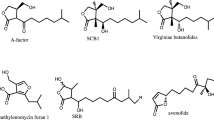
Abstract
The genetic control of polyketide metabolite biosynthesis inStreptomyces sp. producing actinorhodin, daunorubicin, erythromycin, spiramycin, tetracenomycin and tylosin is reviewed. Several examples of positively-acting transcriptional regulators of polyketide metabolism are known, including some two-component sensor kinase-response regulator systems. Translational and posttranslational control mechanisms are only briefly mentioned since very little is known about either of these processes. Examples of how enzyme levels and substrate supply affect polyketide metabolism also are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- act:
-
actinorhodin
- ACP:
-
Acyl Carrier Protein
- NH4+:
-
ammonium ion
- aphII:
-
aminoglycoside phosphotransferase gene
- CoA:
-
Coenzyme A
- dnr:
-
daunorubicin
- hyg:
-
hygromycin phosphotransferase gene
- PKS:
-
Polyketide Synthase
- vdh:
-
valine dehydrogenase
- tcm:
-
tetracenomycin
References
Adamidis T, Riggle P & Champness W (1990) Mutations in a newStreptomyces coelicolor locus which globally block antibiotic biosynthesis but not sporulation. J. Bacteriol. 172: 2962–2969
Adamidis T & Champness W (1992) Genetic analysis ofabsB, aStreptomyces coelicolor locus involved in global antibiotic regulation. J. Bacteriol. 174: 4622–4628
Andersen JF & Hutchinson CR (1992) Characterization ofSaccharopolyspora erythraea cytochrome P450 genes and enzymes, including 6-deoxyerythronolide B hydroxylase. J. Bacteriol. 174: 725–735
Bibb MJ, Biró S, Motamedi H, Collins JF & Hutchinson CR (1989) Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of theStreptomyces glaucescens tcmI genes provides key information about the enzymology of polyketide antibiotic biosynthesis. EMBO J. 8: 2727–2736
Bibb MJ, Janssen GR & Ward JM (1985) Cloning and analysis of the promoter region of the erythromycin-resistance gene (ermE) ofStreptomyces erythreus. Gene 38: E357-E368
Birch A, Leiser A & Robinson JA (1993) Cloning, sequencing and expression of the gene encoding methylmalonyl-CoA mutase fromStreptomyces cinnamonensis. J. Bacteriol. 175: 3511–3519
Bourret RB, Borkovich KA & Simon MI (1991) Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in procaryotes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 60: 401–441
Branã AF & Demain AL (1988) Nitrogen control of antibiotic biosynthesis in actinomycetes. In: Sanchez-Esquivel S (ED) Nitrogen Source Control of Microbial Processes (pp. 99–119). CRC Press, Boca Raton
Burbulys D, Trach KA & Hoch JA (1991) Initiation of sporulation inB. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell 64: 545–552
Caballero JL, Malpartida F & Hopwood DA (1991) Transcriptional organization and regulation of an antibiotic export complex in the producingStreptomyces culture. Mol. Gen. Genet. 228: 372–380
Champness W, Riggle P & Adamidis T (1990) Loci involved in regulation of antibiotic synthesis. J. Cell. Biochem. 14A: 88
Champness W, Riggle P, Adamidis T, Kenney B & Aceti D (1993) Genetic elements involved in global antibiotic regulation inStreptomyces coelicolor. In: Hershberger CL, Skatrud P & Hegeman G (Eds) Genetics and molecular biology of industrial microorganisms (pp. 227–234). American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC
Cortes J, Haydock SF, Roberts GA, Bevitt DJ & Leadlay PF (1990) An unusually large multifunctional polypeptide in the erythromycin-producing polyketide synthase ofSaccharopolyspora erythraea. Nature 348: 176–178
Decker H & Hutchinson CR (1993) Transcriptional analysis of theStreptomyces glaucescens tetracenomycin C biosynthetic gene cluster. J. Bacteriol. 175: 3887–3892
Decker H, Motamedi H & Hutchinson CR (1993) The nucleotide sequence and heterologous expression oftcmG andtcmP, biosynthetic genes for tetracenomycin C inStreptomyces glaucescens. J. Bacteriol. 175: 3876–3886
Decker H, Summers RG & Hutchinson CR (1993) Overproduction of the acyl carrier protein component of a Type II polyketide synthase stimulates production of tetracenomycin biosynthetic intermediates inStreptomyces glaucescens. J. Antibiotics 47: 54–63
Demain AL & Martin JF (1980) Control of antibiotic biosynthesis. Microbiol. Revs. 44: 230–251
