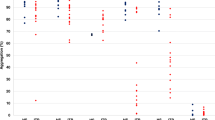
Summary
The platelet glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa receptor can bind fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor, and other adhesive ligands; this binding is the final common pathway mediating platelet aggregation. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the safety and platelet inhibitory characteristics of the Fab fragment of the murine monoclonal anti-GPIIb/IIIa 7E3 antibody (m7E3 Fab) when administered intravenously as a single bolus dose, as a single and repeat bolus dose, and as a single bolus dose followed by continuous infusions of varying duration. Various dosage regimens of m7E3 Fab were studied in 74 patients with stable angina. Dosage regimens included single doses of m7E3 Fab from 0.1 to 0.3 mg/kg, a single dose of 0.20–0.30 mg/kg, and a repeat dose of 0.05 mg/kg, or a loading dose followed by a continuous infusion of m7E3 Fab for up to 36 hours. To assess the effect of m7E3 Fab on platelet function, quantitative blockade of GPIIb/IIIa receptors, inhibition of ex vivo platelet aggregation, and template bleeding time were measured in all patients. Dose-dependent inhibition of platelet function was evident in response to escalating bolus doses of m7E3 Fab, with maximum inhibition observed at 0.25–0.30 mg/kg body weight; at the 0.30 mg/kg dose, mean (±SE) GPIIb/IIIa receptor blockade was 81±3%, ex vivo platelet aggregation in response to 20 µM ADP was 14±6% of baseline, and the median bleeding time was >20 minutes. Although platelet function gradually recovered following a single bolus injection, platelet inhibition could be sustained by continuous, low-dose infusion of the antibody. Platelet inhibition occurred within minutes, but m7E3 Fab that did not bind to platelets cleared rapidly from circulation. Sixteen percent of the m7E3 Fab-injected subjects exhibited low titer, human anti-murine antibody responses. No significant bleeding or allergic reactions were observed in any patients. One of the 74 patients developed transient thrombocytopenia soon after receiving m7E3 Fab. These studies establish that m7E3 Fab can be administered safely at doses that cause profound inhibition of platelet function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Willerson JT, Golino P, Edit J, Campbell WB, Buja LM. Specific platelet mediators and unstable coronary artery lesions. Experimental evidence and potential clinical implications.Circulation 1989;1:198–205.
Grande P, Grauholt AM, Madsen JK. Unstable angina pectoris. Platelet behaviour and prognosis in progressive angina and intermediate coronary syndrome.Circulation 1990;81:116–119.
Sherman CT, Litvock F, Grundfest W, et al. coronary angioscopy in patients with unstable angina pectoris.N Engl J Med 1986;315:913–919.
Fitzgerald DJ, Roy L, Catella F, FitzGerald GA. Platelet activation in unstable coronary artery disease.N Engl J Med 1986;315:983–989.
Jang IK, Gold HK, Ziskind AA. Differential sensitivity of erythrocyte-rich and platelet-rich arterial thrombi to lysis with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator: A possible explanation for resistance to coronary thrombolysis.Circulation 1989;79:920–928.
Fitzgerald DJ, Catella F, Roy L, FitzGerald GA. Marked platelet activation in vivo after intravenous streptokinase in patients with acute myocardial infarction.Circulation 1988;77:142–150.
Golino P, Ashton JH, Glas-Greenwalt P, McNatt J, Buja LM, Willerson JT. Mediation of reocclusion by thromboxane A2 and serotonin after thrombolysis with tissue-type plasminogen activator in a canine preparation of coronary thrombosis.Circulation 1988;77:678–684.
Coller BS. Platelets and thrombolytic therapy.N Engl J Med 1990;322:33–42.
Peerschke EI. The platelet fibrinogen receptor.Semin Hematol 1985;22:241–259.
Phillips DR, Charo IF, Parise LV, Fitzgerald LA. The platelet membrane glycoprotein complex.Blood 1988;71:831–843.
Fitzgerald DJ, Wright F, FitzGerald GA. Increased thromboxane biosynthesis during coronary thrombolysis. Evidence that platelet activation and thromboxane A2 modulate the response to tissue-type plasminogen activator in vivo.Circ Res 1989;65:83–94.
Cohen I, Burk DL, White JG. The effect of peptides and monoclonal antibodies that bind to platelet glycoprotein Iib/IIIa complex on the development of clot tension.Blood 1989;73:1880–1887.
Altieri DC, Edgington TS. A monoclonal antibody reacting with distinct adhesion molecules defines a transition in the functional state of the receptor CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1).J Immunol 1988;141:2656–2660.
