Summary
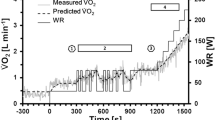
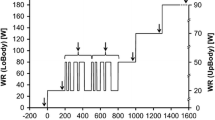
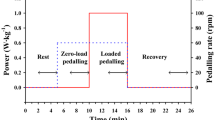
The multifrequent pseudorandom binary sequence (PRBS) technique is a useful tool for studying oxygen uptake (\(\dot VO_2 \)) kinetics within the aerobic range. However, the validity of this multifrequent test may be limited by nonlinearities generated by the circulatory and pulmonary system. To check for such nonlinear effects, we compared the frequency responses computed from two PRBS protocols with the results of pure sinusoidal frequencies varying in amplitude and mean values (periods between 50 s and 450 s). According to our results the\(\dot VO_2 \) frequency response does not seem to depend on the type of testing — PRBS or sine — or the changes within each test, i.e. mean power and power amplitude of the sine tests and the switching frequency of the PRBS. In the range of higher frequencies small differences between the test conditions may have been obscured by the greater scatter of dynamic responses. It was concluded that the\(\dot VO_2 \) frequency response was quasi-linear for periods down to at least 100 s. However, even in this range nonlinearities can be provoked by rest-exercise transitions, by a varying contribution of lactate or by an insufficient noise reduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakker HK, Struikenkamp RS, DeVries GA (1980) Dynamics of ventilation, heart rate, and gas exchange: sinusoidal and impulse work loads in man. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 48: 289–301
Casaburi R, Whipp BJ, Wasserman K, Beaver WL, Koyal SN (1977) Ventilatory and gas exchange dynamics in response to sinusoidal work. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 42: 300–311
Cerretelli P, Pendergast D, Paganelli WC, Rennie DW (1979) Effects of specific muscle training onVO2 on-response and early blood lactate. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 47: 761–769
Eßfeld D, Hoffmann U, Stegemann J (1987)VO2 kinetics in subjects differing in aerobic capacity: investigation by spectral analysis. Eur J Appl Physiol 56: 508–515
Eßfeld D, Hoffmann U, Stegemann J (1991) A model for studying the distortion of muscle oxygen uptake patterns by circulation parameters. Eur J Appl Physiol 62: 83–90
Hagberg JM, Hickson RC, Ehsani AA, Holloszy JO (1980) Faster adjustment to and recovery from submaximal exercise in the trained state. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 48: 218–224
Hickson RC, Bomze HA, Holloszy JO (1978) Faster adjustment of OZ uptake to the energy requirements of exercise in the trained state. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 44: 877–881
Hughson RL, Winter DA, Patla AE, Swanson GD, Cuervo LA (1990) Investigation of\(\dot VO_2 \) kinetics in humans with pseudorandom binary sequence work rate change. J Appl Physiol 68: 796–801
Powers SK, Dodd S, Beadle RE (1985) Oxygen uptake kinetics in trained athletes differing in\(\dot VO_{2\max } \). Eur J Appl Physiol 54: 306–308
Weltman A, Katch V (1967) Min-by-min respiratory exchange and oxygen uptake kinetics during steady-state exercise in subjects of high and low max\(\dot VO_2 \). Res Q 47: 490–498
Whipp BJ, Wasserman K (1972) Oxygen uptake kinetics for various intensities of constant-load work. J Appl Physiol 33: 351–356
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffmann, U., Eßfeld, D., Wunderlich, HG. et al. Dynamic linearity ofVO2 responses during aerobic exercise. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 64, 139–144 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00717951
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00717951