Donadio S, Stassi D, McAlpine JB, Staver MJ, Sheldon PJ, Jackson M, Swanson SJ, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Wang YG, Jarvis B, Hutchinson CR & Katz L (1993) Recent developments in the genetics of erythromycin formation. In: Hershberger CL, Skatrud P & Hegeman G (Eds) Genetics and molecular biology of industrial microorganisms (pp. 257–266). American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC
Donadio S, Staver MJ, McAlpine JB, Swanson SJ & Katz L (1991) Modular organization of genes required for complex polyketide biosynthesis. Science 252: 675–679
Donadio S & Katz L (1992) Organization of the enzymatic domains in the multifunctional polyketide synthase involved in erythromycin formation inSaccharopolyspora erythraea. Gene 111: 51–60
Doull JL & Vining LC (1990) Nutritional control of actinorhodin production byStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2): suppressive effects of nitrogen and phosphate. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32: 449–454
Doull JL & Vining LC (1989) Culture conditions promoting dispersed growth and biphasic production of actinorhodin in shaken cultures ofStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 65: 265–268
Fernandez-Moreno MA, Caballero JL, Hopwood DA & Malpartida F (1991) Theact cluster contains regulatory and antibiotic export genes, direct targets for translational control by thebldA tRNA gene of Streptomyces. Cell 66: 769–780
Fernandez-Moreno MA, Martinez E, Boto L, Hopwood DA & Malpartida F (1992) Nucleotide sequence and deduced functions of a set of cotranscribed genes ofStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2) including the polyketide synthase for the antibiotic actinorhodin. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 19278–19290
Fernandez-Moreno MA, Martin-Triana AJ, Martinez E, Nieme J, Kieser HM, Hopwood DA & Malpartida F (1992)abaA, a new pleiotropic regulatory locus for antibiotic production inStreptomyces coelicolor. J. Bacteriol. 174: 2958–2967
Geistlich M, Losick R, Turner JA & Rao RN (1992) Characterization of a novel regulatory gene governing the expression of a polyketide synthase gene inStreptomyces ambofaciens. Mol. Microbiol. 6: 2019–2029
Gramajo HC, Takano E & Bibb MJ (1993) Stationary-phase production of the antibiotic actinorhodin inStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2) is transcriptionally regulated. Mol. Microbiol. 7: 837–845
Guilfoile PG & Hutchinson CR (1992a) Sequence and transcriptional analysis of theStreptomyces glaucescens tcmAR tetracenomycin C resistance and repressor gene loci. J. Bacteriol. 174: 3651–3658
Guilfoile PG & Hutchinson CR (1992b) TheStreptomyces glaucescens TcmR protein represses transcription of the divergently orientedtcmR andtcmA genes by binding to an intergenic operator region. J. Bacteriol. 174: 3659–3666
Hallam SE, Malpartida F & Hopwood DA (1988) Nucleotide sequence, transcription and deduced function of a gene involved in polyketide antibiotic synthesis inStreptomyces coelicolor. Gene 74: 305–320
Ho CC, Nissom PM & Krishna G (1993) Stimulation of adriamycin biosynthesis inStreptomyces peucetius var.caesius by multiple copies ofafsR, a global regulatory gene ofStreptomyces coelicolor. Abstracts of the Fourth Scientific Meeting of the Malaysian Society for Molecular Biology and Cellular Biology (pp. 40–41), May, 1993
Hobbs G, Frazer CM, Gardner DCJ, Flett F & Oliver SG (1990) Pigmented antibiotic production byStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2): kinetics and the influence of nutrients. J. Gen. Microbiol. 136: 2291–2296
Hobbs G, Obanye AIC, Petty J, Mason JC, Barratt E, Gardner DCJ, Flett F, Smith CP, Broda P & Oliver SG (1992) An integrated approach to studying regulation of production of the antibiotic methylenomycin byStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Bacteriol. 174: 1487–1494
Hodgson DA (1993) Carbon metabolism & Nitrogen metabolite degradation. In: Wellington EMH & Hodgson DA (Eds) Handbook of Biotechnology: Streptomyces (Chapter 3 & 6, in press). Plenum Press, London
Hong SK, Kito M, Beppu T & Horinouchi S (1991) Phosphorylation of the AfsR product, a global regulatory protein for secondary metabolite formation inStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Bacteriol. 173: 2311–2318
