Abstract
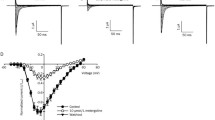
We have previously shown that volatile anesthetics inhibit glutamate-stimulated [3H]MK-801 binding to the ionophore of NMDA receptor complexes in rat brain. In the present study, we examined the influence of enflurane and halothane on NMDA-stimulated45Ca uptake by a microvesicle fraction isolated from rat brain. NMDA stimulated45Ca uptake (30 sec) by rat brain microvesicles by up to 70% with an EC50 of 1.4±0.5 μM. The NMDA-stimulated45Ca uptake was inhibited by MK-801 and D-AP-5 with IC50's of ≈10 μM. Enflurane and halothane inhibited45Ca uptake stimulated by 100 μM NMDA by as much as 60–80% with IC50's of 0.2–0.3 mM, concentrations achieved during routine clinical use. Basal45Ca uptake measured in the absence of agonist was not affected by the anesthetics. Glycine did not affect the level of NMDA-stimulated45Ca uptake, but markedly reduced the inhibition of uptake caused by enflurane and halothane. Preincubation of microvesicles with NMDA resulted in a desensitization of NMDA-stimulated45Ca uptake, with a t1/2 of ≈20 sec. Enflurane and halothane diminished both the extent and rate of development of this desensitization, as did glycine. These findings support the idea that volatile anesthetic interference with neurotransmission at NMDA receptor complexes contributes to the development of the anesthetic state.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Foster, A. C., and Fagg, G. E. 1987. Taking apart NMDA receptors. Nature (Lond.) 329:395–396.
Seeburg, P. H. 1993. The molecular biology of mammalian glutamate receptor channels. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 14:197–303.
Kaplita, P. V., and Ferkany, J. W. 1990. Evidence for direct interactions between NMDA and glycine recognition sites in brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 188:175–179.
Larrabee, M. G., and Posternak, J. M. 1952. Selective action of anesthetics on synapses and axons in mammalian sympathetic ganglia. J. Neurophysiol. 15:91–114.
Franks, N. P., and Lieb, W. R. 1984. Do anesthetics act by competitive binding to specific receptors? Nature (Lond.) 310:599–601.
Franks, N. P., and Lieb, W. R. 1987. What is the molecular nature of general anaesthetic target sites? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 8:169–174.
Scheller, M. S., Zornow, M. H., Fleischer, J. E., Shearman, G. T., and Greber, T. F. 1989. The noncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, MK-801 profoundly reduces volatile anesthetic requirements in rabbits. Neuropharmacology 28:677–681.
Daniell, L. C. 1990. The noncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists, MK-801, phencyclidine, and ketamine, increase the potency of general anesthetics. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 36:111–115.
Daniell, L. C. 1991. Effect of CGS 19755, a competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist, on general anesthetic potency. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 40:767–769.
Daniell, L. C. 1992. Alteration of general anesthetic potency by agonists and antagonists of the polyamine binding site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 261:304–310.
Yang, J., and Zorumski, C. F. 1991. Effects of isoflurane on N-methyl-D-aspartate gated ion channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 625:287–289.
Puil, E., El-Beheiry, H., and Baimbridge, K. G. 1990. Anesthetic effects on glutamate-stimulated increase in intraneuronal calcium. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 255:955–961.
Martin, D. C., Abraham, J. E., Plagenhoef, M., and Aronstam, R. S. 1991. Volatile anesthetics and NMDA receptors. Enflurane inhibition of glutamate-stimulated [3H]MK-801 binding and reversal by glycine. Neurosci. Lett. 132:73–76.
Martin, D. C., Pruett, J. K., and Aronstam, R. S. 1993. Test-tube equilibration of volatile anaesthetic concentrations. Br. J. Anaesthesia 70:365–367.
Foster, A. C., and Wong, E. H. F. 1987. The novel anticonvulsant MK-801 binds to the activated state of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in rat brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 91:403–409.
Baron, B. M., Harrison, B. L., Miller, F. P., McDonald, I. A., Salituro, F. G., Schmidt, C. J., Sorensen, S. M., White, H. S., and Palfreyman, M. G. 1990. Activity of 5,7-dichlorokynurenic acid, a potent antagonist at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-associated glycine binding site. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 38:554–561.
Murphy, D. E., Hutchison, A. J., Hurt, S. D., Williams, M., and Sills, M. A. 1988. Characterization of the binding of [3H]CGS 19755: a novel N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist with nanomolar affinity in rat brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 95:932–938.
Sills, M. A., Fagg, G., Pozza, M., Angst, C., Brundish, D. E., Hurt, S. D., Wilusz, E. J., and Williams, M. 1991. [3H]CGP 39653: a new N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist radioligand with low nanomolar affinity in rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 192:19–24.
Kloog, Y., Nadler, V., and Sokolovsky, M. 1988. Mode of binding of [3H]dibenzocycloalkenimine (MK-801) to the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor and its therapeutic implication. FEBS Lett. 230:167–170.
Huettner, J. E., and Bean, B. P. 1988. Block of N-methyl-D-aspartate-activated current by the anticonvulsant MK-801: selective binding to open channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:1307–1311.
Bonhaus, D. W., and McNamara, J. O. 1992. Uncompetitive antagonist binding: a biochemical index of activation of the NMDA receptor-coupled ion channel. Pages 181–188, in Avanzini, G., Engel Jr., J., Fariello, R. and Heinemann U. I. N. (eds.), Neurotransmitters in Epilepsy, Elsevier, New York.
Davies, S. N., Alford, S. T., Coan, E. J., Lester, R. A. J., and Collinridge, G. L. 1988. Ketamine blocks an NMDA receptor-mediated component of synaptic transmission in rat hippocampus in a voltage-dependent manner. Neurosci. Lett. 92:213–217.
Yamamura, T., Harada, K., Okamura, A., and Kemmotsu, O. 1990. Is the site of action of ketamine anesthesia the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor? Anesthesiology 72:704–710.
Rabe, C. S., and Tabakoff, B. 1990. Glycine site-directed agonists reverse the actions of ethanol at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 38:753–757.
Martin, D. C., Dennison, R. L., and Aronstam, R. S. 1992. Barbiturate interactions with N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in rat brain. Mol. Neuropharmacol. 2:255–259.
Teichberg, V. I., Tal, N., Goldberg, O., and Luini, A. 1984. Barbiturates, alcohols and CNS excitatory neurotransmission: Specific effects on the kainate and quisqualate receptors. Brain Res. 291: 285–292.
Mazze, R. I., Rice, S. A., and Baden, J. M. 1985. Halothane, isoflurane, and enflurane MAC in pregnant and nonpregnant female and male mice and rats. Anesthesiology 62:339–341.
Mayer, M. L., Vyklicky, L., and Clements, J. 1989. Regulation of NMDA receptor desensitization in mouse hippocampal neurons by glycine. Nature (Lond.) 33:425–427.
Lerma, J., Zukin, R. S., and Bennett, M. V. L. 1990. Glycine decreases desensitization of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes and is required for NMDA responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:2354–2358.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aronstam, R.S., Martin, D.C. & Dennison, R.L. Volatile anesthetics inhibit NMDA-stimulated45Ca uptake by rat brain microvesicles. Neurochem Res 19, 1515–1520 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00968999
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00968999