Summary
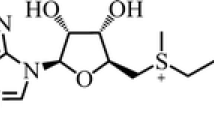
The addition of L-methionine to cultures ofStreptomyces refuineus producing anthramycin, results in an apparent decrease in the antibiotic titer. It has been shown that this effect is not due to the inhibition of tyrosinase, an enzyme implicated in anthramycin biosynthesis. The inhibitory effect also appears unlikely to be due to a regulatory role played by methionine in a non-precursor fashion. Experiments with radiolabeled anthramycin have revealed that the reduced yields of the antibiotic are due to the interaction of anthramycin with generated reactive metabolites produced in the methionine-supplemented cultures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agroudelis, A.D., Eble, T.E., Fox, J.A., Mason, D.J. (1969). Biochemistry8, 3408–3411
Cavallito, C.J. (1946). J.Biol.Chem.164, 29–34
Demain, A.L., Newkirk, J.F. (1962). J.Biol.Chem.10, 321–325
Demain, A.L., Newkirk, J.F., Hendlin, D. (1963). J.Bacteriol.85, 339–344
Drew, S.W., Demain, A.L. (1973). Biotechnol.Bioeng.15, 743–754
Grunberg, E., Prince, H.N., Titsworth, E., Beskid, G., Tendler, M.D. (1966). Chemotherapia11, 249–260
Hornemann, U., Speedie, M.K., Hurley, L.H., Floss, H.G. (1970). Biochem.Biophys. Res.Commun.39, 594–599
Horwitz, S.B., Grollman, A.P. (1968). Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 21–24
Horwitz, S.B., Chang, S.C., Grollman, A.P., Berkovec, A.B. (1971). Science174, 159–161
Hurley, L.H., Zmijewski, M. (1974). J.Chem.Soc. (Chem.Comm.) 337–338
Hurley, L.H., Zmijewski, M., Chang, C.J. (1975). J.Amer.Chem.Soc.97, 4372–4378
Kohn, K.W., Spears, C.L. (1970). J.Mol.Biol.51, 551–572
Kohn, K.W. (1975). Antibiotics, III, J.W. Corcoran and Fred E. Hahn, eds. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer
Mazumdar, S.K., Kutzner, H.J. (1962). Appl.Microbiol.10, 157–165
Rogers, T.O., Birnbaum, J. (1974). Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy5, 121–132
Stefanovich, V., Ceprini, M.O. (1971). J.Pharm.Sci.60, 781–783
Wagner, E.S., Gorman, M. (1971). J.Antibiotics24, 647–650
Yoshida, H., Oka, T., Tanaka, Y., Nakayama, K. (1974). Agr.Biol.Chem.38, 873–874
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gairola, C., Hurley, L. The mechanism for the methionine mediated reduction of anthramycin yields inStreptomyces refuineus fermentations. European J. Appl Microbiol. 2, 95–101 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00942352
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00942352