Hopwood DA & Sherman DH (1990) Molecular genetics of polyketides and its comparison to fatty acid biosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 24: 37–66
Horinouchi H, Malpartida F, Hopwood DA & Beppu T (1989)afsB stimulates transcription of the actinorhodin biosynthetic pathway inStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2) andStreptomyces lividans. Mol. Gen. Genet. 215: 355–357
Horinouchi S, Kito M, Nishiyama M, Furuya K, Hong SK, Miyake K & Beppu T (1990) Primary structure of AfsR, a global regulatory protein for secondary metabolite formation inStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Gene 95: 49–56
Ishizuka H, Horinouchi S, Kieser HM, Hopwood DA & Beppu T (1992) A putative two-component regulatory system involved in secondary metabolism inStreptomyces spp. J. Bacteriol. 174: 7585–7594
Katz L & Donadio S (1993) Polyketide synthesis: prospects for hybrid antibiotics. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 47: 875–912
Khosla C, McDaniel R, Ebert-Khosia S, Torres R, Sherman DH, Bibb MJ & Hopwood DA (1993) Genetic construction and functional analysis of hybrid polyketide synthases containing heterologous acyl carrier proteins. J. Bacteriol. 175: 2197–2204
Lebrihi A, Lamsaif D, Lefebvre G & Germain P (1992) Effect of ammonium ions on spiramycin biosynthesis inStreptomyces ambofaciens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37: 382–387
Lee SH & Lee KJ (1991) Relationship between threonine dehydratase and biosynthesis tylosin inStreptomyces fradiae. J. Gen. Microbiol. 137: 2547–2553
Leskiw BK, Mah R, Lawlor EJ & Chater KF (1993) Accumulation ofbldA-specified tRNA is temporally regulated inStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Bacteriol. 175: 1995–2005
Leskiw BK, Bibb MJ & Chater KF (1991) The use of a rare codon specifically during development? Molec. Microbiol. 5: 2861–2867
Marahiel MA, Nakano MM & Zuber P (1993) Regulation of peptide antibiotic production inBacillus. Mol. Microbiol. 7: 631–636
Matsumoto A, Hong SK, Horinouchi S & Beppu T (1993) Phosphorylation by a protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase of the AfsR protein involved in a secondary metabolism inStreptomyces spp. Cell, in press
Narva KE & Keitelson JS (1990) Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of theredD locus ofStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Bacteriol. 172: 326–333
Neidhardt FC, Ingraham JL & Schaechter M (1990) Physiology of the Bacterial Cell. A Molecular Approach. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Omura S, Tanaka Y, Mamada H & Masuma R (1984a) Effect of ammonium ion, inorganic phosphate and amino acids on the biosynthesis of protylonolide, a precursor of tylosin aglycone. J. Antibiotics 37: 494–502
Omura S, Tsuzuki K, Tanaka Y, Sakakibara H, Mamada H & Masuma R (1983) Ammonium ion suppresses the biosynthesis of tylosin aglycone by interference with valine catabolism inStreptomyces fradiae. J. Antibiotics 36: 1792–1794
Omura S, Taki A, Matsuda K & Tanaka Y (1984b) Ammonium ions suppress the amino acid metabolism involved in the biosynthesis of protylonolide in a mutant ofStreptomyces fradiae. J. Antibiotics 37: 1362–1369
O'Hagen D (1991) The Polyketide Metabolites. Ellis Horwood, Chichester, UK
Parro V, Hopwood DA, Malpartida F & Mellado RP (1991) Transcription of genes involved in the earliest steps of actinorhodin biosynthesis inStreptomyces coelicolor. Nucl. Acids Res. 19: 2623–2627
Paulus TJ, Tuan JS, Luebke VE, Maine GT, DeWitt JP & Katz L (1990) Mutation and cloning oferyG, the structural gene for erythromycinO-methyltransferase fromSaccharopolyspora erythraea, and expression oferyG inEscherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 172: 2541–2546
Reynolds KA, O'Hagen D, Gani D & Robinson JA (1988) Butyrate metabolism in Streptomycetes. Characterization of an intramolecular vicinal interchange rearrangement linking isobutyrate and butyrate inStreptomyces cinnamonensis. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I. 1988: 3195–3208
