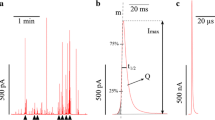
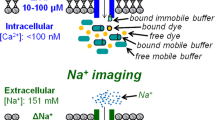
Summary
-
1.
The dispersion of dye molecules and small cations injected from a point source in the cytoplasm of molluscan neurons has been measured photometrically and compared with dispersion in aqueous solution.
-
2.
The diffusion of phenol red and arsenazo III was at least a factor of five slower in the cytoplasm than in saline. Movement of both dyes was slowed by about the same factor in a given cell. The dispersion rate of arsenazo III was not significantly affected by preloading the cytoplasm to dye concentrations up to 0.5 mM.
-
3.
Calcium and barium dispersion was measured in neurons and saline droplets preloaded with arsenazo III, while phenol red absorbance changes were used to follow the dispersion of injected protons. Ba2+ and H+ moved very slowly in the cytoplasm compared to aqueous solution.
-
4.
Ca2+ movement in all probability underwent a similar retardation in the neurons but high-affinity buffering of the cytoplasm severely restricted the spread of detectable amounts of this ion away from the injection site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, Z., and Connor, J. A. (1979). Measurement of calcium influx under voltage clamp in molluscan neurons using the metallochromic dye arsenazo III.J. Physiol. 28661–82.
Ahmed, Z., and Connor, J. A. (1980). Intracellular pH changes induced by calcium influx during electrical activity in molluscan neurons.J. Gen. Physiol. 75403–426.
Ahmed, Z., Kragie, L., and Connor, J. A. (1980). Stoichiometry and apparent dissociation constant of the calcium-arsenazo III reaction under physiological conditions.Biophys. J. 32907–920.
Ambercrombie, R. F., Masukawa, L. M., Sjodin, R. A., and Livengood, D. (1981). Uptake and release of45Ca bymyxicola axoplasm.J. Gen. Physiol. 78413–429.
Baker, P. F. (1972). Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve.Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 24177–223.
Baker, P. F., Hodgkin, A. L., and Ridgway, E. B. (1971). Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 218709–755.
Baker, P. F., and Schlaepfer, W. W. (1978). Uptake and binding of calcium by axoplasm isolated from giant axons ofloligo andmyxicola.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 276103–125.
Baylor, S. M., Chandler, W. K., and Marshall, M. W. (1982). Dichroic components of arsenazo III and dichlorophosphonazo III signals in skeletal muscle fibres.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 331179–210.
Beeler, T. J., Schibeci, A., and Martonosi, A. (1980). The binding of arsenazo III to cell components.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 629317–327.
Brown, H. M., and Meech, R. W. (1979). Light induced changes of internal pH in a barnacle photoreceptor and the effect of internal pH on the receptor potential.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 29773–93.
Connor, J. A. (1977). Time course separation of two inward currents in molluscan neurons.Brain Res. 119487–492.
Connor, J. A. (1979). Calcium current in molluscan neurones: Measurement under conditions which maximize its visibility.J. Physiol. 28641–60.
Connor, J. A., Ahmed, Z., and Ebert, G. (1981). Diffusion of Ca2+, Ba2+, H+ and arsenazo III in neural cytoplasm.Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 715.
Dedman, J. R., Potter, J. D., Jackson, R. L., Johnson, J. D., and Mean, A. R. (1977). Physiocochemical properties of rat testis Ca2+-dependent regulator protein of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase.J. Biol. Chem. 2528415–8422.
Dipolo, R., Requena, J., Brinley, F. J., Mullins, L. J., Scarpa, A., and Tiffert, T. (1976). Ionized calcium concentrations in squid axons.J. Gen. Physiol. 67433–467.
Fuchs, F. (1971). Ion exchange properties of the calcium receptor site of troponin.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 245221–229.
Gorman, A. L. F., and Hermann, A. (1979). Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurons.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 296393–410.
Hagiwara, S. (1973). Ca spike.Adv. Biophys. 471–102.
Hodgkin, A. L., and Keynes, R. D. (1956). Experiments on the injection of substances into squid giant axons by means of a micro syringe.J. Physiol. 131592–616.
Hodgkin, A. L., and Keynes, R. D. (1957). Movements of labelled calcium in giant axons.J. Physiol. 138253–281.
Kendrick, N. C., Ratzlaff, R. W., and Blaustein, M. P. (1977). Arsenazo III as an indicator for ionized calcium in physiological salt solutions: Its use for determination of the CaATP dissociation constant.Anal. Biochem. 83433–450.
Kushmerick, M. J., and Podolsky, R. J. (1969). Ionic mobility in muscle cells.Science 1661297–1298.
Mimura, N., and Asano, A. (1979). Ca2+-sensitive gelatin of actin filaments by a new protein factor.Nature 28244–48.
Owen, J., and Brown, H. M. (1980). Intracellular changes of H+ and Ca2+ activities inaplysia giant neurons as measured with ion sensitive microelectrodes.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 66A197–201.
Rakowski, R. F., and Sommerer, J. C. (1981). Diffusion of the Ca2+ indicator dye arsenazo III in aqueous solution and in frog skeletal muscle fibers.Biophys. J. 33:150a.
Rose, B., and Loewenstein, W. R. (1975). Calcium ion distribution in cytoplasm visualized by aequorin: Distribution in cytosol is restricted due to energized sequestering.Science 1901204.
Thomas, R. C. (1974). Intracellular pH of snail neurons measured with a new pH-sensitive glass microelectrode.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 238158–180.
Thomas, R. C. (1976). The effect of carbon dioxide on the intracellular pH and buffering power of snail neurons.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 255715–735.
Wolff, D. J., Poisier, P. G., Brostrom, C. O., and Brostrom, M. A. (1977). Divalent cation binding properties of bovine brain Ca2+-dependent regulator protein.J. Biol. Chem. 2524108–4117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Connor, J.A., Ahmed, Z. Diffusion of ions and indicator dyes in neural cytoplasm. Cell Mol Neurobiol 4, 53–66 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710942
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710942