Coller BS, Scudder LE, Berger HJ, Iuliucci JD. Inhibition of human platelet function in vivo with a monoclonal antibody. With observations on the newly dead as experimental subjects.Ann Intern Med 1988;109:635–638.
Yasuda T, Gold HK, Fallon JT, et al. Monoclonal antibody against the platelet glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa receptor prevents coronary artery reocclusion after perfusion with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator in dogs.J Clin Invest 1988;81:1284–1291.
Gold HK, Coller BS, Yasuda T, et al. Rapid and sustained coronary artery recanalization with combined bolus injection of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator and monoclonal antiplatelet GPIIb/IIIa antibody in a canine preparation.Circulation 1988;77:670–677.
Coller BS, Peerschke EI, Seligsohn U, Scudder LE, Nurden AT, Rosa JP. Studies on the binding of an anlloimmune and two murine monoclonal antibodies to the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex receptor.J Lab Clin Med 1986;107:384–392.
Coller BS, Scudder LE. Inhibition of dog platelet function by in vivo infusion of F(ab′)2 fragments of a monoclonal antibody to the plateletl glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor.Blood 1985;66:1456–1459.
Coller BS. A new murine monoclonal antibody reports an activation-dependent change in the conformation and/or microenvironment of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex.J Clin Invest 1985;76:101–108.
Coller BS, Folts JD, Smith SR, Scudder LE, Jordan R. Abolition of in vivo platelet thrombus formation in primates with monoclonal antibodies to the platelet GPIIb/IIIa receptor.Circulation 1989;6:1766–1774.
Coller BS, Peerschke EI, Scudder LE, Sullivan CA. A murine monoclonal antibody that completely blocks the binding of fibrinogen to platelets produces a thrombasthenic-like state in normal platelets and binds to glycoproteins IIb and/or IIIa.J Clin Invest 1983;72:325–338.
Mickelson JK, Simpson PJ, Lucchesi BR. Antiplatelet monoclonal F(ab′)2 antibody directed against the platelet GPIIb/IIIa receptor complex prevents coronary artery thrombosis in the canine heart.J Mol Cell Cardiol 1989;21:393–405.
Gold HK, Gimple LW, Yasuda T, et al. Pharmacodynamic study of F(ab′)2 fragments of murine monoclonal antibody 7E3 directed against human platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa in patients with unstable angina pectoris.J Clin Invest 1990;86:651–659.
Watts IS, Keery RJ, Lumley P. Differential ability of agonists to express distinct pools of fibrinogen (GPIIb/IIIa) receptors which can mediate the aggregation of human platelets.Thromb Hemost 1989;62:955–961.
Kroll MH, Schafer AI. Biochemical mechanisms of platelet activation.Blood 1989;74:1181–1195.
Richardson PD, Davies MJ, Born GV. Influence of plaque configuration and stress distribution on fissuring of coronary atherosclerotic plaques.Lancet 1989;2:941–944.
Davies MJ, Bland JM, Hangartner JR, Angelini A, Thomas AC. Factors influencing the presence or absence of acute coronary artery thrombi in sudden ischemic death.Eur Heart J 1989;10:203–208.
Dillman RO. Monoclonal antibodies for treating cancer.Ann Intern Med 1989;111:592–603.
Jordan RE, Wagner CL, McAleer MF, Spitz MS, Mattis JA. Evaluation of the potency and immunogenicity of 7E3 F(ab′)2 and Fab fragments in monkeys.Circulation 1990;82:(Suppl III):661.
Charo IF, Scarborough RM, De Mee CP, Wolf D, Phillips OR, Swift RL. Pharmacodynamics of the GPIIb/IIIa antagonist integrelin: Phase I clinical studies in normal healthy volunteers.Circulation 86:I260.
Bhattacharya S, Weisman HF, Morris KG, et al. Chimerization of monoclonal antibody 7E3 preserves the GPIIb/IIIa receptor blockade and platelet functional inhibition of murine 7E3.Clin Res 1991;39:196A.
Wagner CL, Knight DM, McAleer MF, et al. Immunological comparison of murine and chimeric 7E3 Fab fragments in human clinical trails.J Immunol 1993;150:158A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, S., Jordan, R., Machin, S. et al. Blockade of the human platelet GPIIb/IIIa receptor by a murine monoclonal antibody Fab fragment (7E3): Potent dose-dependent inhibition of platelet function. Cardiovasc Drug Ther 9, 665–675 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878549
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878549