GABA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levi, G. 1984, Release of putative transmitter amino acids. Pages 463–509in Lajtha, A. (ed), Handbook of Neurochemistry, Vol. 6, 2nd edn., Plenum Press, New York.
Oja, S. S., and Kontro, P. 1983. Taurine. Pages 501–533, in Lajtha, A. (ed.), Handbook of Neurochemistry, Vol. 3, 2nd edn, Plenum Press, New York.
Martin, D. L., and Shain, W. 1979. High-affinity transport of taurine and β-alanine and low-affinity transport of γ-aminobutyric acid by a single transport system in cultured glioma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 254:7076–7084.
Kontro, P., and Oja, S. S. 1981. Hypotaurine transport in brain slices: comparison with taurine and GABA. Neurochem. Res. 6:1179–1191.
Kontro, P. 1982. Effects of cations on taurine, hypotaurine, and GABA uptake in mouse brain slices. Neurochem. Res. 7:1391–1401.
Holopainen, I., Kontro, P., Frey, H. J., and Oja, S. S. 1983. Taurine, hypotaurine, and GABA uptake by cultured neuroblastoma cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 10:83–92.
Holopainen, I., and Kontro, P. 1986. High-affinity uptake of taurine and β-alanine in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 11:207–215.
Kontro, P., and Oja, S. S. 1983. Mutual interactions in the transport of taurine, hypotaurine and GABA in brain slices. Neurochem. Res. 8:1377–1387.
Huxtable, R. J., Laird, H. E. II., and Lippincott, S. E. 1979. The transport of taurine in the heart and the rapid depletion of tissue taurine content by guanidinoethyl sulfonate. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 211:465–471.
Korpi, E. R., and Oja, S. S. 1984. Comparison of two superfusion systems for study of neurotransmitter release from rat cerebral cortex slices. J. Neurochem. 43:236–242.
Oja, S. S. and Kontro, P. 1987. Cation effects on taurine release from brain slices: comparison to GABA. J. Neurosci. Res., in press.
Korpi, E. R., and Oja, S. S. 1979. Efflux of phenylalanine from rat cerebral cortex slices as influenced by extra- and intracellular amino acids. J. Neurochem. 32:789–796.
Snedecor, G. W. 1956. Statistical Methods. 5th edn. Iowa State College Press, Ames.
Olsen, R. W., Lamar, E. E., and Bayless, J. D. 1977. Calcium induced release of γ-aminobutyric acid from synaptosomes: effects of tranquilizer drugs. J. Neurochem. 28:299–305.
Brennan, M. J. W., and Cantrill, R. C. 1978. The effect of DABA and β-alanine on the efflux of [3H]GABA from preloaded rat brain synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 31:1339–1341.
Snodgrass, S. R. 1978. Use of3H-muscimol for GABA receptor studies. Nature (Lond.) 273:392–394.
Do Nascimento, J. L. M., and Mello, F. G. 1985. Induced release of γ-aminobutyric acid by a carrier-mediated, highaffinity uptake ofl-glutamate in cultured chick retina cells. J. Neurochem. 45:1820–1827.
Kontro, P. 1979. Components of taurine efflux in rat brain synaptosomes. Neuroscience 4:1745–1749.
Kontro, P. 1984. Comparison of taurine, hypotaurine and β-alanine uptake in brain synaptosomal preparations from developing and adult mouse. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2:465–470.
Johnston, G. A. R., Stephanson, A. L., and Twitchin, B. 1976. Uptake and release of nipecotic acid by rat brain slices. J. Neurochem. 26:83–87.
Early, S. L., Michaelis, E. K., and Mertes, M. P. 1981. Pharmacological specificity of synaptosomal and synaptic membrane γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transport processes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 30:1105–1113.
Levi, G., Banay-Schwartz, M., and Raiteri, M. 1978. Uptake, exchange and release of GABA in isolated nerve endings. Pages 327–350 in Fonnum, F. (ed.) Amino Acids as Chemical Transmitters, Plenum Press, New York.