Romero NM, Parro V, Malpartida F & Mellado RP (1992) Heterologous activation of the actinorhodin biosynthetic pathway inStreptomyces lividans. Nucl. Acids Res. 20: 2767–2772
Rudd BAM & Hopwood DA (1979) Genetics of actinorhodin biosynthesis byStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Gen. Microbiol. 114: 35–43
Shen B, Summers RG, Gramajo H, Bibb MJ & Hutchinson CR (1992) Purification and characterization of the acyl carrier protein of theStreptomyces glaucescens tetracenomycin C polyketide synthase. J. Bacteriol. 174: 3818–3821
Shen B & Hutchinson CR (1993a) Tetracenomycin F1 monooxygenase: oxidation of a naphthacenone to a naphthacenequinone in the biosynthesis of tetracenomycin C inStreptomyces glaucescens. Biochemistry 32: 6656–6663
Shen B & Hutchinson CR (1993b) Tetracenomycin F2 cyclase: Intramolecular aldol condensation in the biosynthesis of tetracenomycin C inStreptomyces glaucescens. Biochemistry 32: 11149–11154
Sherman MM, Yue S & Hutchinson CR (1986) Metabolic interrelationships of carboxylic acid precursors and polyether antibiotics. J. Antibiotics 39: 1135–1143
Stassi D, Donadio S, Staver MJ & Katz L (1993) Identification of aSaccharopolyspora erythraea gene required for the final hydroxylation step in erythromycin biosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 175: 182–189
Stein D & Cohen SN (1989) A cloned regulatory gene ofStreptomyces lividans can suppress the pigment deficiency phenotype of different developmental mutants. J. Bacteriol. 171: 2258–2261
Stock JB, Ninfa AJ & Stock AM (1989) Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 53: 450–490
Stragier P & Losick R (1990) Cascades of sigma factors revisited. Mol. Microbiol. 4: 1801–1806
Stutzman-Engwall KJ, Otten SL & Hutchinson CR (1992) Regulation of secondary metabolism inStreptomyces spp. and overproduction of daunorubicin inStreptomyces peucetius. J. Bacteriol. 174: 144–154
Summers RG, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Motamedi H & Hutchinson CR (1992) Nucleotide sequence of thetcmII-tcmIV region of the tetracenomycin C biosynthetic gene cluster ofStreptomyces glaucescens and evidence that thetcmN gene encodes a multifunctional cyclase-dehydratase-O-methyl transferase. J. Bacteriol. 174: 1810–1820
Summers RG, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Motamedi H & Hutchinson CR (1993) ThetcmVI region of the tetracenomycin C biosynthetic gene cluster ofStreptomyces glaucescens encodes the tetracenomycin F1 monooxygenase, tetracenomycin F2 cyclase, and, most likely, a second cyclase. J. Bacteriol. 175: 7571–7580
Takano E, Gramaja HC, Strauch E, Andres N, White J & Bibb MJ (1992) Transcriptional regulation of theredD transcriptional activator gene accounts for growth-phase-dependent production of the antibiotic undecylprodigiosin inStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol. Microbiol. 6: 2797–2804
Tang L & Hutchinson CR (1993) Sequence, transcriptional, and functional analysis of the valine (branched-chain amino acid) dehydrogenase gene ofStreptomyces coelicolor. J. Bacteriol. 175: 4176–4185
Ward JM, Janssen GR, Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ & Bibb MJ (1986) Construction and characterisation of a series of multicopy promoter-probe plasmid vectors forStreptomyces using the aminoglycoside phosphotransferase gene from Tn5 as indicator. Mol. Gen. Genet. 203: 468–478
Weber JM, Schoner B & Losick R (1989) Identification of a gene required for the terminal step in erythromycin biosynthesis inSaccharopolysporaerythraea (Streptomyceserythreus). Gene 75: 235–241
Weber JM, Leung JO, Maine GT, Potenz RHB, Paulus TJ & DeWitt JP (1990) Organization of a cluster of erythromycin biosynthesis genes inSaccharopolyspora erythraea. J. Bacteriol. 172: 2372–2383
Weber JM, Leung JO, Swanson SJ, Idler KB & McAlpine JB (1991) An erythromycin derivative produced by targeted gene disruption inSaccharopolyspora erythraea. Science 252: 114–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hutchinson, C.R., Decker, H., Madduri, K. et al. Genetic control of polyketide biosynthesis in the genusStreptomyces . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 64, 165–176 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00873025
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00873025