Summary
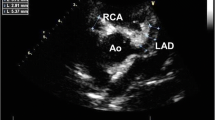
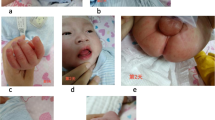
A 7-month-old male infant with clinical symptoms of severe toxic shock syndrome died on day 9 of illness. At autopsy, demonstration of coronary vasculitis together with thrombosis of the left coronary artery revealed the true diagnosis of atypical Kawasaki disease. The marked similarity in many clinical features makes the distinction between these two diseases difficult when atypical clinical presentation of Kawasaki disease is present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burns JC, Wiggins JW, Toews WH, Newburger JW, Leung DYM, Wilson H, Glode MP (1986) Clinical spectrum of Kawasaki disease in infants younger than 6 months of age.J Pediatr 109:759–763
Byard RW, Edmonds JF, Silverman E, Silver MM (1991) Respiratory distress and fever in a 2-month-old infant.J Pediatria.118:306–313
Chow LT, Chow W, Tse CC, Wong EH, Wong K, Yip DC (1992) Kawasaki disease: sudden death as the first presenting symptom.Cardiol Young 2:73–77
Cloney DL, Teja K, Lohr JA (1987) Fatal case of atypical Kawasaki syndrome.Pediatr Infect Dis J 6:297–299
Fujiwara H, Hamashima Y (1978) Pathology of the heart in Kawasaki disease.Pediatrics 61:100–107
Hamashima Y (1980) Kawasaki's disease.Clin Rhhum Dis 6:319–338
Hansen RC (1983) Staphylococal scalded skin syndrome, toxic shock syndrome, and Kawasaki disease.Pediatr Clin North Am 30:533–544
Krapf R, Zimmermann A, Stocker F (1981) Lethal vasculitis of coronary arteries in a neonate and two infants: possible neonatal varian of the MLNS/IPN complex?Helv Paediat Acta 36:589–598
Landing BH, Larson EJ (1977) Are infantile periateritis nodosa with coronary artery involvement and fatal mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome the same? Comparison of 20 patients from North America with patients with Hawaii and Japan.Pediatrics 59:651–662
Levy M, Koren G (1990) Atypical Kawasaki disease: analysis of clinical presentation and diagnostic clues.Pediatr Infect Dis J 9:122–126
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Beiser AS, Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, Colan SD, Duffy CE, Fulton DR, Glode MP, Mason WH, Meissner HC, Rowley AH, Shulman ST, Reddy V, Sundel RP, Wiggins JW, Colton T, Melish ME, Rosen FS (1991) A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki syndrome.N Engl J Med 324:1633–1639
Reller M, DeCristofaro J, Schwartz DC (1984) Coronary aneurysms in a patient with atypical Kawasaki syndrome and a Streptococcal infection.Pediatr Cardiol 5:205–208
Rowley AH, Gonzalez-Crussi F, Gidding SS, Duffy CE, Shulman ST (1987) Incomplete Kawasaki disease with coronary artery involvement.J Pediatr 110:409–413
Schuh S, Laxer RM, Smallhorn JF, Hilliard RI, Rowe RD (1988) Kawasaki disease with atypical presentation.Pediatr Infect Dis J 7:201–203
Wiesenthal AM, Todd JK (1984) Toxic shock syndrome in children aged 10 years or less.Pediatrics 74:112–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gamillscheg, A., Zobel, G., Karpf, E.F. et al. Atypical presentation of Kawasaki disease in an infant. Pediatr Cardiol 14, 223–226 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00795375
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00795375