Summary
-
1.
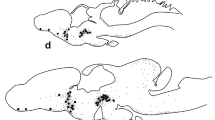
The presence of insulin-like substances has been demonstrated by immunocytochemistry in the central nervous system of the snailHelix aspersa.
-
2.
The immunopositivity has been observed especially in the large perikarya of the mesocerebral green cells [the cerebral green cells (CeGC) stained in green by the alcian blue: alcian yellow technique].
-
3.
The removal of either the mesocerebrum or the CeGC stops the growth of the snail and induces the increase of the glycogen content in the mantle edge.
-
4.
Our results show the existence of insulin-like material in the neurosecretory cells. Previous data having demonstrated the presence of specific binding sites to insulin in the cephalic ganglia ofHelix aspersa, one may suggest that insulin could play a neuromodulatory or a neurotransmittory role in the central nervous system and might control the growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boer, H. H., Roubos, E. W., Van Dalen, H., and Groesbeek, J. R. F. Th. (1977). Neurosecretion in the basommatophoran snailBulinus truncatus (Gastropoda, Pulmonata).Cell Tissue Res. 17657–67.
Boyd, F. T., Jr., Clarke, D. W., Muther, T. F., and Raizada, M. K. (1985). Insulin receptors and insulin modulation of norepinephrine uptake in neuronal cultures from rat brain.J. Biol. Chem. 26015880–15884.
Burton, R. F. (1975). A method of narcotizing snails (Helix pomatia) and cannulating the haemocoel and its application to a study of the role of calcium in the regulation of acid-base balance.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 52483–485.
Chase, R. (1986). Brain cells that command sexual behavior in the snailHelix aspersa.J. Neurobiol. 17669–679.
Dogterom, A. A. (1980). The effect of the growth hormone of the freshwater snailLymnaea stagnalis on biochemical composition and nitrogenous wastes.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 65B163–167.
Ebberink, R. H. M., and Joosse, J. (1985). Molecular properties of various snail peptides from brain and gut.Peptides 6451–457.
Ebberink, R. H. M., Smit, A. B., and Van Minnen, J. (1989). The insulin family: Evolution of structure and function in vertebrates and invertebrates.Biol. Bull. 177176–182.
Geraerts, W. P. M. (1976). Control of growth by the neurosecretory hormone of the light green cells of the freshwater snailLymnaea stagnalis.Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2961–71.
Gomot, L., and Deray, A. (1987). Les escargots.La Recherche 186302–311.
Hansen, G. N., Hansen, B. L., Jorgensen, P. N., and Scharrer, B. (1990). Immunocytochemical localization and immunochemical characterization of an insulin-related peptide in the insectLeucophaea maderae.Cell Tissue Res. 259265–273.
Havrankova, J., and Roth, J. (1978). Insulin receptors are widely distributed in the central nervous system of the rat.Nature 272827–829.
Havrankova, J., Schmechel, D., Roth, J., and Brownstein, M. (1978). Identification of insulin in rat brain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 755737–5741.
Hemminga, M. A. (1984).Regulation of Glycogen Metabolism in the Freshwater Snail Lymnaea stagnalis, Ph.D. thesis, Vrije Universiteit, Academic Press, Amsterdam.
Hendricks, S. A., Agardh, C. D., Taylor, S. I., and Roth, J. (1984). Unique features of the insulin receptor in rat brain.J. Neurochem. 431302–1309.
Joosse, J., and Geraerts, W. P. M. (1983). Endocrinology. In Saleuddin, A. S. M., and Wilbur, K. M. (eds),The Mollusca, Vol. 4. Physiology, Academic Press, New York, pp. 317–406.
Joosse, J., and Van Elk, R. (1986).Trichobilharzia ocellata physiological characterization of giant growth, glycogen depletion and absence of reproductive activity in the intermediate snailLymnaea stagnalis.Exp. Parasitol. 621–3.
Kappy, M., Sellinger, S., and Raizada, M. (1984). Insulin binding in four regions of the developing rat brain.J. Neurochem. 42198–203.
Kunze, H. (1921). Zur Topographie und Histologie des central Nervensystems vonHelix pomatia L.Z. Wiss. Zool. 11825–203.
Plisetskaya, E., and Joosse, J. (1985). Hormonal regulation of carbohydrate metabolism in mollusks. In Lofts, B., and Holmes, W. N. (eds.),Current Trends in Comparative Endocrinology, Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong, pp. 1077–1079.
Saavedra, J. M., Juorio, A. V., Shigematsu, K., and Pinto, J. E. B. (1989). Specific insulin binding sites in snail (Helix aspersa) ganglia.Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 9273–279.
Schot, L. P. C., Boer, H. H., Swaab, D. F., and Van Noorden, S. (1981). Immunocytochemical demonstration of peptidergic neurons in the central nervous system of the pond snailLymnaea stagnalis with antisera raised to biologically active peptides of vertebrates.Cell Tissue Res. 216273–291.
Siegel, S. (1956).The Case of Two Independent Samples in Non Parametric Statistics, International Student Ed., McGraw Hill International, Auckland, p. 116.
Smit, A. B., Vreugdenhil, E., Ebberink, R. H. M., Geraerts, W. P. M., Klootwijk, J., and Joosse, J. (1988). Growth-controlling molluscan neurons produce the precursor of an insulin-related peptide.Nature 331535–538.
Sternberger, L. A. (1979)Immunocytochemistry, 2nd ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Thorpe, A., and Duve, H. (1984). Insulin- and glucagon-like peptides in insects and molluscs.Mol. Physiol. 5235–260.
Van Handel, E. (1965). Estimation of glycogen in small amounts of tissue.Anal. Biochem. 11256–265.
Van Minnen, J., Smit, A. B., and Joosse, J. (1989). Central and peripheral expression of genes coding for egg-laying inducing and insulin-related peptides in a snail.Arch. Histol. Cytol. 52241–252.
Wendelaar Bonga, S. E. (1970). Ultrastructure and histochemistry of neurosecretory cells and neurohaemal areas in the pond snailLymnaea stagnalis.Z. Zellforsch. 105190–224.
Weyhenmeyer, J. A., Relmer, A. M., Reynold, I., and Killian, A. (1985). Light and electron microscopic analysis of insulin binding sites on neurons in dissociated brain cell cultures.Brain Res. Bull. 14415–421.
Wijdenes, J., and Runham, N. W. (1977). Studies on the control of growth inAgriolimax reticulatus (Mollusca, Pulmonata).Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 31154–156.
Wijdenes, J., Van Minnen, J., and Boer, H. H. (1980). A comparative study on neurosecretion demonstrated by the alcian blue-alcian yellow technique in three terrestrial pulmonates (Stylommatophora).Cell Tissue Res. 21047–56.
Wijdenes, J., Schluter, N. C. M., Gomot, L., and Boer, H. H. (1987). In the snailHelix aspersa the gonadotropic hormone-producing dorsal bodies are under inhibitory nervous control of putative growth hormone-producing neuroendocrine cells.Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 68224–229.
Young, W. S., III, Kuhar, M. J., Roth, J., and Brownstein, M. J. (1980). Radiohistochemical localization of insulin receptors in the adult and developing rat brain.Neuropeptides 115–22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomot, A., Gomot, L., Marchand, C.R. et al. Immunocytochemical localization of insulin-related peptide(s) in the central nervous system of the snailHelix aspersa müller: Involvement in growth control. Cell Mol Neurobiol 12, 21–32 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711636
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00711636