Lerma, J., Herranz, A. S., Herreras, O., Mu noz, D., Solis, J. M., Del Rio, R. M., and Delgado, J. M. R. 1985. γ-Aminobutyric acid greatly increases the in vivo extracellular taurine in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 44:983–986.
Szerb, J. C. 1982. Effect of nipecotic acid, a γ-aminobutyric acid transport inhibitor, on the turnover and release of γ-aminobutyric acid in rat cortical slices. J. Neurochem. 39:850–858.
Jaffe, E. H., Hernandez, N., and Holder, L. G. 1984. Study of the mechanism of release of [3H]GABA from a teleost retina in vitro. J. Neurochem. 43:1226–1235.
Lerma, J., Herreras, O., Herranz, A. S., Mu oz, D., and Del Rio, R. M. 1984. In vivo effects of nipecotic acid on levels of extracellular GABA and taurine, and hippocampal excitability. Neuropharmacology 23:595–598.
Kontro, P. 1983. β-Alanine uptake by mouse brain slices. Neuroscience 8:153–159.
Hammerstad, J. P., and Lytle, C. R. 1976. Release of [3H]GABA from rat cortical slices: neuronal vs. glial origin. J. Neurochem. 27:399–403.
Hammerstad, J. P., Cawthon, M. L., and Lytle, C. R. 1979. Release of [3H]GABA from in vitro preparations: comparison of the effect of DABA and β-alanine on the K+ and protoveratrine stimulated release of [3H]GABA from brain slices and synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 32:195–202.
Borg, J., Balcar, V. J., Mark, J., and Mandel, P. 1979. Characterization of taurine uptake by neuronal and glial cells in culture. J. Neurochem. 32:1801–1805.
Moran, J., and Pasantes-Morales, H. 1983. Effects of excitatory amino acids, and of their agonists and antagonists on the release of neurotransmitters from the chick retina. J. Neurosci. Res. 10:261–271.
Kontro, P., and Oja, S. S. 1984. Effects of 2-guanidinoethanesulphonic acid, convulsant and anticonvulsant drugs and amino acids on taurine uptake in mouse brain. Acta Univ. Tamper. [B] 21:30–36.
Mori, A., Katayama, Y., Yokoi, I., and Matsumoto, M. 1981. Inhibition of taurocyamine (guanidinotaurine)-induced seizures by taurine. Pages 41–48 in Schaffer, S. W., Baskin, S. I., and Kocsis, J. J. (eds) The Effects of Taurine on Excitable Tissues, Spectrum Press, Philadelphia.
Baba, A., Yamamoto, T., Morimoto, H., Matsuda, T., and Iwata, H. 1984. Release of [3H]γ-aminobutyric acid by taurocyamine in rat brain slices. Jap. J. Pharmacol. 35:465–467.
Ferkany, J. W., and Coyle, J. T. 1983. Kainic acid selectively stimulates the release of endogenous excitatory acidic amino acids. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 225:399–406.
Poli, A., Contestabile, A., Migani, P., Rossi, L., Rondelli, C., Virgili, M., Bissoli R., and Barnabei, O. 1985. Kainic acid differentially affects the synaptosomal release of endogenous and exogenous amino acid neurotransmitters. J. Neurochem. 45:1677–1686.
Kato, S., Negishi, K., and Tsunenobu, T. 1985. Dopamine inhibits calcium-independent γ-[3H]aminobutyric acid relase induced by kainate and high K+ in the fish retina. J. Neurochem. 44:893–899.
Lehmann, A., Isacsson, H., and Hamberger, A. 1983. Effects of in vivo administration of kainic acid on the extracellular amino acid pool in the rabbit hippocampus. 40:1314–1320.
Lehmann, A., Hagberg, H., Jacobson, J., and Hamberger, A. 1985. Effects of stacus epilepticus on extracellular amino acids in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 359:147–151.
Yarbrough, G. G., Singh, D. K., and Taylor, D. A. 1981. Neuropharmacological characterization of a taurine antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 219:604–613.
Korpi, E. R., Kontro, P., Nieminen, K., Marnela, K.-M., and Oja, S. S. 1981. Spontaneous and depolarization-induced efflux of hypotaurine from mouse cerebral cortex slices: comparison with taurine and GABA. Life Sci. 29:811–816.
Girault, J. A., Barbeito, L., Scampinato, U., Gozlan, H., Glowinski, J., and Besson, M.-J. 1986. In vivo release of endogenous amino acids from the rat striatum: further evidence for a role of glutamate and aspartate in corticostriatal neurotransmission. J. Neurochem. 47:98–106.
Lehmann, A., Sandberg, M., and Huxtable, R. J. 1986. In vivo release of neuroactive amines and amino acids from the hippocampus of seizure-resistant and seizure-susceptible rats. Neurochem. Int. 8:513–520.
Smith, L. F. P., and Pycock, C. J. 1982. Potassium-stimulated release of radiolabelled taurine and glycine from the isolated rat retina. J. Neurochem. 39:653–658.
Kalsner, S. 1985. Is there feedback regulation of neurotransmitter release by autoreceptors? Biochem. Pharmacol. 34:4085–4097.
Brennan, M. J. W., Cantrill, R. C., Oldfield, M., and Krogsgaard-Larsen, P. 1980. Inhibition of γ-aminobutyric acid release by γ-aminobutyric acid agonist drugs. Pharmacology of the γ-aminobutyric acid autoreceptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 19:27–30.
Arbilla, S., Kamal, L., and Langer, S. Z. 1979. Presynaptic GABA autoreceptors on GABAergic nerve endings of the rat substantia nigra. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 57:211–217.
Collins, G. G. S. 1980. Release of endogenous amino acid neurotransmitter candidates from rat olfactory cortex slices: possible regulatory mechanisms and the effects of pentobarbitone. Brain Res. 190:517–528.
Namima, M., Okamoto, K., and Sakai, Y. 1983. Modulatory action of taurine on the release of GABA in cerebellar slices of the guinea pig. J. Neurochem. 40:1–9.
Leach, M. J. 1979. Effect of taurine on release of3H-GABA by depolarizing stimuli from superfused slices of rat brain cerebral cortex in vitro. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 31:533–535.
Kontro, P., and Oja, S. S. 1985. Properties of sodium-independent taurine binding to brain synaptic membranes. Pages 249–259in Oja, S. S. Ahtee, L., Kontro, P., and Paasonen, M. K. (eds.) Taurine: Biological Actions and Clinical Perspectives, Alan R. Liss, New York.
Johnston, G. A. R., and Mitchell, J. F. 1971. Effect of bicuculline, metrazol, picrotoxin and strychnine on the release of [3H]GABA from rat brain slices. J. Neurochem. 18:2441–2446.
Tappaz, M., and Pacheco, H. 1973. Effects of convulsant and anticovvulsant drugs on the spontaneous and induced release of GABA14C from cortex slices of rat brain. J. Pharmacol. (Paris) 4:433–452.
Olsen, R. W., Ticku, M. K., Van Ness, P. C., and Greenlee, D. 1978. Effects of drugs on γ-aminobutyric acid receptors, uptake, release and synthesis in vitro. Brain Res. 139:277–294.
Korf, J., and Venema, K. 1983. Desmethylimipramine enhances the release of endogenous GABA and other neurotransmitter amino acids from the rat thalamus. J. Neurochem. 40:946–950.
Harris, M., Hopkin, J. M., and Neal, M. J. 1973. Effect of centrally acting drugs on the uptake of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br. J. Pharmacol. 47:229–239.
Schmid, R., Sieghart, W., and Karobath, M. 1975. Taurine uptake in synaptosomal fractions of rat cerebral cortex. J. Neurochem. 25:5–9.
Schousboe, A., Fosmark, H., and Svenneby, G. 1976. Taurine uptake in astrocytes cultured from dissociated brain hemispheres. Brain Res. 116:158–164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kontro, P., Oja, S.S. Taurine and GABA release from mouse cerebral cortex slices: Effects of structural analogues and drugs. Neurochem Res 12, 475–482 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00972301
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00972301